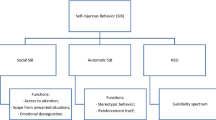
Abstract
The objective of this review is to consider the psychological (largely behavioral) and biological [neurochemical, medical (including genetic), and pharmacological] theories and approaches that contribute to current thinking about the etiology and treatment of self-injurious behavior (SIB) in individuals with autism spectrum disorder and/or intellectual disability. Algorithms for the assessment and treatment of SIB in this context, respectively, from a multidisciplinary, integrative perspective are proposed and challenges and opportunities that exist in clinical and research settings are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboitiz, F., Scheibel, A. B., Fisher, R. S., & Zaidel, E. (1992). Individual differences in brain asymmetries and fiber composition in the human corpus callosum. Brain Research, 598(1), 154–161.
Adamson, W. C., Nellis, B. P., Runge, G., Cleland, C., & Killian, E. (1958). Use of tranquilizers for mentally deficient patients. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, 96(2), 159–164.
Aghajanian, G. K., & Sanders-Bush, E. (2002). Serotonin. In K. L. Davis, D. Charney, J. T. Coyle, & C. Nemeroff (Eds.), Neuropsychopharmacology: The fifth generation of progress (pp. 15–34). Philidelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Alexander, A. L., Lee, J. E., Lazar, M., Boudos, R., DuBray, M. B., Oakes, T. R., et al. (2007). Diffusion tensor imaging of the corpus callosum in autism. Neuroimage, 34(1), 61–73.
Aman, M. G. (1993). Efficacy of psychotropic drugs for reducing self-injurious behavior in the developmental disabilities. Annals of Clinical Psychiatry, 5(3), 171–188.
Aman, M. G., De Smedt, G., Derivan, A., Lyons, B., & Findling, R. L. (2002). Double-blind, placebo-controlled study of risperidone for the treatment of disruptive behaviors in children with subaverage intelligence. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 159(8), 1337–1346.
Aman, M. G., Kasper, W., Manos, G., Mathew, S., Marcus, R., Owen, R., et al. (2010). Line-item analysis of the Aberrant Behavior Checklist: Results from two studies of aripiprazole in the treatment of irritability associated with autistic disorder. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology, 20(5), 415–422.
Aman, M. G., & Madrid, A. (1999). Atypical antipsychotics in persons with developmental disabilities. Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews, 5(4), 253–263.
Aman, M. G., McDougle, C. J., Scahill, L., Handen, B., Arnold, L. E., Johnson, C., et al. (2009). Medication and parent training in children with pervasive developmental disorders and serious behavior problems: Results from a randomized clinical trial. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 48(12), 1143–1154.
Aman, M. G., Teehan, C. J., White, A. J., Turbott, S. H., & Vaithianathan, C. (1989). Haloperidol treatment with chronically medicated residents: Dose effects on clinical behavior and reinforcement contingencies. American Journal of Mental Retardation, 93(4), 452–460.
Aman, M. G., & White, A. J. (1988). Thioridazine dose effects with reference to stereotypic behavior in mentally retarded residents. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 18(3), 355–366.
Anderson, L. T., & Ernst, M. (1994). Self-injury in Lesch-Nyhan disease. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 24(1), 67–81.
Anderson, G. M., Gutknecht, L., Cohen, D. J., Brailly-Tabard, S., Cohen, J. H., Ferrari, P., et al. (2002). Serotonin transporter promoter variants in autism: Functional effects and relationship to platelet hyperserotonemia. Molecular Psychiatry, 7(8), 831–836.
Anderson, L. T., Herrmann, L., & Dancis, J. (1976). The effect of L-5-hydroxytryptophan on self-mutilation in Lesch-Nyhan disease: A negative report. Neuropadiatrie, 7(4), 439–442.
Arnold, L. E., Vitiello, B., McDougle, C. J., Scahill, L., Shah, B., Gonzales, N. M., et al. (2003). Parent-defined target symptoms respond to risperidone in RUPP autism study: Customer approach to clinical trials. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 42(12), 1443–1450.
Arron, K., Oliver, C., Moss, J., Berg, K., & Burbidge, C. (2011). The prevalence and phenomenology of self-injurious and aggressive behaviour in genetic syndromes. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 55(2), 109–120.
Baghdadli, A., Pascal, C., Grisi, S., & Aussilloux, C. (2003). Risk factors for self-injurious behaviours among 222 young children with autistic disorders. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 47(8), 622–627.
