Abstract
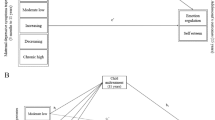
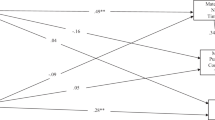
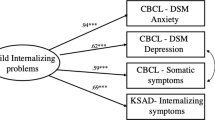
The experience of childhood maltreatment is associated with greater psychological difficulties in survivors of maltreatment and their later children. While this intergenerational pattern is well-established, little is known about the mechanisms leading to negative outcomes in the children of maltreated parents. Moreover, many studies to date have focused on young children, with less research on adolescent children. In a sample of mother–adolescent child dyads (N = 241), we explored links between mothers’ experiences of childhood maltreatment and adolescents’ internalizing and externalizing symptoms over a 3-year period, as well as whether maternal emotion regulation difficulties and invalidating emotion socialization practices partially explained any links. Latent growth curve analysis revealed that internalizing symptoms increased slightly over the 3-year period, whereas externalizing symptoms remained stable on average. Mothers who reported higher levels of childhood maltreatment had adolescent children with greater overall levels of internalizing and externalizing symptoms, but not greater increases over time. Maternal emotion regulation partially mediated the association between maternal history of childhood maltreatment and offspring externalizing symptoms but not internalizing symptoms. Maternal emotion socialization did not account for either association. Our results suggest that mothers’ experiences of childhood maltreatment are associated with greater overall psychological difficulties in their adolescent children, and mothers’ own emotion dysregulation partially accounts for that association for externalizing symptoms.
Highlight
-
Examined mediators of association of parental history of childhood maltreatment and child symptoms.
-
Used Latent Growth Curve analysis to study adolescent child symptoms longitudinally.
-
Maternal emotion regulation mediated association between maltreatment history and externalizing symptoms.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alink, L. R. A., Cicchetti, D., Kim, J., & Rogosch, F. A. (2009). Mediating and moderating processes in the relation between maltreatment and psychopathology: mother–child relationship quality and emotion regulation. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 37, 831–843.
Bater, L. R., & Jordan, S. S. (2017). Child routines and self-regulation serially mediate parenting practices and externalizing problems in preschool children. Child Youth and Forum, 46, 243–259.
Berlin, L. J., Appleyard, K., & Dodge, K. A. (2011). Intergenerational continuity in child maltreatment: mediating mechanisms and implications for prevention. Child Development, 82, 162–176.
Bernstein, D. P., Fink, L., Handelsman, L., & Foote, J. (1994). Childhood Trauma Questionnaire (CTQ) [Database record]. APA PsycTests.
Buckholdt, K. E., Parra, G. R., & Jobe-Shields, L. (2014). Intergenerational transmission of emotion dysregulation through parental invalidation of emotions: implications for adolescent internalizing and externalizing behaviors. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 23, 324–332.
Burns, E. E., Jackson, J. L., & Harding, H. G. (2010). Child maltreatment, emotion regulation, and posttraumatic stress: the impact of emotional abuse. Journal of Aggression, Maltreatment & Trauma, 19, 801–819.
Chaplin, T. M., Poon, J. A., Thompson, J. C., Hansen, A., Dziura, S. L., Turpyn, C. C., Niehaus, C. E., Sinha, R., Chassin, L., & Ansell, E. B. (2019). Sex‐differentiated associations among negative parenting, emotion‐related brain function, and adolescent substance use and psychopathology symptoms. Social Development, 28(3), 637–656.
Choi, K. W., Houts, R., Arseneault, L., Pariante, C., Sikkema, K. J., & Moffitt, T. E. (2019). Maternal depression in the intergenerational transmission of childhood maltreatment and its sequelae: Testing postpartum effects in a longitudinal birth cohort. Development and Psychopathology, 31, 143–156.
Cicchetti, D., & Toth, S. L. (2005). Child maltreatment. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 1(1), 409–438.
Cooke, J. E., Racine, N., Plamondon, A., Tough, S., & Madigan, S. (2019). Maternal adverse childhood experiences, attachment style, and mental health: pathways of transmission to child behavior problems. Child Abuse & Neglect, 93, 27–37.
Dong, M., Anda, R. F., Felitti, V. J., Dube, S. R., Williamson, D. F., Thompson, T. J., Loo, C. M., & Giles, W. H. (2004). The interrelatedness of multiple forms of childhood abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction. Child Abuse & Neglect, 28(7), 771–784.
Dutcher, C. D., Vujanovic, A. A., Paulus, D. J., & Bartlett, B. A. (2017). Childhood maltreatment severity and alcohol use in adult psychiatric inpatients: The mediating role of emotion regulation difficulties. General hospital psychiatry, 48, 42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2017.06.014.
