Abstract
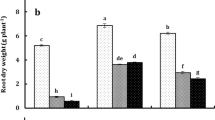
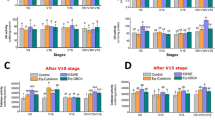
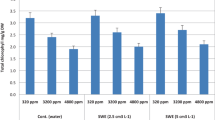
There is no doubt that at the recent years scientists are seeking for using safe, cheap, environment friendly methods in agriculture. One of these methods is using algal extracts which reduce the harmful effect of salinity in the soil. A field experiment was conducted to study the effects of priming seeds and foliar applications of seaweed extracts (SWEs) of Halimeda opuntia and Padina pavonica on shoot and root lengths, fresh and dry matter yields, sodium, potassium, pigment, and compatible compounds (soluble carbohydrates, soluble proteins, total free amino acids, and proline contents), and the content of total phenols and alkaloids of the maize plants. The salted plants were foliar sprayed with each extract twice. The foliar treatment with each algal extract significantly increased the fresh and dry weight of root and shoot, and improved the potassium, chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and carotenoids contents compared to the control (untreated stressed plants), especially with Padina extract. Generally, sodium, carbohydrates and proline contents were decreased, while protein, phenols and alkaloids were increased in treated plants in comparison with untreated maize plants. LC-HR-ESI–MS identified some 27 and 14 metabolites belonging to diverse classes were dereplicated from P. pavonia and H. opuntia, respectively, of which phytohormones, phenolic derivatives, and terpenes, were the main classes of both algal extracts.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Abd El-Baky HH, Hussein M, El-Baroty GS (2008) Algal extracts improve antioxidant defense abilities and salt tolerance of wheat plant irrigated with sea water. Afr J Bio Res 2:151–164
Abdel Latef AAH, Srivastava AK, Saber H, Alwaleed EA, Tran L-SP (2017) Sargassum muticum and Jania rubens regulate amino acid metabolism to improve growth and alleviate salinity in chickpea. Sci Rep 7:10537
Abdelmohsen UR, Cheng C, Viegelmann C, Zhang T, Grkovic T, Ahmed S, Quinn RJ, Hentschel U, Edrada-Ebel R (2014) Dereplication strategies for targeted isolation of new antitrypanosomal actinosporins A and B from a marine sponge associated-Actinokineospora sp. EG49. Mar Drugs 12:1220–1244
Aleem AA (1993) The marine algae of Alexandria. University of Alexandria, Alexandria, Egypt
Alhadrami HA, Sayed AM, El-Gendy AO, Shamikh YI, Gaber Y, Bakeer W, Sheirf NH, Attia EZ, Shaban GM, Khalifa BA, Ngwa CJ, Pradel G, Rateb ME, Hassan HM, Alkhalifah DHM, Abdelmohsen UR, Hozzein WN (2021) A metabolomic approach to target antimalarial metabolites in the Artemisia annua fungal endophytes. Sci Rep 11:2770
Aly M, El-Sabbagh S, El-Shouny W, Ebrahim M (2003) Physiological response of Zea mays to NaCl stress with respect to Azotobacter chroococcum and Streptomyces niveus. Pak J Biol Sci 6:2073–2080
APHA (2005) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington DC
Azzedine F, Gherroucha H, Baka M (2011) Improvement of salt tolerance in durum wheat by ascorbic acid application. J Stress Physiol Biochem 7:27–37
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare I (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Battacharyya D, Babgohari MZ, Rathor P, Prithiviraj B (2015) Seaweed extracts as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci Hortic 196:39–48
Burkill H, Okpuzor G, Whinril G, Khal H (2008) Phytochemical constituents of some Nigeria medicinal plants. Afr J Biotechnol 4:685–688
Carpýcý EB, Celýk N, Bayram G (2009) Effects of salt stress on germination of some maize (Zea mays L.) cultivars. Afr J Biotech 8:4918–4922
