Abstract
Allelochemical use has been demonstrated as an eco-friendly method for control of algal growth. The present study was carried out to assess the effect of rice straw extract applications on the growth of the microalga Chlorella sp. and the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. isolated from the Abbassa fish pond. Experiments were performed by preparing five treatments having different rice straw extract concentrations and a control without extract. Growth of Anabaena over 2 weeks was effectively inhibited by both water and methanol extracts and inhibition rates were dose-dependent. Inhibition was > 95% for the 1, 5, and 10 mg L−1 water extract treatments. In contrast, growth of Chlorella was stimulated by both extracts. Some phenolic-specific compounds responsible for allelopathic effect were identified using HPLC analysis. We conclude that the aqueous extract of rice straw is capable of significantly inhibiting the growth of Anabaena sp., providing a cheap and eco-friendly alternative for control of blooms of this cyanobacterium in fish ponds and other aquatic ecosystems. Additional assessment is required to determine the effects of these extracts for other cyanobacteria and microalgae.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
31 August 2019
The original version of this article unfortunately contained a mistake.
References
Abd El-Moneem A, El-Sheekh M, Hussian A (2012) Allelopathic activities of decomposing barley straw in growth of some algal species and community structure in Nile River. Global J Biotech Biochem Res 2:21–37
Akpinar O, Gunay K, Yilmaz Y, Levent O, Bostanci S (2010) Enzymatic processing and antioxidant activity of agricultural waste autohydrolysis liquors. Bioresources 5:699–711
Battchikova N, Vainonen JP, Vorontsova N, Keränen M, Carmel D, Aro EM (2010) Dynamic changes in the proteome of Synechocystis 6803 in response to CO2 limitation revealed by quantitative proteomics. J Proteome Res 9:5896–5912
Bischoff HW, Bold HC (1963) Phycological studies IV. Some soil algae from enchanted rock and related algal species, vol 63. University of Texas, Austin, Austin, pp 1–95
Choe S, Jung IH (2002) Growth inhibition of freshwater algae by ester compounds released from rotted plants. J Ind Eng Chem 8:297–304
Chung IM, Ahn JK, Yun SJ (2001) Assessment of allelopathic potential of barnyard grass (Echinochloacrus-galli) on rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. Crop Prot 20:921–928
Eladel HM, Abd-Elhay R, Anees D (2018) Effect of rice straw application on water quality and microalgal flora in fish ponds. Egypt J Bot 59:133–142
Elzaawely AA, Hanafey FM, El-Sayed MEA, Mohamed EA (2017) Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of rice straw extract. Int Lett Nat Sci 64:1–9
Emily KP, Tracey LM (2008) Effects of harmful algal blooms on competitors: allelopathic mechanisms of the red tide dinoflagellate Karenia brevis. Limnol Oceanogr 53:531–541
Feng J, Zhu Q, Wu WZ (2008) Mechanisms of algal inhibition by rice straw extract. Environ Sci 29:3376–3381 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ferrier MD, Butler BR Sr, Terlizzi DE, Lacouture RV (2005) The effects of barley straw (Hordeum vulgare) on the growth of freshwater algae. Bioresour Technol 96:1788–1795
Hua Q, Liu Y-G, Yan Z-L, Zeng G-M, Liu S-B, Wang W-J, Tan X-F, Deng J-Q, Tang X, Wang Q-P (2018) Allelopathic effect of the rice straw aqueous extract on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:953–959
Islami HR (2010) The comparison of inhibitory effects of barley and rice straws to control of algae and aquatic weeds in fish ponds. PhD Thesis, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran
Ismail HI, Chan KW, Mariod AA, Ismail M (2010) Phenolic content and antioxidant activity of cantaloupe (Cucumis melo) methanolic extracts. Food Chem 119:643–647
Jia YH, Yang Z, Su W, Johnson D, Kong FX (2014) Controlling of cyanobacteria bloom during bottleneck stages of algal cycling in shallow Lake Taihu (China). J Freshw Ecol 29:129–140
Jung KA, Woo SA, Lim SR, Park JM (2015) Pyrolytic production of phenolic compounds from the lignin residues of bioethanol processes. Chem Eng J 259:107–116
Kang P, Kim B, Mitchell MJ (2017) Effects of rice and rye straw extracts on the growth of a cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa. Paddy Water Environ 15:617–623
Karimi E, Mehrabanjoubani P, Keshavarzian M, Oskoueian E, Jaafar HZ, Abdolzadeh A (2014) Identification and quantification of phenolic and flavonoid components in straw and seed husk of some rice varieties (Oryza sativa L.) and their antioxidant properties. J Sci Food Agric 94:2324–2330
Körner S, Nicklisch A (2002) Allelopathic growth inhibition of selected phytoplankton species by submerged macrophytes. J Phycol 38:852–871
Legrand C, Rengefors K, Fistarol GO, Granėli E (2003) Allelopathy in phytoplankton—biochemical, ecological and evolutionary aspects. Phycologia. 42:406–419
Li FM, Hu HY (2005) Isolation and characterization of novel antialgal allelochemical from Phragmites communis. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:6545–6553
Lika K, Papadakis IA (2009) Modeling the biodegradation of phenolic compounds by microalgae. J Sea Res 62:135–146
Liu YH, Zeng RS, Chen S, Liu DL, Luo SM, Wu H, An M (2007) Plant autotoxicity research in southern China. Allelopath J 19:61–74
