Abstract
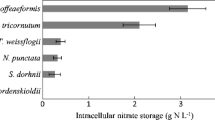
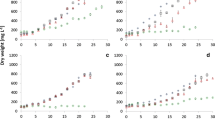
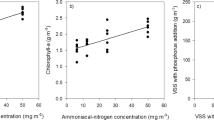
There is growing interest in finding microalgae species that efficiently convert dissolved nutrients contained in aquaculture effluents into highly valuable biomass. The different nitrogen forms that are present in aquaculture effluents are particularly concerning. This study demonstrated that the dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae can acclimate to both combined and sole nitrogen sources such as nitrate, ammonium, and urea over a wide concentration range. As far as is known, it is the first time that a species of the genus Amphidinium has been successfully cultured with urea as the sole source of nitrogen. In the presence of 882 μM of nitrate, A. carterae tolerated urea concentrations up to 5000 μM. With respect to ammonium-N tolerance, it has been observed that it is lethal at concentrations higher than 441 μM. A robust laboratory experimental design was critical for accurately assessing this acclimation. Alternative N sources did not affect the production of high-value specific polyketide secondary metabolites from A. carterae, such as amphidinols, with an average concentration of 0.435 ± 0.038% biomass d.w. An analysis of the symbiotic microbial assemblages developed in a long-term A. carterae culture in an open raceway pond, and the fact that it is able to metabolize all three nitrogen sources simultaneously, supports the idea that this microalga has the potential to be successfully cultured with aquaculture effluents.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abadie E, Kaci L, Berteaux T, Hess P, Sechet V, Masseret E, Rolland J, Laabir M (2015) Effect of nitrate, ammonium and urea on growth and pinnatoxin G production of Vulcanodinium rugosum. Mar Drugs 13:5642–5656
Abreu AC, Molina-Miras A, Aguilera-Sáez LM, López-Rosales L, Cerón-García MC, Sánchez-Mirón A, Olmo-García L, Carrasco-Pancorbo A, García-Camacho F, Molina-Grima E (2019) Production of amphidinols and other bioproducts of interest by the marine microalga Amphidinium carterae unraveled by nuclear magnetic resonance metabolomics approach coupled to multivariate data analysis. J Agric Food Chem 67:9667–9682
American Public Health Association (APHA), (1995) In: Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American water works association and water pollution control federation. APHA, Washington DC.
Andreotti V, Chindris A, Brundu G, Vallainc D, Francavilla M, García J (2017) Bioremediation of aquaculture wastewater from Mugil cephalus (Linnaeus, 1758) with different microalgae species. Chem Ecol 33:750–761
Andreotti V, Solimeno A, Chindris A, Marazzi F, García J (2019) Growth of Tetraselmis suecica and Dunaliella tertiolecta in aquaculture wastewater: numerical simulation with the BIO_ALGAE model. Water Air Soil Pollut 230:60
ASTM D1426-08, (2008) Standard Test Methods for Ammonia Nitrogen In Water, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, www.astm.org
Attasat S, Wanichpongpan P, Ruenglertpanyakul W (2013) Cultivation of microalgae (Oscillatoria okeni and Chlorella vulgaris) using tilapia-pond effluent and a comparison of their biomass removal efficiency. Water Sci Technol 67:271–277
Azaman SNA, Nagao N, Yusoff FM, Tan SW, Yeap SK (2017) A comparison of the morphological and biochemical characteristics of Chlorella sorokiniana and Chlorella zofingiensis cultured under photoautotrophic and mixotrophic conditions. PeerJ 5:e3473
Borges M-T, Silva P, Moreira L, Soares R (2005) Integration of consumer-targeted microalgal production with marine fish effluent biofiltration–a strategy for mariculture sustainability. J Appl Phycol 17:187–197
Burkholder JM, Glibert PM, Skelton HM (2008) Mixotrophy, a major mode of nutrition for harmful algal species in eutrophic waters. Harmful Algae 8:77–93
Chen J, Wei D, Pohnert G (2017) Rapid estimation of astaxanthin and the carotenoid-to-chlorophyll ratio in the green microalga Chromochloris zofingiensis using flow cytometry. Mar Drugs 15:231–253
Chen J-H, Kato Y, Matsuda M, Chen C-Y, Nagarajan D, Hasunuma T, Kondo A, Dong C-D, Lee D-J, Chang J-S (2019) A novel process for the mixotrophic production of lutein with Chlorella sorokiniana MB-1-M12 using aquaculture wastewater. Bioresour Technol 290:121786