Chakraborty K, Joseph D (2018) Effect of antioxidant compounds from seaweeds on storage stability of C20–22 polyunsaturated fatty acid concentrate prepared from dogfish liver oil. Food Chem 260:135–144
Cirillo C, De Micco V, Arena C, Carillo P, Pannico A, De Pascale S, Rouphael Y (2019) Biochemical, physiological and anatomical mechanisms of adaptation of Callistemon citrinus and Viburnum lucidum to NaCl and CaCl2 salinization. Front Plant Sci 10:742
Claussen W (2005) Proline as a measure of stress in tomato plants. Plant Sci 168:241–248
da Cunha JG, Cavalcante ÍHL, da Silva MA, e Amariz RA, do Carmo RN, Lobo JT (2022) Proline and algal extract to alleviate the abiotic stress in mango ‘Tommy Atkins’ in the tropical semiarid. Erwerbs-Obstbau 64:115–126
De Saeger J, Van Praet S, Vereecke D, Park J, Jacques S, Han T, Depuydt S (2020) Toward the molecular understanding of the action mechanism of Ascophyllum nodosum extracts on plants. J Appl Phycol 32:573–597
Deinlein U, Stephan AB, Horie T, Luo W, Xu G, Schroeder JI (2014) Plant salt-tolerance mechanisms. Trends Plant Sci 19:371–379
Dell’Aversana E, Hessini K, Ferchichi S, Fusco GM, Woodrow P, Ciarmiello LF, Abdelly C, Carillo P (2021) Salinity duration differently modulates physiological parameters and metabolites profile in roots of two contrasting barley genotypes. Plants (Basel) 10:307
Demiral T, Türkan I (2004) Does exogenous glycinebetaine affect antioxidative system of rice seedlings under NaCl treatment? J Plant Physiol 161:1089–1100
Dmytryk A, Chojnacka K (2018) Algae as fertilizers, biostimulants, and regulators of plant growth. In: Chojnacka K, Wieczorek PP, Schroeder G, Michalak I (eds) Algae Biomass: Characteristics and Applications: Towards Algae-based Products, Springer, Cham, pp 115–122
Edwards M, Hanniffy D, Heesch S, Hernandez-Kantun J, Queguineur B, Ratcliff J, Soler-Vila A, Wan A (2014) Macroalgae fact-sheets. J NUI: Galway, Ireland:40
El-Sayed S, Hellal F, Nofal O, El-Karamany M, Bakry B (2015) Influence of algal extracts on yield and chemical composition of moringa and alfalfa grown under drought condition. Int J Environ Sci Nat Res 4:151–157
El-Soud WA, Hegab MM, AbdElgawad H, Zinta G, Asard H (2013) Ability of ellagic acid to alleviate osmotic stress on chickpea seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 71:173–183
Ewis M, El-Latif A, Badawi M (2016) Response of maize (Zea mays L.) to moisture stress under different nitrogen fertilization levels. J Soil Sci Agric Eng 7:865–872
Fales FW (1951) The assimilation and degradation of carbohydrates by yeast cells. J Biol Chem 193:113–124
Geilfus C-M (2018) Chloride: from nutrient to toxicant. Plant Cell Physiol 59:877–886
Gómez-Cadenas A, Arbona V, Jacas J, Primo-Millo E, Talon M (2002) Abscisic acid reduces leaf abscission and increases salt tolerance in citrusplants. J Plant Growth Regul 21:234–240
Haroun S, Hussein M (2003) The promotive effect of algal biofertilizers on growth, protein pattern and some metabolic activities of Lupinus termis plants grown in siliceous soil. Asian J Plant Sci 2:944–951
Havre GN (1961) The flame photometric determination of sodium, potassium and calcium in plant extracts with special reference to interference effects. Anal Chim Acta 25:557–566
Hegazi MM, Pérez-Ruzafa A, Almela L, Marı́a-Emilia C, (1998) Separation and identification of chlorophylls and carotenoids from Caulerpa prolifera, Jania rubens and Padina pavonica by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 829:153–159
Hussain M, Park H-W, Farooq M, Jabran K, Lee DJ (2013) Morphological and physiological basis of salt resistance in different rice genotypes. Int J Agric Biol 15:113–118