Martin D, Ridge I (1999) The relative sensitivity of algae to decomposing barley straw. J Appl Phycol 11:285–291
Mattice JD, Lavy T, Skulman TW, Dilday RH (1998) Searching for allelochemicals in rice that control ducksalad. In: Olofsdotter M (ed) Allelopathy in rice. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, pp 81–98
Men Y-J, Hu H-Y, Li F-M (2007) Effects of the novel allelochemical ethyl 2-methylacetoacetate from the reed (Phragmitis australis Trin) on the growth of several common species of green algae. J Appl Phycol 19:521–527
Mohan MS (2012) Comparative study of rice straw and ragi straw for the inhibition of algal bloom in fresh water. Int Res J Biol Sci 1:31–37
Mulderij G, Van Donk E, Roelofs JGM (2003) Differential sensitivity of green algae to allelopathic substances from Chara. Hydrobiologia 491:261–271
Park MH, Han MS, Ahn CY, Kim HS, Yoon BD, Oh HM (2006) Growth inhibition of bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa by rice straw extract. Appl Microbiol 43:307–312
Parks J, Rice EL (1969) Effects of certain plants of old-field succession on the growth of blue-green algae. Bull Torrey Bot Club. 96:345–360
Pei HY, Ma CX, Hu WR, Sun F (2014) The behaviors of Microcystis aeruginosa cells and extracellular microcystins during chitosan flocculation and flocs storage processes. Bioresour Technol 151:314–322
Pillinger JM, Cooper JA, Ridge I (1994) Role of phenolic compounds in the antialgal activity of barley straw. J Chem Ecol 20:1557–1569
Rice EL (1980) Effect of decaying rice straw on growth and nitrogen fixation of blue green algae. Bot Bull Academia Sinica 21:111–117
Ridge I, Pillinger J (1996) Towards understanding the nature of algal inhibitors from barley straw. Hydrobiologia 340:301–305
Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury J, Herdman M, Stanier R (1979) Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 111:1–61
Rubeena US, Ulavi S, Kumar BM (2014) Algae control using rice straw. Int J civil Eng Technol 5:43–48
Seal AN, Pratley JE, Haig T, An M (2004) Identification and quantification of compounds in a series of allelopathic and non-allelopathic rice root exudates. J Chem Ecol 30:1647–1662
Silva JPA, Carneiro LM, Roberto IC (2013) Treatment of rice straw hemicellulosic hydrolysates with advanced oxidative processes: a new and promising detoxification method to improve the bioconversion process. Biotechnol Biofuels 6:1–13
Su W, Hagström JA, Jia Y, Lu Y, Kong F (2014) Effects of rice straw on the cell viability, photosynthesis, and growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 32:120–129
Su W, Chen J, Zhang SP, Kong FX (2017) Selective inhibition of rice straw extract on growth of cyanobacteria and Chlorophyta. Environ Sci 38:2901–2909
Suggett DJ, Borowitzka MA, Prášil O (eds) (2011) Chlorophyll a fluorescence in aquatic sciences: methods and applications. Springer, Dordrecht
Suzuki Y, Takabayashi T, Kawaguchi T, Matsunaga K (1998) Isolation of an allelopathic substance from the crustose coralline algae, Lithophyllum spp., and its effect on the brown alga, Laminaria religiosa Miyabe (Phaeophyta). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 225:69–77
Thi HL, Hyuk P, Ji PY (2015) Allelopathy in Sorghum bicolor L. Moenoa a review on environmentally friendly solution for weed control. Res Crops 16:657–662
Tiffany LW, Park SW, Vivanco MJ (2004) Biochemical and physiological mechanisms mediated by allelochemicals. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:472–479
Venkataraman GS (1969) The cultivation of algae. Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi
Vollenweider RA (1969) A manual on methods for measuring primary production in aquatic environments. IBP Handbook No. 12. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford
Wang J, Dai C, Zhang X, Lu Y (2018) Elucidating the molecular mechanism of the inhibitory effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate on Microcystis aeruginosa. J Appl Phycol 30:1747–1758
Xiao X, Chen Y, Liang X, Lou L, Tang X (2010) Effects of Tibetan hulless barley on bloom-forming cyanobacterium (Microcystis aeruginosa) measured by different physiological and morphologic parameters. Chemosphere. 81:118–1123
Zhang C, Yi YL, Hao K, Liu GL, Wang GX (2013) Algicidal activity of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bung on Microcystis aeruginosa-towards identification of algicidal substance and determination of inhibition mechanism. Chemosphere. 93:997–1004
Zhu J, Liu B, Wang J, Gao Y, Wu Z (2010) Study on the mechanism of allelopathic influence on cyanobacteria and chlorophytes by submerged macrophyte (Myriophyllum spicatum) and its secretion. Aquat Toxicol 98:196–203
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
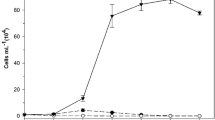
The original version of this article was revised: On top of the blue curve in Figure 4 are the wrong signs. Figure 4 is now corrected.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eladel, H., Battah, M., Dawa, A. et al. Effect of rice straw extracts on growth of two phytoplankton isolated from a fish pond. J Appl Phycol 31, 3557–3563 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-01766-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-01766-0