Collos Y, Harrison PJ (2014) Acclimation and toxicity of high ammonium concentrations to unicellular algae. Mar Pollut Bull 80:8–23
Collos Y, Vaquer A, Laabir M, Abadie E, Laugier T, Pastoureaud A, Souchu P (2007) Contribution of several nitrogen sources to growth of Alexandrium catenella during blooms in Thau lagoon, southern France. Harmful Algae 6:781–789
Contreras A, García F, Molina E, Merchuk JC (1998) Interaction between CO2-mass transfer, light availability, and hydrodynamic stress in the growth of Phaeodactylum tricornutum in a concentric tube airlift photobioreactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 60:317–325
Crab R, Avnimelech Y, Defoirdt T, Bossier P, Verstraete W (2007) Nitrogen removal techniques in aquaculture for a sustainable production. Aquaculture 270:1–14
Dagenais-Bellefeuille S, Morse D (2013) Putting the N in dinoflagellates. Front Microbiol 4:369
Davidson K, Gowen RJ, Tett P, Bresnan E, Harrison PJ, McKinney A, Milligan S, Mills DK, Silke J, Crooks A-M (2012) Harmful algal blooms: how strong is the evidence that nutrient ratios and forms influence their occurrence? Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 115:399–413
Deviller G, Aliaume C, Nava MAF, Casellas C, Blancheton JP (2004) High-rate algal pond treatment for water reuse in an integrated marine fish recirculating system: effect on water quality and sea bass growth. Aquaculture 235:331–344
Dixon G, Syrett P (1988a) The growth of dinoflagellates in laboratory cultures. New Phytol 109:297–302
Dixon GK, Syrett PJ (1988b) Interactions between the uptake and assimilation of inorganic nitrogen and carbon in Amphidinium spp. (Dinophyceae). J Exp Bot 39:1299–1311
Erickson RJ (1985) An evaluation of mathematical models for the effects of pH and temperature on ammonia toxicity to aquatic organisms. Water Res 19:1047–1058
Gallardo-Rodríguez JJ, Sánchez-Mirón A, Cerón-García MC, Belarbi EH, García-Camacho F, Chisti Y, Molina-Grima E (2009) Macronutrients requirements of the dinoflagellate Protoceratium reticulatum. Harmful Algae 8:239–246
Gallardo-Rodríguez J, Sánchez-Mirón A, García-Camacho F, López-Rosales L, Chisti Y, Molina-Grima E (2012) Bioactives from microalgal dinoflagellates. Biotechnol Adv 30:1673–1684
Gao F, Li C, Yang Z-H, Zeng G-M, Feng L-J, J-z L, Liu M, H-w C (2016) Continuous microalgae cultivation in aquaculture wastewater by a membrane photobioreactor for biomass production and nutrients removal. Ecol Eng 92:55–61
García-Camacho F, Sánchez-Miron A, Molina-Grima E, Camacho-Rubio F, Merchuck JC (2012) A mechanistic model of photosynthesis in microalgae including photoacclimation dynamics. J Theor Biol 304:1–15
Guillard RRL (1975) Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In: Smith WL, Chanley MH (eds) Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals. Springer, Boston, MA, pp 29–60
Guo Z, Liu Y, Guo H, Yan S, Mu J (2013) Microalgae cultivation using an aquaculture wastewater as growth medium for biomass and biofuel production. J Environ Sci 25:S85–S88
Halfhide T, Åkerstrøm A, Lekang OI, Gislerød HR, Ergas SJ (2014) Production of algal biomass, chlorophyll, starch and lipids using aquaculture wastewater under axenic and non-axenic conditions. Algal Res 6:152–159
Harisson PT, Berges JA (2005) Marine culture media. In: Andersen R (ed) Algal culturing techniques. Elsevier Academic Press, Burlington, pp 21–34
Harrison WG (1976) Nitrate metabolism of the red tide dinoflagellate Gonyaulax polyedra Stein. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 21:199–209
Henderson TJ (2002) Quantitative NMR spectroscopy using coaxial inserts containing a reference standard: purity determinations for military nerve agents. Anal Chem 74:191–198
Ho K-C, Xu SJ-L, Wu K-C, Lee FW-F (2013) Effective growth of dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum by cultivating the cells using municipal wastewater as nutrient source. Water Sci Technol 68:1100–1106
Hussenot J, Lefebvre S, Brossard N (1998) Open-air treatment of wastewater from land-based marine fish farms in extensive and intensive systems: current technology and future perspectives. Aquat Living Resour 11:297–304
Hyka P, Lickova S, Přibyl P, Melzoch K, Kovar K (2013) Flow cytometry for the development of biotechnological processes with microalgae. Biotechnol Adv 31:2–16
Jeanfils J, Canisius M, Burlion N (1993) Effect of high nitrate concentrations on growth and nitrate uptake by free-living and immobilized Chlorella vulgaris cells. J Appl Phycol 5:369–374
