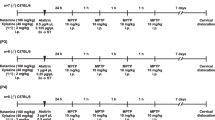
Abstract
GM1-gangliosidosis (GM1G) is caused by a deficiency of β-galactosidase, resulting in the excessive accumulation of GM1-ganglioside (GM1) in lysosomes of cells, particularly in the nerve cells (neurons). There is no treatment available for patients with GM1G. Meanwhile, cyclodextrins (CyDs) are cyclic oligosaccharides, which are widely used in the pharmaceutical field. We previously reported that 2, 6-di-O-methyl-α-CyD (DM-α-CyD) extracted phospholipids from lipid rafts, which are abundant with sphingolipids including GM1. Therefore, in the present study, we investigated the effects of α-CyDs on GM1 levels in GM1G model cells and in brain of GM1G model mice. The interaction of DM-α-CyD with GM1 was stronger than that of 2-hydroxypropyl-α-CyD. Additionally, DM-α-CyD significantly reduced GM1 levels in GM1G model cells at 1 mM for 24 h. Furthermore, DM-α-CyD decreased GM1 levels in brain after an intraventricular administration to GM1G model mice without any significant side effects. These results strongly suggest that DM-α-CyD decreased the accumulation of GM1 in not only GM1G model cells but also GM1G model mice. Collectively, DM-α-CyD may have the potential as a therapeutic drug for GM1G.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vellodi, A.: Lysosomal storage disorders. Br. J. Haematol. 128, 413–431 (2005)
Winchester, B., Vellodi, A., Young, E.: The molecular basis of lysosomal storage diseases and their treatment. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 28, 150–154 (2000)
Brunetti-Pierri, N., Scaglia, F.: GM1 gangliosidosis: review of clinical, molecular, and therapeutic aspects. Mol. Genet. Metab. 94, 391–396 (2008)
Front, S., Biela-Banas, A., Burda, P., Ballhausen, D., Higaki, K., Caciotti, A., Morrone, A., Charollais-Thoenig, J., Gallienne, E., Demotz, S., Martin, O.R.: (5aR)-5a-C-Pentyl-4-epi-isofagomine: a powerful inhibitor of lysosomal beta-galactosidase and a remarkable chaperone for mutations associated with GM1-gangliosidosis and Morquio disease type B. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 126, 160–170 (2017)
Takai, T., Higaki, K., Aguilar-Moncayo, M., Mena-Barragan, T., Hirano, Y., Yura, K., Yu, L., Ninomiya, H., Garcia-Moreno, M.I., Sakakibara, Y., Ohno, K., Nanba, E., Ortiz Mellet, O., Garcia Fernandez, J.M., Suzuki, Y.: A bicyclic 1-deoxygalactonojirimycin derivative as a novel pharmacological chaperone for GM1 gangliosidosis. Mol. Ther. 21, 526–532 (2013)
Tapmura, A., Higaki, K., Ninomiya, H., Takai, T., Matsuda, J., Iida, M., Ohno, K., Suzuki, Y., Nanba, E.: Lysosomal accumulation of Trk protein in brain of GM1-gangliosidosis mouse and its restoration by chemical chaperone. J. Neurochem. 118, 399–406 (2011)
Suzuki, Y., Ichinomiya, S., Kurosawa, M., Ohkubo, M., Watanabe, H., Iwasaki, H., Matsuda, J., Noguchi, Y., Takimoto, K., Itoh, M., Tabe, M., Iida, M., Kubo, T., Ogawa, S., Nanba, E., Higaki, K., Ohno, K., Brady, R.O.: Chemical chaperone therapy: clinical effect in murine GM1-gangliosidosis. Ann. Neurol. 62, 671–675 (2007)
Condori, J., Acosta, W., Ayala, J., Katta, V., Flory, A., Martin, R., Radin, J., Cramer, C.L., Radin, D.N.: Enzyme replacement for GM1-gangliosidosis: uptake, LYSOSOMAL activation, and cellular disease correction using a novel β-galactosidase: RTB lectin fusion. Mol. Genet. Metab. 117, 199–209 (2016)
Samoylova, T.I., Martin, D.R., Morrison, N.E., Hwang, M., Cochran, A.M., Samoylov, A.M., Baker, H.J., Cox, N.R.: Generation and characterization of recombinant feline β-galactosidase for preclinical enzyme replacement therapy studies in GM1 gangliosidosis. Metab. Brain Dis. 23, 161–173 (2008)
Hayward, C., Patel, H.C., Manohar, S.G., Lyon, A.R.: Gene therapy for GM1 gangliosidosis: challenges of translational medicine. Ann. Transl. Med. 3, S28 (2015)
Weismann, C.M., Ferreira, J., Keeler, A.M., Su, Q., Qui, L., Shaffer, S.A., Xu, Z., Gao, G., Sena-Esteves, M.: Systemic AAV9 gene transfer in adult GM1 gangliosidosis mice reduces lysosomal storage in CNS and extends lifespan. Hum. Mol. Genet. 24, 4353–4364 (2015)