Hussain I, Ashraf MA, Anwar F, Rasheed R, Niaz M, Wahid A (2014) Biochemical characterization of maize (Zea mays L.) for salt tolerance. Plant Biosyst 148:1016–1026
Ibrahim WM, Ali RM, Hemida KA, Sayed MA (2014) Role of Ulva lactuca extract in alleviation of salinity stress on wheat seedlings. Sci World J 2014:847290
Iqbal N, Masood A, Khan NA (2012) Phytohormones in salinity tolerance: ethylene and gibberellins cross talk. In: Khan NA, Nazar R, Iqbal N, Anjum NA (eds) Phytohormones and abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 77–98
Jerkovic I, Kranjac M, Marijanovic Z, Roje M, Jokic S (2019) Chemical diversity of headspace and volatile oil composition of two brown algae (Taonia atomaria and Padina pavonica) from the Adriatic Sea. Molecules 24:495
Kaur H, Bhardwaj RD, Grewal SK (2017) Mitigation of salinity-induced oxidative damage in wheat (Triticum aestivum L) seedlings by exogenous application of phenolic acids. Acta Physiol Plant 39:221
Khan MIR, Fatma M, Per TS, Anjum NA, Khan NA (2015) Salicylic acid-induced abiotic stress tolerance and underlying mechanisms in plants. Front Plant Sci 6:1–17
Ktari L, Guyot M (1999) A cytotoxic oxysterol from the marine alga Padina pavonica (L.) Thivy. J Appl Phycol 11:511
Kumar S, Li G, Yang J, Huang X, Ji Q, Liu Z, Ke W, Hou H (2021) Effect of salt stress on growth, physiological parameters, and ionic concentration of water dropwort (Oenanthe javanica) cultivars. Front Plant Sci 12:660409
Li W, Li Q (2017) Effect of environmental salt stress on plants and the molecular mechanism of salt stress tolerance. Int J Environ Sci Nat Res 7:81–86
Linić I, Mlinarić S, Brkljačić L, Pavlović I, Smolko A, Salopek-Sondi B (2021) Ferulic acid and salicylic acid foliar treatments reduce short-term salt stress in Chinese cabbage by increasing phenolic compounds accumulation and photosynthetic performance. Plants 10:2346
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Maas EV, Hoffman GJ (1977) Crop salt tolerance–current assessment. J Irrig Drain Div 103:115–134
Mahmoud MMR (2017) Ameliorative effect of salicylic acid on growth, minerals and nitrogenous compounds of Vicia faba L. plants under salt stress. Egypt J Bot 57:11–29
Mahomoodally MF, BibiSadeer N, Zengin G, Cziaky Z, Jeko J, Diuzheva A, Sinan KI, Palaniveloo K, Kim DH, Rengasamy KR (2020) In vitro enzyme inhibitory properties, secondary metabolite profiles and multivariate analysis of five seaweeds. Mar Drugs 18:198
Metzner H, Rau H, Senger H (1965) Untersuchungen zur synchronisierbarkeit einzelner pigmentmangel-mutanten von Chlorella. Planta 65:186–194
Mohamed AA, Eichler-Lobermann B, Schnug E (2007) Response of crops to salinity under Egyptian conditions: a review. Landbauforschung 57:119
Murugan K, Iyer VV (2014) Antioxidant activity and gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis of extracts of the marine algae, Caulerpa peltata and Padina gymnospora. Indian J Pharm Sci 76:548–552
Nounjan N, Nghia PT, Theerakulpisut P (2012) Exogenous proline and trehalose promote recovery of rice seedlings from salt-stress and differentially modulate antioxidant enzymes and expression of related genes. J Plant Physiol 169:596–604
Osman HE, Salem OM (2011) Effect of seaweed extracts as foliar spray on sunflower yield and oil content. Egypt J Phycol 12:57
Parvin K, Nahar K, Hasanuzzaman M, Bhuyan M, Mohsin SM, Fujita M (2020) Exogenous vanillic acid enhances salt tolerance of tomato: Insight into plant antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems. Plant Physiol Biochem 150:109–120
Paul VJ, Fenical W (1984) Novel bioactive diterpenoid metabolites from tropical marine algae of the genus Halimeda (Chlorophyta). Tetrahedron 40:3053–3062
