Abstract
Background
Traditional cardiac pacemakers commonly have a range of complications related to the presence of intracardiac leads. A new class of extravascular and leadless pacemakers has recently emerged with the potential to mitigate these complications and expand access to cardiac pacing. The objective of this study is to evaluate the implantation, short-term chronic safety, and performance of a novel subxiphoidal extracardiac pacemaker.
Methods
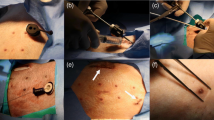
Normal Yorkshire Cross swine (n = 16) were implanted with the subxiphoidal pacemaker. The pacemaker was inserted through a midline chest incision and clipped to the underside of the sternum, with the stimulation electrode placed on the anterior pericardium. Animals were chronically paced and followed for 90 days post-implant, with periodic measurement of pacing capture threshold (PCT) and electrode impedance.
Results
All 16 animals were successfully implanted with the study device. At implant, a consistent average PCT of 2.2 ± 0.4 V at a pulse width of 1.0 ms was observed in all animals, with an average implant impedance of 648 ± 44 Ω. Chronic pacing was programmed at a rate of 60 bpm, an amplitude of 3.4 ± 0.7 V, and a pulse width of 1.0 ms. PCT rose to 4.6 ± 0.8 V at 14 days and stabilized; at 90 days, PCT was 3.8 ± 1.2 V and electrode impedance was 533 ± 105 Ω. All implanted animals completed the study with no clinically significant findings, no clinically significant abnormalities, and with no adverse events that affected animal welfare.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated the safety and feasibility of a novel subxiphoidal extracardiac pacemaker to deliver short-term chronic extravascular therapy. Further studies are required to assess the safety, feasibility, and long-term chronic pacing performance in human subjects.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duray GZ, Ritter P, El-Chami M, Narasimhan C, Omar R, Tolosana JM, Zhang S, Soejima K, Steinwender C, Rapallini L, Cicic A, Fagan DH, Liu S, Reynolds D. Long-term performance of a transcatheter pacing system: 12-Month results from the Micra Transcatheter Pacing Study. Heart Rhythm. 2017;14:702–9.
Kirkfeldt RE, Johansen JB, Nohr EA, Jorgensen OD, Nielsen JC. Complications after cardiac implantable electronic device implantations: an analysis of a complete, nationwide cohort in Denmark. Eur Heart J. 2014;35:1186–94.
Udo EO, Zuithoff NP, van Hemel NM, de Cock CC, Hendriks T, Doevendans PA, Moons KG. Incidence and predictors of short- and long-term complications in pacemaker therapy: the FOLLOWPACE study. Heart Rhythm. 2012;9:728–35.
El-Chami MF, Bockstedt L, Longacre C, Higuera L, Stromberg K, Crossley G, Kowal RC, Piccini JP. Leadless vs. transvenous single-chamber ventricular pacing in the Micra CED study: 2-year follow-up. Eur Heart J. 2022;43:1207–15.
Reddy VY, Exner DV, Cantillon DJ, Doshi R, Bunch TJ, Tomassoni GF, Friedman PA, Estes NA 3rd, Ip J, Niazi I, Plunkitt K, Banker R, Porterfield J, Ip JE, Dukkipati SR. Percutaneous Implantation of an Entirely Intracardiac Leadless Pacemaker. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1125–35.
Reynolds D, Duray GZ, Omar R, Soejima K, Neuzil P, Zhang S, Narasimhan C, Steinwender C, Brugada J, Lloyd M, Roberts PR, Sagi V, Hummel J, Bongiorni MG, Knops RE, Ellis CR, Gornick CC, Bernabei MA, Laager V, Stromberg K, Williams ER, Hudnall JH, Ritter P. A Leadless Intracardiac Transcatheter Pacing System. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:533–41.
Ammari Z, Syed M, Al-Sarie M, Karim S, Grubb B. Safety and Efficacy of Leadless Pacemakers: A New Era of Pacing. J Innov Card Rhythm Manag. 2018;9:3215–20.
Hauser RG, Gornick CC, Abdelhadi RH, Tang CY, Kapphahn-Bergs M, Casey SA, Okeson BK, Steele EA, Sengupta JD. Leadless pacemaker perforations: Clinical consequences and related device and user problems. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2022;33:154–9.
Clark BC, Kumthekar R, Mass P, Opfermann JD, Berul CI. Chronic performance of subxiphoid minimally invasive pericardial Model 20066 pacemaker lead insertion in an infant animal model. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2020;59:13–9.
Carnicer-Lombarte A, Chen ST, Malliaras GG, Barone DG. Foreign Body Reaction to Implanted Biomaterials and Its Impact in Nerve Neuroprosthetics. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:622524.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and conformed to the Food and Drug Administration “Principles of Good Laboratory Practice (GLP)” and the National Institute of Health “Guide and Care for Use of Laboratory Animals.”
Conflict of interest
Drs. Libbus, Tholakanahalli, Roukoz, and Knoper are consultants to Calyan Technologies. Mr. Verma, Ms. Isac, and Dr. Manicka are employees of Calyan Technologies.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Libbus, I., Tholakanahalli, V., Roukoz, H. et al. Safety and performance of a novel subxiphoidal pacemaker system. J Interv Card Electrophysiol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-024-01778-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-024-01778-y