Abstract
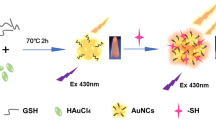
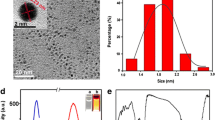
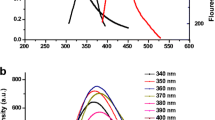
A new calix platform i.e. resorcinarene tetra hydrazide (RTH) has been synthesized and duly characterized by IR, NMR and ESI–MS. Only one agent i.e. RTH has been used as reducing as well as stabilizing agent for the synthesis of gold nanoparticles (AuNps). The synthesised RTH-AuNPs were characterized and analyzed by UV/Vis-spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray analysis. RTH-AuNps were checked for their stability at different pH and temperature. RTH-AuNps having characteristic surface plasmon resonance and being fluorescent in nature were explored for their interaction behavior with different amino acids (AA) by UV–Visible and fluorescence spectroscopy. Among various AA RTH-AuNps were found to be meticulously selective and sensitive for phenylalanine (PHE) by means of fluorescence quenching. This assay allowed rapid and accurate determination of PHE in aqueous medium at room temperature with a linear range of detection from 100 to 820 nM. Furthermore, the RTH-AuNps were also used for successful determination of PHE in human serum providing a scope of detection and determination of PHE in biological samples.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AuNps:
-
Gold nanoparticles
- RTH:
-
Resorcinarene tetrahydrazide
- RTH-AuNps:
-
Resorcinarene tetrahydrazide stabilized gold nanoparticles
References
Lyshevski, S.E.: Nano and molecular electronics handbook. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2010)
Novotny, L., Hecht, B.: Principles of nano-optics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2012)
Skomski, R.: Nanomagnetics. J. Phys. 15(20), R841 (2003)
Candelaria, S.L., Shao, Y., Zhou, W., Li, X., Xiao, J., Zhang, J.-G., Wang, Y., Liu, J., Li, J., Cao, G.: Nanostructured carbon for energy storage and conversion. Nano Energy 1(2), 195–220 (2012)
Polshettiwar, V., Varma, R.S.: Green chemistry by nano-catalysis. Green Chem. 12(5), 743–754 (2010)
Dreaden, E.C., Alkilany, A.M., Huang, X., Murphy, C.J., El-Sayed, M.A.: The golden age: gold nanoparticles for biomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41(7), 2740–2779 (2012)
Lo, L., Li, Y., Yeung, K., Yuen, C.: Indicating the development stage of nanotechnology in the textile and clothing industry. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 4(6), 667–679 (2007)
Mu, L., Sprando, R.L.: Application of nanotechnology in cosmetics. Pharm. Res. 27(8), 1746–1749 (2010)
Naveenraj, S., Anandan, S., Kathiravan, A., Renganathan, R., Ashokkumar, M.: The interaction of sonochemically synthesized gold nanoparticles with serum albumins. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 53(3), 804–810 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2010.03.039
Wangoo, N., Bhasin, K.K., Mehta, S.K., Suri, C.R.: Synthesis and capping of water-dispersed gold nanoparticles by an amino acid: bioconjugation and binding studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 323(2), 247–254 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2008.04.043
Huang, X., El-Sayed, M.A.: Gold nanoparticles: optical properties and implementations in cancer diagnosis and photothermal therapy. J. Adv. Res. 1(1), 13–28 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.jare.2010.02.002
Chuang, Y.-C., Li, J.-C., Chen, S.-H., Liu, T.-Y., Kuo, C.-H., Huang, W.-T., Lin, C.-S.: An optical biosensing platform for proteinase activity using gold nanoparticles. Biomaterials 31(23), 6087–6095 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.04.026
Mihailescu, G., Olenic, L., Pruneanu, S., Bratu, I., Kacso, I.: The effect of pH on amino acids binding to gold nanoparticles. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 9(3), 756–759 (2007)