Baek, R.C., Broekman, M.L., Leroy, S.G., Tierney, L.A., Sandberg, M.A., d’Azzo, A., Seyfried, T.N., Sena-Esteves, M.: AAV-mediated gene delivery in adult GM1-gangliosidosis mice corrects lysosomal storage in CNS and improves survival. PloS ONE 5, e13468 (2010)
Loftsson, T., Brewster, M.E.: Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins. 1. Drug solubilization and stabilization. J. Pharm. Sci. 85, 1017–1025 (1996)
Rajewski, R.A., Stella, V.J.: Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins. 2. In vivo drug delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 85, 1142–1169 (1996)
Uekama, K.: Design and evaluation of cyclodextrin-based drug formulation. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 52, 900–915 (2004)
Uekama, K., Hirayama, F., Irie, T.: Cyclodextrin drug carrier systems. Chem. Rev. 98, 2045–2076 (1998)
Motoyama, K., Toyodome, H., Onodera, R., Irie, T., Hirayama, F., Uekama, K., Arima, H.: Involvement of lipid rafts of rabbit red blood cells in morphological changes induced by methylated β-cyclodextrins. Biol Pharm Bull 32, 700–705 (2009)
Motoyama, K., Arima, H., Toyodome, H., Irie, T., Hirayama, F., Uekama, K.: Effect of 2,6-di-O-methyl-α-cyclodextrin on hemolysis and morphological change in rabbit’s red blood cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 29, 111–119 (2006)
Darblade, B., Caillaud, D., Poirot, M., Fouque, M., Thiers, J.C., Rami, J., Bayard, F., Arnal, J.F.: Alteration of plasmalemmal caveolae mimics endothelial dysfunction observed in atheromatous rabbit aorta. Cardiovasc. Res. 50, 566–576 (2001)
Parpal, S., Karlsson, M., Thorn, H., Stralfors, P.: Cholesterol depletion disrupts caveolae and insulin receptor signaling for metabolic control via insulin receptor substrate-1, but not for mitogen-activated protein kinase control. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 9670–9678 (2001)
Tanaka, Y., Yamada, Y., Ishitsuka, Y., Matsuo, M., Shiraishi, K., Wada, K., Uchio, Y., Kondo, Y., Takeo, T., Nakagata, N., Higashi, T., Motoyama, K., Arima, H., Mochinaga, S., Higaki, K., Ohno, K., Irie, T.: Efficacy of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin in Niemann-Pick disease type C model mice and its pharmacokinetic analysis in a patient with the disease. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 38, 844–851 (2015)
Liu, B., Turley, S.D., Burns, D.K., Miller, A.M., Repa, J.J., Dietschy, J.M.: Reversal of defective lysosomal transport in NPC disease ameliorates liver dysfunction and neurodegeneration in the npc1 –/– mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 2377–2382 (2009)
Camargo, F., Erickson, R.P., Garver, W.S., Hossain, G.S., Carbone, P.N., Heidenreich, R.A., Blanchard, J.: Cyclodextrins in the treatment of a mouse model of Niemann-Pick C disease. Life Sci. 70, 131–142 (2001)
Maeda, Y., Motoyama, K., Higashi, T., Horikoshi, Y., Takeo, T., Nakagata, N., Kurauchi, Y., Katsuki, H., Ishitsuka, Y., Kondo, Y., Irie, T., Furuya, H., Era, T., Arima, H.: Effects of cyclodextrins on GM1-gangliosides in fibroblasts from GM1-gangliosidosis patients. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 67, 1133–1142 (2015)
Yan, Y., Shin, S., Jha, B.S., Liu, Q., Sheng, J., Li, F., Zhan, M., Davis, J., Bharti, K., Zeng, X., Rao, M., Malik, N., Vemuri, M.C.: Efficient and rapid derivation of primitive neural stem cells and generation of brain subtype neurons from human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2, 862–870 (2013)
Matsuda, J., Suzuki, O., Oshima, A., Ogura, A., Noguchi, Y., Yamamoto, Y., Asano, T., Takimoto, K., Sukegawa, K., Suzuki, Y., Naiki, M.: β-Galactosidase-deficient mouse as an animal model for GM1-gangliosidosis. Glycoconj. J. 14, 729–736 (1997)
Nabi, I.R., Le, P.U.: Caveolae/raft-dependent endocytosis. J. Cell Biol. 161, 673–677 (2003)
Connors, K.A.: The stability of cyclodextrin complexes in solution. Chem. Rev. 97, 1325–1358 (1997)
