Abstract
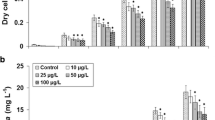
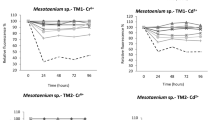
There has been concern over the adverse ecotoxicological effects of atrazine and endosulfan on microalgae. This study aimed to assess the effects of these two widely used pesticides on growth, pigmentation, and oxidative response of microalgal isolates from a farmland and a eutrophic lake in Malaysia, in comparison with the model species Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Results showed that the microalgae originated from the eutrophic lake were generally more sensitive to the pesticides than those from the farmland. The microalgae were more sensitive to atrazine (EC50 = 43.07–> 5000 μg L−1) than endosulfan (EC50 = 1.51–> 50 mg L−1). Amongst the microalgae, Scenedesmus arcuatus was most sensitive to atrazine (EC50 = 43.07 μg L−1) while Chlorella sp. 1 was most sensitive to endosulfan (EC50 = 1.51 mg L−1). Microalgae from the farmland were generally very tolerant to endosulfan (EC50 > 50 mg L−1). Photosynthetic pigment content (pg cell−1) increased in S. arcuatus after exposure to atrazine while the content decreased in most of the microalgae after exposure to endosulfan. Oxidative response to the pesticides varied amongst the tested microalgae and time point measured. Both ROS levels and lipid peroxidation decreased in Chlorella sp. 5 after exposure to atrazine at 96 h compared to 48 h. In S. arcuatus, there was no pronounced increase in SOD and catalase activities despite the increase in ROS and lipid peroxidation after exposure to atrazine. Indigenous microalgae such as S. arcuatus could be a useful bioassay organism for toxicity testing of the pesticides while tolerant species from the farmland could be useful for bioremediation of endosulfan contamination.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah PM, Abdul Aziz YF, Rozali Othman M, Wan Mohd Khalik WMA (2015) Organochlorine pesticides residue level in surface water of Cameron Highlands, Malaysia. Iranica J Energy Environ 6
Ahmad AL, Tan LS, Shukor SR (2008) Dimethoate and atrazine retention from aqueous solution by nanofiltration membranes. J Hazard Mater 151:71–77
Anonymous (2017) NIES collection - microbial culture collection - strain data. http://mcc.nies.go.jp/strainList.do?strainId=26&strainNumberEn=NIES-35. Accessed 9 June 2018
Bai X, Sun C, Xie J, Song H, Zhu Q, Su Y, Qian H, Fu Z (2015) Effects of atrazine on photosynthesis and defense response and the underlying mechanisms in Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:17499–17507
Baxter L, Brain RA, Lissemore L, Solomon KR, Hanson ML, Prosser RS (2016) Influence of light, nutrients, and temperature on the toxicity of atrazine to the algal species Raphidocelis subcapitata: implications for the risk assessment of herbicides. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 132:250–259
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 44:276–287
Behra R, Genoni G, Joseph A (1999) Effect of atrazine on growth, photosynthesis, and between-strain variability in Scenedesmus subspicatus (Chlorophyceae). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 37:36–41
Berard A, Leboulanger C, Pelte T (1999) Tolerance of Oscillatoria limnetica Lemmermann to atrazine in natural phytoplankton populations and in pure culture: influence of season and temperature. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 37:472–479
Berard A, Rimet F, Capowiez Y, Leboulanger C (2004) Procedures for determining the pesticide sensitivity of indigenous soil algae: a possible bioindicator of soil contamination? Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 46:24–31
Blaise C, Vasseur P (2005) Algal microplate toxicity test. In: Blaise C, Férard JF (eds) Small-scale freshwater toxicity investigations. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 137–179
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Camuel A, Guieysse B, Alcantara C, Bechet Q (2017) Fast algal eco-toxicity assessment: influence of light intensity and exposure time on Chlorella vulgaris inhibition by atrazine and DCMU. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 140:141–147
