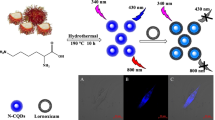
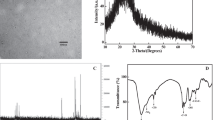
Boletus brunneissimus Chiu carbon dots (Bb-CDs) with good fluorescence performance were successfully prepared by the hydrothermal method (200°C, 12 h) using the edible fungus Boletus brunneissimus Chiu as the carbon source. The Bb-CD fluorescent nanoprobe was applied to detection of riboflavin, and its fluorescence-quenching mechanism was investigated. The structure and optical properties of the Bb-CDs were characterized by transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy. In the riboflavin concentration (C) range of 0–50 μM, the fluorescence-quenching effect of the Bb-CDs (y) showed a good linear relationship with the riboflavin concentration. The linear equation was y = 0.00304C + 0.02151 (R2 = 0.99497), and the detection limit was 45 nM. Therefore, the Bb-CDs showed high detection sensitivity and a low detection limit for riboflavin. Moreover, the fluorescence-quenching mechanism of the Bb-CDs by riboflavin belonged to the fluorescent inner filter effect. The Bb-CDs were successfully used as a fluorescent nanoprobe to detect riboflavin in actual fruit samples, which provides a new concept for application of CDs to biological detection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Zhang, M. Jiang, N. Niu, et al., ChemSusChem, 11, No. 1, 11–24 (2018).
L. Zheng, Y. Chi, Y. Dong, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 131, No. 13, 4564–4565 (2009).
A. B. Bourlinos and D. Petridis, J. Mater. Sci., 38, No. 5, 959–963 (2003).
Y. Ding, J. Zheng, J. Wang, et al., J. Mater. Chem. C, 7, No. 6, 1502–1509 (2019).
Q. Yang, J. Duan, W. Yang, et al., Appl. Surf. Sci., 1079–1085 (2018).
J. B. Essner, J. A. Kist, L. Polo-Parada, et al., Chem. Mater., 30, No. 6, 1878–1887 (2018).
J. Zhu, H. Shao, X. Bai, et al., Nanotechnology, 29, No. 24, Article ID 245702 (2018).
K. P. Ji, Y. Cao, C. X. Zhang, et al., Mycologic. Prog., 10, 293–300 (2011).
C. X. Zhang, M. X. He, Y. Cao, et al., Mycologia, 107, No. 1, 12–20 (2015).
R. Sanmee, B. Dell, P. Lumyong, et al., Food Chem., 82, No. 4, 527–532 (2003).
P. Heinemann and J. Rammeloo, Mycotaxon, 15, 384–404 (1982).
R. Wading, Mycologic. Res., 105, No. 12, 1440–1448 (2001).
V. M. Bandala, L. Montoya, and D. Jarvio, Persoonia, 18, No. 3, 365–380 (2004).
P. S. Barbara, New Zealand J. Botany, 25, No. 2, 185–215 (1987).
Z. Sun, X. Li, Y. Wu, et al., New J. Chem., 42, No. 6, 4603–4611 (2018).
F. Yuan, T. Yuan, L. Sui, et al., Nat. Commun., 9, No. 1, 1–11 (2018).
K. Jiang, Y. Wang, X. Gao, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 57, No. 21, 6216–6220 (2018).
Z. Wei, B. Wang, Y. Liu, et al., New J. Chem., 43, No. 2, 718–723 (2019).
K. Kim and J. Kim, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 18, No. 2, 1320–1322 (2018).
L. Liu, H. Gong, D. Li, et al., J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 18, No. 8, 5327–5332 (2018).
R. Atchudan, T. N. J. I. Edison, K. R. Aseer, et al., Biosens. Bioelectron., 99, 303–311 (2018).
B. T. Hoan, P. D. Tam, and V. H. Pham, J. Nanotechnol. (2019).
Y. Song, X. Yan, Z. Li, et al., J. Mater. Chem. B, 6, No. 19, 3181–3187 (2018).
A. K. Singh, V. K. Singh, M. Singh, et al., J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem., 376, 63–72 (2019).
M. Shahshahanipour, B. Rezaei, A. A. Ensafi, et al., Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 98, 826–833 (2019).
S. K. Bajpai, A. D'Souza, and B. Suhail, Int. Nano Lett., 9, No. 3, 203–212 (2019).
S. Nandi, M. Ritenberg, and R. Jelinek, Analyst, 140, No. 12, 4232–4237 (2015).
W. Gao, S. Thamphiwatana, P. Angsantikul, et al., WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol., 6, No. 6, 532–547 (2014).
A. Rodriguez-Rojas, J. Rodriguez-Beltran, A. Couce, and J. Blázquez, Int. J. Med. Microbiol., 303, Nos. 6–7, 293–297 (2013).
L. Xiao and H. Sun, Nanoscale Horizons, 3, No. 6, 565–597 (2018).
H. Ding, J.-S. Wei, N. Zhong, et al., Langmuir, 33, No. 44, 12635–12642 (2017).
V. Sharma, P. Tiwari, and S. M. Mobin, J. Mater. Chem. B, 5, No. 45, 8904–8924 (2014).
L. Wang and H. S. Zhou, Anal. Chem., 86, No. 18, 8902–8905 (2014).
D. B. Mccormick, Nutr. Rev., 30, No. 4, 75–79 (1972).
M. Kilic and B. Ensing, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 16, No. 35, 18993–19000 (2014).
C. J. Bates, A. M. Prentice, A. A. Paul, et al., Trans. Roy. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg., 76, No. 2, 253–258 (1982).
P. A. Prasad, M. S. Bamji, A. V. Lakshmi, et al., Nutr. Res., 10, No. 3, 275–281 (1990).
M. J. Soares, K. Satyanarayana, M. S. Bamji, et al., Br. J. Nutr., 69, No. 2, 541–551 (1993).
J. Chen, B. Q. Li, Y. Q. Cui, et al., J. Food Compos. Anal., 41, 122–128 (2015).
I. Márqucz-Sillero, S. Cárdenas, and M. Valcárcel, J. Chromatogr. A, 1313, 253–258 (2013).
J. Eiff, Y. B. Monakhova, and B. Diehl, J. Agric. Food Chem., 63, No. 12, 3135–3143 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Abstract of article is published in Zhurnal Prikladnoi Spektroskopii, Vol. 89, No. 6, p. 904, November–December, 2022.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, L., Xia, Z., Zhang, Y. et al. Nanosensor Composed of N-Doped Carbon Dots for Highly Selective Detection of Riboflavin. J Appl Spectrosc 89, 1212–1219 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-023-01488-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-023-01488-9