Neufeld, E.B., Wastney, M., Patel, S., Suresh, S., Cooney, A.M., Dwyer, N.K., Roff, C.F., Ohno, K., Morris, J.A., Carstea, E.D., Incardona, J.P., Strauss, J.F. 3rd, Vanier, M.T., Patterson, M.C., Brady, R.O., Pentchev, P.G., Blanchette-Mackie, E.J.: The Niemann-Pick C1 protein resides in a vesicular compartment linked to retrograde transport of multiple lysosomal cargo. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 9627–9635 (1999)
Higgins, M.E., Davies, J.P., Chen, F.W., Ioannou, Y.A.: Niemann-Pick C1 is a late endosome-resident protein that transiently associates with lysosomes and the trans-Golgi network. Mol. Genet. Metab. 68, 1–13 (1999)
Fantur, K., Hofer, D., Schitter, G., Steiner, A.J., Pabst, B.M., Wrodnigg, T.M., Stutz, A.E., Paschke, E.: DLHex-DGJ, a novel derivative of 1-deoxygalactonojirimycin with pharmacological chaperone activity in human GM1-gangliosidosis fibroblasts. Mol. Genet. Metab. 100, 262–268 (2010)
Rosenbaum, A.I., Zhang, G., Warren, J.D., Maxfield, F.R.: Endocytosis of β-cyclodextrins is responsible for cholesterol reduction in Niemann-Pick type C mutant cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 5477–5482 (2010)
Takamura, A., Higaki, K., Kajimaki, K., Otsuka, S., Ninomiya, H., Matsuda, J., Ohno, K., Suzuki, Y., Nanba, E.: Enhanced autophagy and mitochondrial aberrations in murine GM1-gangliosidosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 367, 616–622 (2008)
Sano, R., Annunziata, I., Patterson, A., Moshiach, S., Gomero, E., Opferman, J., Forte, M., d’Azzo, A.: GM1-ganglioside accumulation at the mitochondria-associated ER membranes links ER stress to Ca2+-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis. Mol. Cell 36, 500–511 (2009)
Ottinger, E.A., Kao, M.L., Carrillo-Carrasco, N., Yanjanin, N., Shankar, R.K., Janssen, M., Brewster, M., Scott, I., Xu, X., Cradock, J., Terse, P., Dehdashti, S.J., Marugan, J., Zheng, W., Portilla, L., Hubbs, A., Pavan, W.J., Heiss, J., Vite, C.H., Walkley, S.U., Ory, D.S., Silber, S.A., Porter, F.D., Austin, C.P., McKew, J.C.: Collaborative development of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin for the treatment of Niemann-Pick type C1 disease. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 14, 330–339 (2014)
Aqul, A., Liu, B., Ramirez, C.M., Pieper, A.A., Estill, S.J., Burns, D.K., Liu, B., Repa, J.J., Turley, S.D., Dietschy, J.M.: Unesterified cholesterol accumulation in late endosomes/lysosomes causes neurodegeneration and is prevented by driving cholesterol export from this compartment. J. Neurosci. 31, 9404–9413 (2011)
Davidson, C.D., Ali, N.F., Micsenyi, M.C., Stephney, G., Renault, S., Dobrenis, K., Ory, D.S., Vanier, M.T., Walkley, S.U.: Chronic cyclodextrin treatment of murine Niemann-Pick C disease ameliorates neuronal cholesterol and glycosphingolipid storage and disease progression. PloS ONE 4, e6951 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grant-in-Aid for JSPS Research Fellow (16J11970) and Health and Labor Sciences Research Grant in Japan (17bk01040015h0005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest in this paper.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10847_2018_835_MOESM1_ESM.pptx
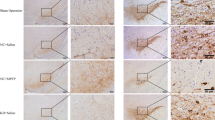
Supplementary Figure S1 TUNEL analysis of brain after intraventricular injection of DM-α-CyD to WT mice. Twenty four h after intraventricular injection of 1 μL of solution containing 431.6 mM DM-α-CyD to WT mice, the brain was collected and 7 μm sequential coronal sections were prepared. TUNEL assay was performed by using the Apoptosis in Situ Detection Kit. The images were representative data of 3 experiments. (PPTX 65 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maeda, Y., Motoyama, K., Higashi, T. et al. Lowering effect of dimethyl-α-cyclodextrin on GM1-ganglioside accumulation in GM1-gangliosidosis model cells and in brain of β-galactosidase-knockout mice. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 93, 53–66 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-018-0835-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-018-0835-8