Wei, X., Qi, L., Tan, J., Liu, R., Wang, F.: A colorimetric sensor for determination of cysteine by carboxymethyl cellulose-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta. 671(1–2), 80–84 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.aca.2010.05.006
Misra, T.K., Chen, T.S., Liu, C.Y.: Phase transfer of gold nanoparticles from aqueous to organic solution containing resorcinarene. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 297(2), 584–588 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2005.11.013
Stavens, K.B., Pusztay, S.V., Zou, S., Andres, R.P., Wei, A.: Encapsulation of neutral gold nanoclusters by resorcinarenes. Langmuir 15(24), 8338–8339 (1999)
Wei, A., Kim, B., Pusztay, S.V., Tripp, S.L., Balasubramanian, R.: Resorcinarene-encapsulated nanoparticles: building blocks for self-assembled nanostructures. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 41, 83–86 (2001)
Yao, Y.姚.S., Yan(孙燕) Han, Ying(韩莹) Yan, Chaoguo*(颜朝国): Preparation of resorcinarene-functionalized gold nanoparticles and their catalytic activities for reduction of aromatic nitro compounds. Chin. J. Chem. 28, 705–712 (2010)
Kim, B., Balasubramanian, R., Pe´rez-Segarra, W., Wei, A., Decker, B., Mattay, J.: Self-assembly of resorcinarene-stabilized gold nanoparticles: influence of the macrocyclic headgroup. Supramol. Chem. 17(1–2), 173–180 (2005)
Balasubramanian, R., Kim, B., Tripp, S.L., Wang, X., Lieberman, M., Wei, A.: Dispersion and stability studies of resorcinarene-encapsulated gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 18, 3676–3681 (2002)
Shen, M., Chen, W.F., Sun, Y., Yan, C.-G.: Synthesis and characterization of water-soluble gold colloids stabilized with aminoresorcinarene. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 68, 2252–2261 (2007)
Bhatt, K.D., Vyas, D.J., Makwana, B.A., Darjee, S.M., Jain, V.K.: Highly stable water dispersible calix[4]pyrrole octa-hydrazide protected gold nanoparticles as colorimetric and fluorometric chemosensors for selective signaling of Co(II) ions. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 121, 94–100 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.saa.2013.10.076
Vyas, D.J., Makwana, B.A., Gupte, H.S., Bhatt, K.D., Jain, V.K.: An efficient one pot synthesis ofwater-dispersible calix[4]arene polyhydrazide protected gold nanoparticles—a “turn off” fluorescent sensor for Hg[II] ions. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol 12(1–7), 73–80 (2012). doi:10.1166/jnn.2012.5837
Makwana, B.A., Vyas, D.J., Bhatt, K.D., Jain, V.K., Agrawal, Y.K.: Highly stable antibacterial silver nanoparticles as selective fluorescent sensor for Fe3+ ions. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 134, 73–80 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.saa.2014.05.044
Blikova, Y.N., Otkidach, K.N., Shvedene, N.V., Pletnev, I.V., Sheina, N.M., Gorbunova, Y.G.: Metal phthalocyanine and crown ether-based membranes for the potentiometric determination of phenylalanine methyl ester using an ion-selective electrode. J. Anal. Chem. 59(6), 584–589 (2004). doi:10.1023/B:JANC.0000030884.77442.12
Kamruzzaman, M., Alam, A.-M., Kim, K.M., Lee, S.H., Kim, Y.H., Kim, G.-M., Dang, T.D.: Microfluidic chip based chemiluminescence detection of l-phenylalanine in pharmaceutical and soft drinks. Food Chem. 135(1), 57–62 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.04.062
Li, C.F., Du, L.M., Wu, H., Chang, Y.X.: Determination of l-phenylalanine by cucurbit[7]uril sensitized fluorescence quenching method. Chin. Chem. Lett. 22(7), 851–854 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2010.12.029
Hood, A., Grange, D.K., Christ, S.E., Steiner, R., White, D.A.: Variability in phenylalanine control predicts IQ and executive abilities in children with phenylketonuria. Mol. Genet. Metab. 111, 445–451 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2014.01.012