Pereira L, Morrison L, Shukla PS, Critchley AT (2020) A concise review of the brown macroalga Ascophyllum nodosum (Linnaeus) Le Jolis. J Appl Phycol 32:3561–3584
Pradheeban L, Nissanka S, Suriyagoda L (2017) Influence of whole and sub soil salinity on growth, development, physiology and yield of selected rice varieties cultivated in Jaffna district. Sri Lanka Trop AgriRes 28:389–401
Rahneshan Z, Nasibi F, Moghadam AA (2018) Effects of salinity stress on some growth, physiological, biochemical parameters and nutrients in two pistachio (Pistacia vera L.) rootstocks. J Plant Interact 13:73–82
Rajamani K, Thirugnanasambandan SS (2018) Polyphenols from brown alga, Padina boergesenii (Allendar & Kraft) decelerates renal cancer growth involving cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis in renal carcinoma cells. Environ Toxicol 33:1135–1142
Rengasamy KRR, Amoo SO, Aremu AO, Stirk WA, Gruz J, Šubrtová M, Doležal K, Van Staden J (2015) Phenolic profiles, antioxidant capacity, and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of eight South African seaweeds. J Appl Phycol 27:1599–1605
Rouphael Y, Colla G (2018) Synergistic biostimulatory action: Designing the next generation of plant biostimulants for sustainable agriculture. Front Plant Sci 9:1–7
Rushdi MI, Abdel-Rahman IA, Attia EZ, Abdelraheem WM, Saber H, Madkour HA, Amin E, Hassan HM, Abdelmohsen UR (2020a) A review on the diversity, chemical and pharmacological potential of the green algae genus Caulerpa. S Afr J Bot 132:226–241
Rushdi MI, Abdel-Rahman IAM, Saber H, Attia EZ, Abdelraheem WM, Madkour HA, Abdelmohsen UR (2020b) The genus Turbinaria: chemical and pharmacological diversity. Nat Prod Res 35:4560–4578
Rushdi MI, Abdel-Rahman IAM, Saber H, Attia EZ, Abdelraheem WM, Madkour HA, Hassan HM, Elmaidomy AH, Abdelmohsen UR (2020c) Pharmacological and natural products diversity of the brown algae genus Sargassum. RSC Adv 10:24951–24972
Rushdi MI, Abdel-Rahman IAM, Saber H, Attia EZ, Madkour HA, Abdelmohsen UR (2021) A review on the pharmacological potential of the genus Padina. S Afr J Bot 141:37–48
Rushdi MI, Abdel-Rahman IAM, Attia EZ, Saber H, Saber AA, Bringmann G, Abdelmohsen UR (2022) The biodiversity of the genus Dictyota: Phytochemical and pharmacological natural products prospectives. Molecules 27:672
Saleh J, Maftoun M, Safarzadeh S, Gholami A (2009) Growth, mineral composition, and biochemical changes of broad bean as affected by sodium chloride and zinc levels and sources. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 40:3046–3060
Sali A, Rusinovci I, Fetahu S, Gashi B, Simeonovska E (2015) The effect of salt stress on the germination of maize (Zea mays L.) seeds and photosynthetic pigments. Acta Agric Slov 105:85–94
Sayed AM, Sherif NH, El-Gendy AO, Shamikh YI, Ali AT, Attia EZ, El-Katatny MH, Khalifa BA, Hassan HM, Abdelmohsen UR (2020) Metabolomic profiling and antioxidant potential of three fungal endophytes derived from Artemisia annua and Medicago sativa. Nat Prod Res 36:2404–2408
Selmar D (2008) Potential of salt and drought stress to increase pharmaceutical significant secondary compounds in plants. J Landbauforschung Volkenrode 58:139
Sethupathy S, Shanmuganathan B, Kasi PD, Karutha Pandian S (2016) Alpha-bisabolol from brown macroalga Padina gymnospora mitigates biofilm formation and quorum sensing controlled virulence factor production in Serratia marcescens. J Appl Phycol 28:1987–1996
Shaikh W, Shameel M, Usmanghani K, Ahmad VU (1991) Phycochemical examination of Padina tetrastromatica (Dictyotales, Phaeophyta). Pak J Pharm Sci 4:55–61