Jegatheesan V, Shu L, Visvanathan C (2011) Aquaculture effluent: impacts and remedies for protecting the environment and human health. In: Nriagu JO (ed) Encyclopedia of environmental health. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 123–135
Jing X, Lin S, Zhang H, Koerting C, Yu Z (2017) Utilization of urea and expression profiles of related genes in the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum donghaiense. PLoS One 12:e0187837e
Khatoon H, Haris H, Rahman NA, Zakaria MN, Begum H, Mian S (2018) Growth, proximate composition and pigment production of Tetraselmis chuii cultured with aquaculture wastewater. J Ocean Univ China 17:641–646
Landsberg JH (2002) The effects of harmful algal blooms on aquatic organisms. Rev Fish Sci 10:113–390
Lauritano C, De Luca D, Ferrarini A, Avanzato C, Minio A, Esposito F, Ianora A (2017) De novo transcriptome of the cosmopolitan dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae to identify enzymes with biotechnological potential. Sci Rep 7:11701
Lee JJ, Shpigel M, Freeman S, Zmora O, Mcleod S, Bowen S, Pearson M, Szostek A (2003) Physiological ecology and possible control strategy of a toxic marine dinoflagellate, Amphidinium sp., from the benthos of a mariculture pond. Aquaculture 217:351–371
Levasseur M, Thompson PA, Harrison PJ (1993) Physiological acclimation of marine phytoplankton to different nitrogen sources. J Phycol 29:587–595
Li M, Callier MD, Blancheton J-P, Galès A, Nahon S, Triplet S, Geoffroy T, Menniti C, Fouilland E, Roque d’orbcastel E (2019) Bioremediation of fishpond effluent and production of microalgae for an oyster farm in an innovative recirculating integrated multi-trophic aquaculture system. Aquaculture 504:314–325
Liu C-L, Place AR (2017) Use of antibiotics for maintenance of axenic cultures of Amphidinium carterae for the analysis of translation. Mar Drugs 15:242
Liu M, Huang X, Zhang R, Li C, Gu B (2018) Uptake of urea nitrogen by Oocystis borgei in prawn (Litopenaeus vannamei) aquaculture ponds. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 101:586–591
López-Rodríguez M, Cerón-García M, López-Rosales L, González-López C, Molina-Miras A, Ramírez-González A, Sánchez-Mirón A, García-Camacho F, Molina-Grima E (2019) Assessment of multi-step processes for an integral use of the biomass of the marine microalga Amphidinium carterae. Bioresour Technol 282:370–377
López-Rosales L, García-Camacho F, Sánchez-Mirón A, Contreras-Gómez A, Molina-Grima E (2015) An optimisation approach for culturing shear-sensitive dinoflagellate microalgae in bench-scale bubble column photobioreactors. Bioresour Technol 197:375–382
López-Rosales L, García-Camacho F, Sánchez-Mirón A, Beato EM, Chisti Y, Grima EM (2016) Pilot-scale bubble column photobioreactor culture of a marine dinoflagellate microalga illuminated with light emission diodes. Bioresour Technol 216:845–855
Marinho YF, Brito LO, Silva Campos CVF, Severi W, Andrade HA, Galvez AO (2017) Effect of the addition of Chaetoceros calcitrans, Navicula sp. and Phaeodactylum tricornutum (diatoms) on phytoplankton composition and growth of Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) postlarvae reared in a biofloc system. Aquac Res 48:4155–4164
Matantseva O, Skarlato S, Vogts A, Pozdnyakov I, Liskow I, Schubert H, Voss M (2016) Superposition of individual activities: urea-mediated suppression of nitrate uptake in the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum revealed at the population and single-cell levels. Front Microbiol 7:1310
Milhazes-Cunha H, Otero A (2017) Valorisation of aquaculture effluents with microalgae: the integrated multi-trophic aquaculture concept. Algal Res 24:416–424
Molina-Miras A, López-Rosales L, Sánchez-Mirón A, Cerón-García MC, Seoane-Parra S, García-Camacho F, Molina-Grima E (2018a) Long-term culture of the marine dinoflagellate microalga Amphidinium carterae in an indoor LED-lighted raceway photobioreactor: production of carotenoids and fatty acids. Bioresour Technol 265:257–267
Molina-Miras A, Morales-Amador A, de Vera C, López-Rosales L, Sánchez-Mirón A, Souto M, Fernández J, Norte M, García-Camacho F, Molina-Grima E (2018b) A pilot-scale bioprocess to produce amphidinols from the marine microalga Amphidinium carterae: isolation of a novel analogue. Algal Res 31:87–98