Prinsen, H.C.M.T., Holwerda-Loof, N.E., de Sain-van der Velden, M.G.M., Visser, G., Verhoeven-Duif, N.M.: Reliable analysis of phenylalanine and tyrosine in a minimal volume of blood. Clin. Biochem. 46(13–14), 1272–1275 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2013.05.054
Pimentel, F.B., Alves, R.C., Costa, A.S.G., Torres, D., Almeida, M.F., Oliveira, M.B.P.P.: Phenylketonuria: protein content and amino acids profile of dishes for phenylketonuric patients. The relevance of phenylalanine. Food Chem. 149, 144–150 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.10.099
Zhang, K., Yan, H.-T., Zhou, T.: Spectrofluorimetric determination of phenylalanine based on fluorescence enhancement of europium ion immobilized with sol–gel method. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 83(1), 155–160 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.saa.2011.08.007
Cheng, C., Wu, S.-C.: Simultaneous analysis of aspartame and its hydrolysis products of Coca-Cola Zero by on-line postcolumn derivation fluorescence detection and ultraviolet detection coupled two-dimensional high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1218(20), 2976–2983 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2011.03.033
Wang, L., Li, L.-L., Ma, H.L., Wang, H.: Recent advances in biocompatible supramolecular assemblies for biomolecular detection and delivery. Chin. Chem. Lett. 24(5), 351–358 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2013.03.018
Vyas, D.J., Makwana, B.A., Gupte, H.S., Bhatt, K.D., Jain, V.K.: An efficient one pot synthesis of water-dispersible calix[4]arene polyhydrazide protected gold nanoparticles-a turn off fluorescent sensor for Hg[II] Ions. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 12(5), 3781–3787 (2012)
Nickel, U., zu Castell, A., Pöppl, K., Schneider, S.: A silver colloid produced by reduction with hydrazine as support for highly sensitive surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Langmuir 16(23), 9087–9091 (2000)
Chen, M., Feng, Y.G., Wang, X., Li, T.C., Zhang, J.Y., Qian, D.J.: Silver nanoparticles capped by oleylamine: formation, growth, and self-organization. Langmuir 23(10), 5296–5304 (2007)
Newman, J., Blanchard, G.: Formation of gold nanoparticles using amine reducing agents. Langmuir 22(13), 5882–5887 (2006)
Oshima, T., Goto, M., Furusaki, S.: Extraction behavior of amino acids by calix [6] arene carboxylic acid derivatives. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 43(1), 77–86 (2002)
Farokhcheh, A., Alizadeh, N.: Amino acid detection using fluoroquinolone–Cu2+ complex as a switch-on fluorescent probe by competitive complexation without derivatization. J. Lumin. 145, 708–712 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.jlumin.2013.08.039
Jans, H., Huo, Q.: Gold nanoparticle-enabled biological and chemical detection and analysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41(7), 2849–2866 (2012)
Chen, W., Tu, X., Guo, X.: Fluorescent gold nanoparticles-based fluorescence sensor for Cu2+ ions. Chem. Commun. 13, 1736–1738 (2009). doi:10.1039/B820145E
Sperling, R.A., Gil, P.R., Zhang, F., Zanella, M., Parak, W.J.: Biological applications of gold nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 37(9), 1896–1908 (2008)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial assistance provided by University Grant Commission (New Delhi). The authors also acknowledge Sophisticated Analytical Instrument Facility (Panjab University), Central Salt & Marine Chemicals Research Institute (Bhavanagar) and Gujarat Forensic Sciences University (Gandhinagar) for providing instrumental facilities and Information and Library Network (Ahmedabad) for e-journals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, D.R., Darjee, S.M., Bhatt, K.D. et al. Calix protected gold nanobeacon as turn-off fluorescent sensor for phenylalanine. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 82, 425–436 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-015-0509-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-015-0509-8