Eisenberg, N., Cumberland, A., & Spinrad, T. L. (1998). Parental socialization of emotion. Psychological Inquiry, 9(4), 241–273.
Esteves, K., Gray, S. A., Theall, K. P., & Drury, S. S. (2017). Impact of physical abuse on internalizing behavior across generations. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 26(10), 2753–2761.
Fang, X., Brown, D. S., Florence, C. S., & Mercy, J. A. (2012). The economic burden of child maltreatment in the United States and implications for prevention. Child Abuse & Neglect, 36(2), 156–165.
Fanti, K. A., & Henrich, C. C. (2010). Trajectories of pure and co-occurring internalizing and externalizing problems from age 2 to age 12: Findings from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Study of Early Child Care. Developmental Psychology, 46(5), 1159–1175.
Gadow, K. D., Sprafkin, J., Carlson, G. A., Schneider, J., Nolan, E. E., Mattison, R. E., & Rundberg-Rivera, V. (2002). A DSM-IV–referenced, adolescent self-report rating scale. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 41(6), 671–679.
Ghandour, R. M., Sherman, L. J., Vladutiu, C. J., Ali, M. M., Lynch, S. E., Bitsko, R. H., & Blumberg, S. J. (2019). Prevalence and treatment of depression, anxiety, and conduct problems in U.S. children. The Journal of Pediatrics, 206, 256–267.e3.
Gonçalves, S. F., Chaplin, T. M., Turpyn, C. C., Niehaus, C. E., Curby, T. W., Sinha, R., & Ansell, E. B. (2019). Difficulties in emotion regulation predict depressive symptom trajectory from early to middle adolescence. Child psychiatry and human development, 50(4), 618–630.
Gratz, K. L., & Roemer, L. (2004). Multidimensional assessment of emotion regulation and dysregulation: Development, factor structure, and initial validation of the difficulties in emotion regulation scale. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 26(1), 41–54.
Greene, C. A., Haisley, L., Wallace, C., & Ford, J. D. (2020). Intergenerational effects of childhood maltreatment: a systematic review of the parenting practices of adult survivors of childhood abuse, neglect, and violence. Clinical Psychology Review, 101891.
Hankin, B. L., Mermelstein, R., & Roesch, L. (2007). Sex differences in adolescent depression. Stress exposure and reactivity models. Child Development, 78, 279–295.
Havighurst, S., & Kehoe, C. (2017). The role of parental emotion regulation in parent emotion socialization: Implications for intervention. In K. Deater-Decard & R. Panneton (Eds.), Parental stress and Early Child Development (pp. 285–307). Springer, Cham.
Heleniak, C., Jenness, J. L., Vander Stoep, A., McCauley, E., & McLaughlin, K. A. (2016). Childhood maltreatment exposure and disruptions in emotion regulation: A transdiagnostic pathway to adolescent internalizing and externalizing psychopathology. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 40(3), 394–415.
Hong, F., Tarullo, A. R., Mercurio, A. E., Liu, S., Cai, Q., & Malley-Morrison, K. (2018). Childhood maltreatment and perceived stress in young adults: The role of emotion regulation strategies, self-efficacy, and resilience. Child Abuse & Neglect, 86, 136–146.
Kaufman, J., & Zigler, E. (1987). Do abused children become abusive parents? American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 57(2), 186–192.
Kim, J., & Cicchetti, D. (2010). Longitudinal pathways linking child maltreatment, emotion regulation, peer relations, and psychopathology. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 51, 706–716.
Kim, H., Wildeman, C., Jonson-Reid, M., & Drake, B. (2017). Lifetime prevalence of investigating child maltreatment among US children. American Journal of Public Health, 107(2), 274–280.
Kovacs, M. (2001). Children’s Depression Inventory (CDI) Technical Manual New York. NY: Multi-Health Systems.
Leerkes, E. M., Bailes, L. G., & Augustine, M. E. (2020). The intergenerational transmission of emotion socialization. Developmental Psychology, 56(3), 390.
Leve, L. D., Kim, H. K., & Pears, K. C. (2005). Childhood temperament and family environment as predictors of internalizing and externalizing trajectories from ages 5 to 17. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 33(5), 505–520.
MacDonald, K., Thomas, M. L., Sciolla, A. F., Schneider, B., Pappas, K., Bleijenberg, G., Bohus, G., Bekh, B., Carpenter, L., Carr, A., Dannlowski, U., Dorahy, M., Fahlke, C., Finzi-Dottan, R., Karu, T., Gerdner, A., Glaesmer, H., Jörgen Grabe, H., Heins, M., & Wingenfeld, K. (2016). Minimization of childhood maltreatment is common and consequential: results from a large, multinational sample using the childhood trauma questionnaire. PLoS One, 11(1), e0146058.
