Abstract
Background
Conventional catheter ablation of right-sided accessory pathways (RAPs) can be challenging.
Objective
To determine if a subvalvular catheter approach for RAPs targeting the ventricular insertion site, as on the left side, can improve catheter stability and tissue contact and thus increase acute and chronic ablation success rates.
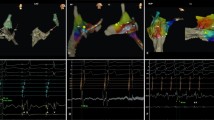
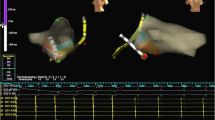
Methods and results
We retrospectively compared 22 patients (pts) with conventional catheter ablation of RAPs (group 1) with 9 consecutive pts (group 2) undergoing catheter ablation of a RAP using a subvalvular catheter approach targeting the ventricular site of AP. Ablation failed in 2/22 group 1 vs 0/9 group 2 pts (ns) and recurrences of AP conduction were registered in 4/19 group 1 vs 1/9 group 2 pts (ns) during follow-up. Significant shorter values were found in group 2 pts compared with group 1 for number of RF applications (3.6 ± 1.6 vs 8.2 ± 4.3), AP block time (6.2 ± 2.4 vs 9.2 ± 3.9 min), fluoroscopy time (17.2 ± 6.9 vs 25.6 ± 10.3 min), and procedure time (70.8 ± 23.9 vs 138 ± 44.4 min). There were no procedure related complications.
Conclusion
Catheter ablation of RAPs using a subvalvular approach seems as effective and safe compared with conventional ablation but with reduced procedure time and radiation exposure and might be at least considered an alternative after failed conventional catheter ablation of RAPs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jackman WM, Wang XZ, Friday KJ, Roman CA, Moulton KP, Beckman KJ, et al. Catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular pathways (Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome) by radiofrequency current. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:1605–11.
Kay GN, Epstein AE, Dailey SM, Plumb VJ. Role of radiofrequency ablation in the management of supraventricular arrhythmias: experience in 760 consecutive patients. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1993;4:371–89.
Haissaguerre M, Gaita F, Marcus FI, Clementy J. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of accessory pathways: a contemporary review. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1994;5:532–52.
Langberg JJ, Calkins H, Kim YN, Sousa J, el-Atassi R, Leon A, et al. Recurrence of conduction in accessory atrioventricular connections after initially successful radiofrequency catheter ablation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1992;19:1588–92.
Timmermans C, Smeets JL, Rodriguez LM, Oreto G, Medina E, Notheis W, et al. Recurrence rate after accessory pathway ablation. Br Heart J. 1994;72:571–4.
Xie B, Heald SC, Camm AJ, Rowland E, Ward DE. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular pathways: primary failure and recurrence of conduction. Heart. 1997;77:363–8.
Morady F, Strickberger A, Man KC, Daoud E, Niebauer M, Goyal R, et al. Reasons for prolonged or failed attempts at radiofrequency catheter ablation of accessory pathways. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996;27:683–9.
Yang J, Yang G, Chen H, Ju W, Yang B, Zhang F, et al. An alternative under-valve approach to ablate right-sided accessory pathways. Heart Rhythm. 2019;16:51–6.
Zeljko HM, Yue A. Catheter inversion technique for ablation of parahisian accessory pathway. Europace. 2015;17:1707.
Calkins H, Prystowsky E, Berger RD, Saul JP, Klein LS, Liem LB, et al. Recurrence of conduction following radiofrequency catheter ablation procedures: relationship to ablation target and electrode temperature. The Atakr multicenter investigators group. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1996;7:704–12.
Wong T, Hussain W, Markides V, Gorog DA, Wright I, Peters NS, et al. Ablation of difficult right-sided accessory pathways aided by mapping of tricuspid annular activation using a halo catheter : halo-mapping of right sided accessory pathways. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2006;16:175–82.
Olgun H, Karagoz T, Celiker A. Coronary microcatheter mapping of coronary arteries during radiofrequency ablation in children. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2010;27:75–9.
Yamane T, Jais P, Shah DC, Hocini M, Peng JT, Deisenhofer I, et al. Efficacy and safety of an irrigated-tip catheter for the ablation of accessory pathways resistant to conventional radiofrequency ablation. Circulation. 2000;102:2565–8.
Lesh MD, Van Hare GF, Scheinman MM, Ports TA, Epstein LA. Comparison of the retrograde and transseptal methods for ablation of left free wall accessory pathways. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993;22:542–9.
Otomo K, Gonzalez MD, Beckman KJ, Nakagawa H, Becker AE, Shah N, et al. Reversing the direction of paced ventricular and atrial wavefronts reveals an oblique course in accessory AV pathways and improves localization for catheter ablation. Circulation. 2001;104:550–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wieczorek, M., Tajtaraghi, S. & Hoeltgen, R. A subvalvular catheter approach for radiofrequency ablation of right-sided accessory pathways. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 56, 29–36 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-019-00597-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-019-00597-w