Nasir NM, Bakar NSA, Lananan F, Hamid SHA, Lam SS, Jusoh A (2015) Treatment of African catfish, Clarias gariepinus wastewater utilizing phytoremediation of microalgae, Chlorella sp. with Aspergillus niger bio-harvesting. Bioresour Technol 190:492–498
Pagand P, Blancheton JP, Lemoalle J, Casellas C (2000) The use of high rate algal ponds for the treatment of marine effluent from a recirculating fish rearing system. Aquac Res 31:729–736
Podevin M, De Francisci D, Holdt SL, Angelidaki I (2015) Effect of nitrogen source and acclimatization on specific growth rates of microalgae determined by a high-throughput in vivo microplate autofluorescence method. J Appl Phycol 27:1415–1423
Przytocka-Jusiak M, Mlynarczyk A, Kulesza M, Mycielski R (1977) Properties of Chlorella vulgaris strain adapted to high concentration of ammonium nitrogen. Acta Microbiol Pol 26:185–197
Riaño B, Molinuevo B, García-González M (2011) Treatment of fish processing wastewater with microalgae-containing microbiota. Bioresour Technol 102:10829–10833
Schulz C, Gelbrecht J, Rennert B (2003) Treatment of rainbow trout farm effluents in constructed wetland with emergent plants and subsurface horizontal water flow. Aquaculture 217:207–221
Sfez S, Van Den Hende S, Taelman SE, De Meester S, Dewulf J (2015) Environmental sustainability assessment of a microalgae raceway pond treating aquaculture wastewater: from up-scaling to system integration. Bioresour Technol 190:321–331
Solomon CM, Collier JL, Berg GM, Glibert PM (2010) Role of urea in microbial metabolism in aquatic systems: a biochemical and molecular review. Aquat Microb Ecol 59:67–88
Spotte S, Adams G (1983) Estimation of the allowable upper limit of ammonia in saline waters. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 10:207–210
Srimongkol P, Tongchul N, Phunpruch S, Karnchanatat A (2019) Ability of marine cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. VDW to remove ammonium from brackish aquaculture wastewater. Agric Water Manag 212:155–161
Stolte W, McCollin T, Noordeloos AA, Riegman R (1994) Effect of nitrogen source on the size distribution within marine phytoplankton populations. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 184:83–97
Voltolina D, Nieves M, Navarro G, Oliva T, Peraza D (1998) The importance of acclimation for the evaluation of alternative media for microalgae growth. Aquac Eng 19:7–15
Wang J, Zhou W, Chen H, Zhan J, He C, Wang Q (2018) Ammonium nitrogen tolerant Chlorella strain screening and its damaging effects on photosynthesis. Front Microbiol 9:3250
Wasielesky W Jr, Atwood H, Stokes A, Browdy CL (2006) Effect of natural production in a zero exchange suspended microbial floc based super-intensive culture system for white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 258:396–403
Zhang X, Ma L, Tian X, Huang H, Yang Q (2015a) Biodiversity study of intracellular bacteria closely associated with paralytic shellfish poisoning dinoflagellates Alexandrium tamarense and A. minutum. Int J Env Resour 4:23–27
Zhang X, Tian X, Ma L, Feng B, Liu Q, Yuan L, Fan C, Huang H, Yang Q (2015b) Biodiversity of the symbiotic bacteria associated with toxic marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. J Biosci Med 3:23
Zhuang Y, Zhang H, Hannick L, Lin S (2015) Metatranscriptome profiling reveals versatile N-nutrient utilization, CO2 limitation, oxidative stress, and active toxin production in an Alexandrium fundyense bloom. Harmful Algae 42:60–70
Acknowledgments
The microalgae Amphidinium carterae Dn241 EHU was kindly donated by Dr. S. Seoane (Culture Collection of the Plant Biology and Ecology Department of the University of the Basque Country).
Funding
This research was funded by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (CTQ2014-55888-C3-02) and the European Regional Development Fund Program. Professor Alfredo Olivera-Gálvez is supported by the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) through the aid grant PDE 203104/2017-0.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molina-Miras, A., López-Rosales, L., Cerón-García, M.C. et al. Acclimation of the microalga Amphidinium carterae to different nitrogen sources: potential application in the treatment of marine aquaculture effluents. J Appl Phycol 32, 1075–1094 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-020-02049-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-020-02049-9