CAP (Consumers Association of Penang) 2010. Is our rice safe from banned endosulfan? http://consumer.org.my/food/safety/140-is-our-rice-safe-from-banned-endosulfan. Accessed 5 October 2018
Cheloni G, Slaveykova VI (2013) Optimization of the C11-BODIPY581/591 dye for the determination of lipid oxidation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by flow cytometry. Cytometry 83:952–961
Chia MA, Dauda S, Jibril TZ (2016) Toxicity of atrazine to Scenedesmus quadricauda under different nitrogen concentrations. Environ Earth Sci 75:960
Daam MA, van den Brink PJ (2010) Implications of differences between temperate and tropical freshwater ecosystems for the ecological risk assessment of pesticides. Ecotoxicology 19:24–37
Davis AM, Lewis SE, Bainbridge ZT, Glendenning L, Turner RD, Brodie JE (2012) Dynamics of herbicide transport and partitioning under event flow conditions in the lower Burdekin region, Australia. Mar Pollut Bull 65:182–193
DeLorenzo ELA, Taylor SALM (2002) Toxicity and bioconcentration potential of the agricultural pesticide endosulfan in phytoplankton and zooplankton. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 42:173–181
DeLorenzo ME, Leatherbury M, Weiner JA, Lewitus AJ, Fulton MH (2004) Physiological factors contributing to the species-specific sensitivity of four estuarine microalgal species exposed to the herbicide atrazine. Aquat Ecosyst Health Manage 7:137–146
Downie D (2003) Global POPs policy: the 2001 Stockholm convention on persistent organic pollutants. In: Downie D, Fenge T (eds) Northern lights against POPs: combating toxic threats in the Arctic. McGill-Queens University Press, Montreal, pp 133–159
Duke SO (1990) Overview of herbicide mechanisms of action. Environ Health Perspect 87:263–271
Esperanza M, Houde M, Seoane M, Cid A, Rioboo C (2017) Does a short-term exposure to atrazine provoke cellular senescence in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii? Aquat Toxicol 189:184–193
Fairchild JF, Ruessler DS, Carlson AR (1998) Comparative sensitivity of five species of macrophytes and six species of algae to atrazine, metribuzin, alachlor, and metolachlor. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:1830–1834
FAO (Food and Agricultural Organisation) (2016) Prevention and disposal of obsolete pesticides. http://www.fao.org/agriculture/crops/obsolete-pesticides/prevention-and-disposal-of-obsolete-pesticides/en/. Accessed 5 October 2018
Fernández-Naveira A, Rioboo C, Cid A, Herrero C (2016) Atrazine induced changes in elemental and biochemical composition and nitrate reductase activity in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Eur J Phycol 51:338–345
Flood SL, Burkholder JM (2018) Chattonella subsalsa (Raphidophyceae) growth and hemolytic activity in response to agriculturally-derived estuarine contaminants. Harmful Algae 76:66–79
González-Barreiro Ó, Rioboo C, Cid A, Herrero C (2004) Atrazine-induced chlorosis in Synechococcus elongatus cells. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 46:301–307
Graymore M, Stagnitti F, Allinson G (2001) Impacts of atrazine in aquatic ecosystems. Environ Int 26:483–495
Guo R, Lee MA, Ki JS (2013) Different transcriptional responses of heat shock protein 70/90 in the marine diatom Ditylum brightwellii exposed to metal compounds and endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Chemosphere 92:535–543
Helweg A, Bay H, Hansen HPB, Rabølle M, Sonnenborg A, Stenvang L (2002) Pollution at and below sites used for mixing and loading of pesticides. Int J Environ Anal Chem 82:583–590
Hii YS, Shia KL, Chuah TS, Hing LS (2009) Physiological responses of Chaetoceros sp. and Nannochloropsis sp. to short-term 2, 4-D, dimethylamine and endosulfan exposure. Aquat Ecosyst Health Manage 12:375–389
Hogue C (2011) Endosulfan banned worldwide. Chem Eng News 89(19):15
Howe PL, Reichelt-Brushett AJ, Clark MW, Seery CR (2017) Toxicity estimates for diuron and atrazine for the tropical marine cnidarian Exaiptasia pallida and in-hospite Symbiodinium spp. using PAM chlorophyll-a fluorometry. J Photochem Photobiol B 171:125–132
