Abstract
Purpose
Leadless pacemaker (LP) extraction is a relatively new field with limited operator experience. We sought to report a comparison of retrieval process for Nanostim vs Micra transcatheter LPs.
Methods
The list of retrievals for the Micra transcatheter pacemaker system (TPS) was obtained from Medtronic whereas Nanostim data was obtained from centers that participated in the Leadless II study. Details of retrieval such as indication, days post implantation, complications, and post procedure device management were obtained from the manufacturer database for each site, and any missing details were obtained from individual operators. Extractions performed on the same day were labeled as “Early” and thereafter were labeled as “Late.”
Results
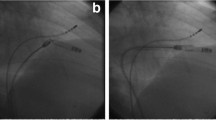
A total of 113 retrievals were attempted (73 in Nanostim and 40 in Micra TPS). The most common reasons for retrieval were battery advisory and inadequate pacing threshold (n = 16) for Nanostim and Micra, respectively. Success rate in Nanostim group was around 90% (66/73) compared with 100% in Micra group (p = 0.049). Late retrieval occurred in 50% of Micra TPS cases (20/40) compared with 100% of Nanostim LP cases. Median time to extraction was 46 days for Micra TPS and 256 days for Nanostim LP (p < 0.001). Rate of serious adverse events with Nanostim extraction was 3% (n = 2/73).
Conclusion
Overall, LP extraction is feasible and safe to perform irrespective of the duration and type of the device.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knops RE, Tjong FV, Neuzil P, et al. Chronic performance of a leadless cardiac pacemaker: 1-year follow-up of the LEADLESS trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. Apr 21 2015;65:1497–504.
Roberts PR, Clementy N, Al Samadi F, et al. A leadless pacemaker in the real-world setting: the Micra transcatheter pacing system post-approval registry. Heart rhythm Sep. 2017;14:1375–9.
Ritter P, Duray GZ, Zhang S, et al. Micra transcatheter pacing study G. the rationale and design of the Micra transcatheter pacing study: safety and efficacy of a novel miniaturized pacemaker. Europace May. 2015;17:807–13.
Koruth JS, Rippy MK, Khairkhahan A, et al. Percutaneous retrieval of implanted leadless pacemakers: feasibility at 2.5 years post-implantation in an in vivo ovine model. JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology 2015/12/01/ 2015;1:563–570.
Lakkireddy D, Knops R, Atwater B, et al. A worldwide experience of the management of battery failures and chronic device retrieval of the Nanostim leadless pacemaker. Heart rhythm Dec. 2017;14:1756–63.
Reddy VY, Miller MA, Knops RE, et al. Retrieval of the leadless cardiac pacemaker: a multicenter experience. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol Dec. 2016;9.
Afzal MR, Daoud EG, Cunnane R, et al. Techniques for successful early retrieval of the micra transcatheter pacing system: a worldwide experience. Heart rhythm Feb 7 2018.
Acknowledgments
We thank the following clinician scientists for their work:
Vivek Y. Reddy MD1
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, USA
3Homolka Hospital, Prague, Czech Republic
Marc A. Miller MD1
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, USA
Reinoud E. Knops MD2
Amsterdam Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Petr Neuzil MD PhD3
Prague, Czech Republic
Pascal Defaye MD4,
CHU, Grenoble, France;
Werner Jung MD5
Schwarzwald Baar Klinikum, Villingen-Schwenningen, Germany
Rahul Doshi MD6
USC University Hospital, Los Angeles, USA
Mark Castellani MD7
Sparrow Research, Lansing, USA
Adam Strickberger MD8
Inova Fairfax Hospital, Fairfax, USA
Hardwin R. Mead MD9
Sequoia Hospital, Redwood City, USA
Harish Doppalapudi MD10
University of Alabama, Birmingham, USA
Dhanunjaya Lakkireddy MD11
University of Kansas Medical Center
Matthew Bennett MD12
Vancouver General Hospital, Vancouver, Canada
Srinivas Dukkipati MD1
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, USA
Johannes Sperzel MD13
Hospital Kerckhoff Klinik, Bad Nauheim, Germany
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
DL is a consultant to Johnson & Johnson, Abbott, Biotronik, Pfizer, and Boston Sci. RG is a consultant/speaker of Abbott Medical, Boston Scientific, Zoll Medical, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb and a physician advisor of HealthTrust PG, Abiomed.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dar, T., Akella, K., Murtaza, G. et al. Comparison of the safety and efficacy of Nanostim and Micra transcatheter leadless pacemaker (LP) extractions: a multicenter experience. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 57, 133–140 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-019-00684-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-019-00684-y