Abstract
Background
There are conflicting data regarding the relationship between high-sensitivity cardiac Troponin I (Hs-cTnI) and the ablation effectiveness quotient (AEQ) with arrhythmia recurrence following atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation. Our goals were to evaluate the impact of the Ablation Index (AI) software on Hs-cTnI and AEQ levels and to assess whether these markers are predictors of arrhythmia recurrence.
Methods
Prospective single-center study of 75 consecutive patients referred for paroxysmal AF ablation from October 2017 to January 2019. Procedural endpoints and 2-year outcomes were assessed and compared to those of 75 propensity score-matched patients submitted to non-AI-guided pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) [control group].
Results
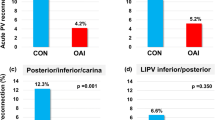
Compared to the control group, patients having AI-guided PVI had lower Hs-cTnI values (1580 [IQR 1180–2140] ng/L vs. 2600 [IQR 1840 – 3900], p < 0.001) and a lower AEQ (0.9 [IQR 0.6–1.2] ng/L/s vs. 1.4 [0.8–1.6] ng/L/s, p < 0.001). After a median follow-up of 26 (IQR 20–32) months, there was a significant reduction in arrhythmia recurrence in the AI group (15% vs. 31%, HR 0.67 [95% CI, 0.32–1.40], p = 0.02). However, neither Hs-cTnI nor AEQ was predictors of arrhythmia recurrence in AI-guided PVI.
Conclusions
The use of the AI software led to reduced levels of Hs-cTnI and lower AEQ in AF patients submitted to PVI. However, none of these markers predicted arrhythmia recurrence.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blum S, Aeschbacher S, Meyre P, Zwimpfer L, Reichlin T, Beer JH, et al. Incidence and Predictors of Atrial Fibrillation Progression. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019;8(20): e012554.
Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, Ahlsson A, Atar D, Casadei B, et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur Heart J. 2016;37(38):2893–962.
Ganesan AN, Shipp NJ, Brooks AG, Kiklik P, Lau DH, Lim HS, et al. Long-term outcomes of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013;2(2): e004549.
Nakanishi K, Fukuda S, Yamashita H, Hasegawa T, Kosaka M, Shirai N, et al. High-sensitive cardiac troponin T as a novel predictor for recurrence of atrial fibrillation after radiofrequency catheter ablation. Europace. 2017;19(12):1951–7.
Yoshida K, Yui Y, Kimata A, Koda N, Kato J, Baba M, et al. Troponin elevation after radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: relevance to AF substrate, procedural outcomes, and reverse structural remodeling. Heart Rhythm. 2014;11(8):1336–42.
Bai Y, Guo SD, Liu Y, Ma CS, Lip GYH. Relationship of troponin to incident atrial fibrillation occurrence, recurrence after radiofrequency ablation and prognosis: a systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression. Biomarkers. 2018;23(6):512–7.
Wynn GJ, Das M, Bonnett LJ, Hall MCS, Snowdon RL, Waktare JEP, et al. A novel marker to predict early recurrence after atrial fibrillation ablation: the ablation effectiveness quotient. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2015;26(4):397–403.
Das M, Duytschaever M, Gupta D, Lukac P, Sorrel J, Philips T, et al. Ablation Index Predicts Sites of Acute Reconnection After Pulmonary Vein Isolation : A Multi-Center Retrospective Analysis. Heart Rhythm. 2015;12:S97–154.
Das M, Loveday JJ, Wynn GJ, Gomes S, Saeed Y, Bonnett LJ, et al. Ablation index, a novel marker of ablation lesion quality: prediction of pulmonary vein reconnection at repeat electrophysiology study and regional differences in target values. Europace. 2017;19(5):775–83.
Phlips T, Taghji P, El Haddad M, Wolf M, Knecht S, Vandekerckhove Y, et al. Improving procedural and one-year outcome after contact force-guided pulmonary vein isolation: the role of interlesion distance, ablation index, and contact force variability in the ’CLOSE’-protocol. Europace. 2018;20(Fl_3):f419-27.
Ho SY, Cabrera JA, Sanchez-Quintana D. Left atrial anatomy revisited. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2012;5:220–8.
Taghji P, El Haddad M, Phlips T, Wolf M, Knecht S, Vandekerckhove Y, et al. Evaluation of a Strategy Aiming to Enclose the Pulmonary Veins With Contiguous and Optimized Radiofrequency Lesions in Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: A Pilot Study. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2018;4(1):99–108.
Calkins H, Hindricks G, Cappato R, Kim YH, Saad EB, Aguinaga L et al. 2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Europace. 2018; 20(1):e1-e160.
Nakagawa H, Ikeda A, Govari A, Thanassis P, Constantine G, Bar-Tal M, et al. Prospective study to test the ability to create RF lesions at predicted depths of 3, 5, 7 and 9mm using a new formula incorporating contact force, radiofrequency power and application time (Force-Power-Time Index) in the beating canine heart. Heart Rhythm. 2013;10(S481).
El Haddad M, Taghji P, Philips T, Wolf M, Demolder A, Choudhury R, et al. Determinants of acute and late pulmonary vein reconnection in contact force-guided pulmonary vein isolation: identifying the weakest link in the ablation chain. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2017;10(4): e004867.
Neuzil P, Reddy VY, Kautzner J, Petru J, Wichterle D, Shah D, et al. Electrical reconnection after pulmonary vein isolation is contingent on contact force during initial treatment: results from the EFFICAS I study. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2013;6(2):327–33.
Fishbein MC, Wang T, Matijasevic M, Hong L, Apple FS. Myocardial tissue troponins T and I. An immunohistochemical study in experimental models of myocardial ischemia. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2003; 12(2):65–71.
Lim HS, Schultz C, Dang J, Alasady M, Lau DH, Brooks AG, et al. Time course of inflammation, myocardial injury, and prothrombotic response after radiofrequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2014;7(1):83–9.
Zeljkovic I, Knecht S, Pavlovic N, Celikyrut U, Spies F, Burri S, et al. High-sensitive cardiac troponin T as a predictor of efficacy and safety after pulmonary vein isolation using focal radiofrequency, multielectrode radiofrequency and cryoballoon ablation catheter. Open Heart. 2019;6(1): e000949.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
P.A.S has received speaker fees from Biosense Webster, Boston Scientific, Medtronic and Abbott. S.B. has received training grants from Biosense Webster and Biotronik. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Approved by the ethical committee.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sousa, P.A., Puga, L., Barra, S. et al. High-sensitivity Troponin I and Ablation Effectiveness Quotient after Ablation Index-guided pulmonary vein isolation—markers of arrhythmia recurrence?. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 65, 115–121 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-022-01229-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-022-01229-6