Jablonowski ND, Schäffer A, Burauel P (2011) Still present after all these years: persistence plus potential toxicity raise questions about the use of atrazine. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 18:328–331
Kegley SE, Hill BR, Orme S, Choi AH (2010) PAN pesticide database. Pesticide Action Network, North America http:www.pesticideinfo.org. Accessed 7 October 2018
Kumar S, Habib K, Fatma T (2008) Endosulfan induced biochemical changes in nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria. Sci Total Environ 403:130–138
Kumar N, Bora A, Kumar R, Amb MK (2012) Differential effects of agricultural pesticides endosulfan and tebuconazole on photosynthetic pigments, metabolism and assimilating enzymes of three heterotrophic, filamentous cyanobacteria. J Biol Environ Sci 6:67–75
Kwon CS, Penner D (1995) The interaction of insecticides with herbicide activity. Weed Technol 9:119–124
Li Y, Schellhorn HE (2007) Rapid kinetic microassay for catalase activity. J Biomol Tech 18:185–187
Lichtenthaler HK, Buschmann C (2001) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: measurement and characterization by UV-VIS spectroscopy. Curr Protocol Food Anal Chem F4:1 (Supplement 1)
Ma J, Lin F, Wang S, Xu L (2003) Toxicity of 21 herbicides to the green alga Scenedesmus quadricauda. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 71:594–601
Magnusson M, Heimann K, Negri AP (2008) Comparative effects of herbicides on photosynthesis and growth of tropical estuarine microalgae. Mar Pollut Bull 56:1545–1552
Majewska M, Harshkova D, Gusciora M, Aksmann A (2018) Phytotoxic activity of diclofenac: evaluation using a model green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with atrazine as a reference substance. Chemosphere 209:989–997
Mallick N, Mohn FH (2000) Reactive oxygen species: response of algal cells. J Plant Physiol 157:183–193
Menezes RG, Qadir TF, Moin A, Fatima H, Hussain SA, Madadin M, Pasha SB, Al Rubaish FA, Senthilkumaran S (2017) Endosulfan poisoning: an overview. J Forensic Legal Med 51:27–33
Mohapatra P, Mohanty R (1992) Growth pattern changes of Chlorella vulgaris and Anabaena doliolum due to toxicity of dimethoate and endosulfan. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 49:576–581
Nichols HW (1973) Growth media - freshwater. In: Stein JR (ed) Handbook of phycological methods: culture methods and growth measurements. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 7–24
Noctor G, Lelarge-Trouverie C, Mhamdi A (2015) The metabolomics of oxidative stress. Phytochemistry 112:33–53
Norberg-King T (1993) A linear interpolation method for sublethal toxicity: the inhibition concentration (ICp) approach. National Effluent Toxicity Assessment Center Technical Report, Version 2, vol 2, pp 3–93
OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) (2011) Test no. 201: freshwater alga and cyanobacteria, growth inhibition test, OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals, Section 2. OECD Publishing, Paris, p 25
Ogawa Y, Kobayashi T, Nishioka A, Kariya S, Hamasato S, Seguchi H, Yoshida S (2003) Radiation-induced reactive oxygen species formation prior to oxidative DNA damage in human peripheral T cells. Int J Mol Med 11:149–152
Petersen K, Heiaas HH, Tollefsen KE (2014) Combined effects of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, biocides and organic contaminants on the growth of Skeletonema pseudocostatum. Aquat Toxicol 150:45–54
Prasad SM, Kumar D, Zeeshan M (2005) Growth, photosynthesis, active oxygen species and antioxidants responses of paddy field cyanobacterium Plectonema boryanum to endosulfan stress. J Gen Appl Microbiol 51:115–123
Prasad SM, Zeeshan M, Kumar D (2011) Toxicity of endosulfan on growth, photosynthesis, and nitrogenase activity in two species of Nostoc (Nostoc muscorum and Nostoc calcicola). Toxicol Environ Chem 93:513–525
Qian H, Daniel Sheng G, Liu W, Lu Y, Liu Z, Fu Z (2008) Inhibitory effects of atrazine on Chlorella vulgaris as assessed by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:182–187
Ricart M, Barcelo D, Geiszinger A, Guasch H, de Alda ML, Romani AM, Vidal G, Villagrasa M, Sabater S (2009) Effects of low concentrations of the phenylurea herbicide diuron on biofilm algae and bacteria. Chemosphere 76:1392–1401