McLaughlin, K. A., Hatzenbuehler, M. L., Mennin, D. S., & Nolen-Hoeksema, S. (2011). Emotion dysregulation and adolescent psychopathology: A prospective study. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 49(9), 544–554.
Meyer, S., Raikes, H. A., Virmani, E. A., Waters, S., & Thompson, R. A. (2014). Parent emotion representations and the socialization of emotion regulation in the family. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 38(2), 164–173.
Morris, A. S., Silk, J. S., Steinberg, L., Myers, S. S., & Robinson, L. R. (2007). The role of the family context in the development of emotion regulation. Social Development, 16(2), 361–388.
O’Neal, C. R., & Magai, C. (2005). Do parents respond in different ways when children feel different emotions? The emotional context of parenting. Development and Psychopathology, 17(2), 467–487.
Osborne, K. R., Duprey, E. B., Caughy, M. O. B., & Oshri, A. (2021). Parents’ maltreatment histories, dimensions of emotion regulation, and connections to offspring self-regulation: A sex-specific transmission pathway. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 1–13.
Plant, D. T., Pawlby, S., Pariante, C. M., & Jones, F. W. (2018). When one childhood meets another – maternal childhood trauma and offspring child psychopathology: a systematic review. Clinical Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 23(3), 483–500.
Plant, D. T., Barker, E. D., Waters, C. S., Pawlby, S., & Pariante, C. M. (2013). Intergenerational transmission of maltreatment and psychopathology: the role of antenatal depression. Psychological Medicine, 43(3), 519–528.
Radloff, L. S. (1977). The CES-D Scale: a self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Applied Psychological Measurement, 1(3), 385–401.
Rodriguez, V. J., Are, F., Madden, A., Shaffer, A., & Suveg, C. (2021). Intergenerational transmission of childhood maltreatment mediated by maternal emotion dysregulation. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 1–8.
Russotti, J., Warmingham, J. M., Handley, E. D., Rogosch, F. A., & Cicchetti, D. (2021). Child maltreatment: an intergenerational cascades model of risk processes potentiating child psychopathology. Child Abuse & Neglect, 112, 104829.
Savage, L., Tarabulsy, G., Pearson, J., Collin-Vézina, D., & Gagné, L. (2019). Maternal history of childhood maltreatment and later parenting behavior: a meta-analysis. Development and Psychopathology, 31(1), 9–21.
Schwerdtfeger, K. L., Larzelere, R. E., Werner, D., Peters, C., & Oliver, M. (2013). Intergenerational transmission of trauma: the mediating role of parenting styles on toddlers’ DSM-related symptoms. Journal of Aggression, Maltreatment & Trauma, 22(2), 211–229.
Sobel, M. E. (1982). Asymptotic confidence intervals for indirect effects in structural equations models. In S. Leinhart (Ed.), Sociological methodology (pp. 290–312). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Su, Y., D’Arcy, C., & Meng, X. (2020). Intergenerational effect of maternal childhood maltreatment on next generation’s vulnerability to psychopathology: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Trauma, Violence, & Abuse, 1524838020933870.
Thompson, R. A., Meyer, S. (2007). The socialization of emotion regulation in the family. In Gross, J. (Ed.), Handbook of emotion regulation (pp. 249–268). New York, NY: Guilford.
Thompson, R. A. (1994). Emotion regulation: a theme in search of definition. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 59(2/3), 25–52. JSTOR.
Valentino, K., Nuttall, A. K., Comas, M., Borkowski, J. G., & Akai, C. E. (2012). Intergenerational continuity of child abuse among adolescent mothers: authoritarian parenting, community violence, and race. Child Maltreatment, 17(2), 172–181.
Wang, X. (2021). Intergenerational effects of childhood maltreatment: The roles of parents’ emotion regulation and mentalization. Child Abuse & Neglect, 104940.
Warmingham, J. M., Rogosch, F. A., & Cicchetti, D. (2020). Intergenerational maltreatment and child emotion dysregulation. Child Abuse & Neglect, 102, 104377.
Wechsler, D. (2011). Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence–Second Edition (WASI-II). San Antonio, TX: NCS Pearson.
World Health Organization (WHO). (2016). Child maltreatment. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/child-maltreatment.
Zielinski, D. S. (2009). Child maltreatment and adult socioeconomic well-being. Child Abuse & Neglect, 33(10), 666–678.
Funding
This research was supported through a National Institute of Health (NIH), National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) Award (RO1-DA033431, R01-DA033431-S1; PI: Chaplin).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, L.N., Renshaw, K.D., Mauro, K.L. et al. Intergenerational Effects of Childhood Maltreatment: Role of Emotion Dysregulation and Emotion Socialization. J Child Fam Stud 32, 2187–2197 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-023-02608-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-023-02608-x