Sharma A, Shahzad B, Rehman A, Bhardwaj R, Landi M, Zheng B (2019) Response of phenylpropanoid pathway and the role of polyphenols in plants under abiotic stress. Molecules 24:2452
Sofy MR, Sharaf A, Osman MS, Sofy AR (2017) Physiological changes, antioxidant activity, lipid peroxidation and yield characters of salt stressed barely plant in response to treatment with Sargassum extract. Int J Adv Res Biol Sci 4:90–109
Son S, Chitnis VR, Liu A, Gao F, Nguyen TN, Ayele BT (2016) Abscisic acid metabolic genes of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): identification and insights into their functionality in seed dormancy and dehydration tolerance. Planta 244:429–447
Stein W, Moore S (1948) Photometric ninhydrin method for use in the chromatography of amino acids. J Biol Chem 176:367
Sytar O, Mbarki S, Zivcak M, Brestic M (2018) The involvement of different secondary metabolites in salinity totlerance of crops. In: Kumar V, Wani S, Suprasanna P, Tran LS (eds) Salinity responses and tolerance in plants, vol 2. Springer, Cham, pp 21–48
Taïbi K, Taïbi F, Abderrahim LA, Ennajah A, Belkhodja M, Mulet JM (2016) Effect of salt stress on growth, chlorophyll content, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defence systems in Phaseolus vulgaris L. South Afr J Bot 105:306–312
Tarakhovskaya ER, Maslov YI, Shishova MF (2007) Phytohormones in algae. Russ J Plant Physiol 54:163–170
Tian F, Hou M, Qiu Y, Zhang T, Yuan Y (2020) Salinity stress effects on transpiration and plant growth under different salinity soil levels based on thermal infrared remote (TIR) technique. Geoderma 357:113961
Wan Y-Y, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Zhou Z-Q, Li X, Shi Q, Wang X-J, Bai J-G (2014) Caffeic acid protects cucumber against chilling stress by regulating antioxidant enzyme activity and proline and soluble sugar contents. Acta Physiol Plant 37:1706
Wang Y, Mopper S, Hasenstein KH (2001) Effects of Salinity on Endogenous aba, iaa, Ja, and Sa in Iris hexagona. J Chem Ecol 27:327–342
Zewail R (2014) Effect of seaweed extract and amino acids on growth and productivity and some biocostituents of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L) plants. J Plant Prod 5:1441–1453
Zhang X, Schmidt R (2000) Hormone-containing products’ impact on antioxidant status of tall fescue and creeping bentgrass subjected to drought. Crop Sci 40:1344–1349
Zhao Y (2010) Auxin biosynthesis and its role in plant development. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:49–64
Zheng W, Wang SY (2001) Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds in selected herbs. J Agric Food Chem 49:5165–5170
Zhu J-K (2007) Plant salt stress. Encyclopedia of Life Sciences, John Wiley & Sons, pp 1–3
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Minia University and South Valley University for supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: [Nora Hassan Youssef, Hani Saber, Mohammed I. Rushdi]; Methodology: [Nora Hassan Youssef, Hani Saber, Mohammed I. Rushdi]; Formal analysis and investigation: [Hani Saber, Eman Zekry Attia, Ahmed G. Darwish]; Writing—original draft preparation: Nora Hassan Youssef, Mohammed I. Rushdi]; Writing—review and editing: [Eman Zekry Attia, Iman A. M. Abdel-Rahman, Ahmed G. Darwish and Usama Ramadan Abdelmohsen], Supervision: [Usama Ramadan Abdelmohsen].
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Attia, E.Z., Youssef, N.H., Saber, H. et al. Halimeda opuntia and Padina pavonica extracts improve growth and metabolic activities in maize under soil-saline conditions. J Appl Phycol 34, 3189–3203 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-022-02844-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-022-02844-6