Roger PA, Ladha JK (1992) Biological N2 fixation in wetland rice fields: estimation and contribution to nitrogen balance. Plant Soil 141:41–55
Saadati N, Abdullah MP, Zakaria Z, Rezayi M, Hosseinizare N (2012) Distribution and fate of HCH isomers and DDT metabolites in a tropical environment–case study Cameron Highlands–Malaysia. Chem Central J 6:130–130
Sass JB, Colangelo A (2006) European Union bans atrazine, while the United States negotiates continued use. Int J Occup Environ Health 12:260–267
Seguin F, Le Bihan F, Leboulanger C, Bérard A (2002) A risk assessment of pollution: induction of atrazine tolerance in phytoplankton communities in freshwater outdoor mesocosms, using chlorophyll fluorescence as an endpoint. Water Res 36:3227–3236
Sethunathan N, Megharaj M, Chen ZL, Williams BD, Lewis G, Naidu R (2004) Algal degradation of a known endocrine disrupting insecticide, α-endosulfan, and its metabolite, endosulfan sulfate, in liquid medium and soil. J Agric Food Chem 52:3030–3035
Silva MH, Beauvais SL (2010) Human health risk assessment of endosulfan. I: toxicology and hazard identification. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 56:4–17
Tang JX, Hoagland KD, Siegfried BD (1997) Differential toxicity of atrazine to selected freshwater algae. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 59:631–637
Tang J, Hoagland KD, Siegfried BD (1998) Uptake and bioconcentration of atrazine by selected freshwater algae. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:1085–1090
Tasmin R, Shimasaki Y, Tsuyama M, Qiu X, Khalil F, Okino N, Yamada N, Fukuda S, Kang IJ, Oshima Y (2014) Elevated water temperature reduces the acute toxicity of the widely used herbicide diuron to a green alga, Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:1064–1070
Vavilala SL, Sinha M, Gawde KK, Shirolikar SM, D'Souza JS (2016) KCl induces a caspase-independent programmed cell death in the unicellular green chlorophyte Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Chlorophyceae). Phycologia 55:378–392
Vega FA, Covelo EF, Andrade ML (2007) Accidental organochlorine pesticide contamination of soil in Porriño, Spain. J Environ Qual 36:272–279
Vonberg D, Vanderborght J, Cremer N, Pütz T, Herbst M, Vereecken H (2014) 20 years of long-term atrazine monitoring in a shallow aquifer in western Germany. Water Res 50:294–306
Wolfe M, Seiber J (1993) Environmental activation of pesticides. Occup Med (Philadelphia, Pa) 8:561–573
Yamagishi T, Horie Y, Tatarazako N (2017) Synergism between macrolide antibiotics and the azole fungicide ketoconazole in growth inhibition testing of the green alga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Chemosphere 174:1–7
Yeo BS, Chu WL, Wong CY, Kok YY, Phang SM, Tan BK, Mustafa EM (2018) Combined effects of glufosinate ammonium and temperature on the growth, photosynthetic pigment content and oxidative stress response of Chlorella sp. and Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. J Appl Phycol 30:3043–3055
Zakaria Z, Heng LY, Abdullah P, Osman R, Din L (2003) The environmental contamination by organochlorine insecticides of some agricultural areas in Malaysia. Malay J Chem 5:78–85
Zhang W, Jiang F, Ou J (2011) Global pesticide consumption and pollution: with China as a focus. Proceed Int Acad Ecol Environ Sci 1:125
Acknowledgments
The first author would like to express her appreciation to MOE for the MyBrain Scholarship in supporting her doctoral study.
Funding
This research project received funding support from the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS) from the Ministry of Education (MOE), Malaysia (FRGS/2/2014/STWN01/IMU/01/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 5310 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chin, YY., Chu, WL., Kok, YY. et al. Sensitivity of selected tropical microalgae isolated from a farmland and a eutrophic lake to atrazine and endosulfan. J Appl Phycol 31, 2981–2998 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-01800-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-01800-1