Baghdadli, A., Picot, M. C., Pry, R., Michelon, C., Burzstejn, C., Lazartigues, A., et al. (2008). What factors are related to a negative outcome of self-injurious behaviour during childhood in pervasive developmental disorders? Journal of Applied Research in Intellectual Disabilities, 21(2), 142–149.
Baldessarini, R. J., & Frankenburg, F. R. (1991). Clozapine: A novel antipsychotic agent. The New England Journal of Medicine, 324(11), 746–754.
Barrera, F. J., Violo, R. A., & Graver, E. E. (2007). On the form and function of severe self-injurious behavior. Behavioral Interventions, 22(1), 5–33.
Baumeister, A. A., & Frye, G. D. (1984). Self-injurious behavior in rats produced by intranigral microinjection of GABA agonists. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 21(1), 89–95.
Baumeister, A. A., & Frye, G. D. (1985). The biochemical basis of the behavioral disorder in the Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 9(2), 169–178.
Baxter, C., Cummins, R. A., & Yiolitis, L. (2000). Parental stress attributed to family members with and without intellectual disability: A longitudinal study. Journal of Intellectual and Developmental Disability, 25(2), 105–118.
Beadle-Brown, J., Murphy, G., & Wing, L. (2005). Long-term outcome for people with severe intellectual disabilities: Impact of social impairment. American Journal of Mental Retardation, 110(1), 1–12.
Bear, D., Levin, K., Blumer, D., Chetham, D., & Ryder, J. (1982). Interictal behaviour in hospitalised temporal lobe epileptics: Relationship to idiopathic psychiatric syndromes. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 45(6), 481–488.
Bitsika, V., & Sharpley, C. F. (2004). Stress, anxiety and depression among parents of children with autism spectrum disorder. Australian Journal of Guidance and Counselling, 14(2), 151–161.
Blacher, J., Lopez, S., Shapiro, J., & Fusco, J. (1997). Contributions to depression in latina mothers with and without children with retardation: Implications for caregiving. Family Relations, 46(4), 325–334.
Blake, B. L., Muehlmann, A. M., Egami, K., Breese, G. R., Devine, D. P., & Jinnah, H. A. (2007). Nifedipine suppresses self-injurious behaviors in animals. Developmental Neuroscience, 29(3), 241–250.
Blatt, G. J. (2011). The GABA system in autism. In E. Hollander, A. Kolevzon, & J. T. Coyle (Eds.), Textbook of autism spectrum disorders (pp. 323–326). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing Inc.
Blatt, G. J., Fitzgerald, C. M., Guptill, J. T., Booker, A. B., Kemper, T. L., & Bauman, M. L. (2001). Density and distribution of hippocampal neurotransmitter receptors in autism: An autoradiographic study. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 31(6), 537–543.
Bloch, M. R., Elliott, M., Thompson, H., & Koran, L. M. (2001). Fluoxetine in pathologic skin-picking: Open-label and double-blind results. Psychosomatics, 42(4), 314–319.
Blumer, D. (2000). Dysphoric disorders and paroxysmal affects: Recognition and treatment of epilepsy-related psychiatric disorders. Harvard Review of Psychiatry, 8(1), 8–17.
Borrero, J. C., Vollmer, T. R., Wright, C. S., Lerman, D. C., & Kelley, M. E. (2002). Further evaluation of the role of protective equipment in the functional analysis of self-injurious behavior. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 35(1), 69–72.
Bosch, J., Van Dyke, C., Smith, S. M., & Poulton, S. (1997). Role of medical conditions in the exacerbation of self-injurious behavior: An exploratory study. Mental Retardation, 35(2), 124–130.
Boyer, W. F., & Feighner, J. P. (1992). An overview of paroxetine. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 53, 3–6.
Brahm, N. C., Fast, G. A., & Brown, R. C. (2008). Buspirone for autistic disorder in a woman with an intellectual disability. The Annals of Pharmacotherapy, 42(1), 131–137.
Brandt, B. R., & Rosen, I. (1998). Impaired peripheral somatosensory function in children with Prader-Willi syndrome. Neuropediatrics, 29(3), 124–126.
Breau, L. M., Camfield, C. S., Symons, F. J., Bodfish, J. W., Mackay, A., Finley, G. A., et al. (2003). Relation between pain and self-injurious behavior in nonverbal children with severe cognitive impairments. The Journal of Pediatrics, 142(5), 498–503.
Breau, L. M., McGrath, P. J., Camfield, C., Rosmus, C., & Finley, G. A. (2000). Preliminary validation of an observational pain checklist for persons with cognitive impairments and inability to communicate verbally. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 42(9), 609–616.
Breese, G. R., Baumeister, A. A., McCown, T. J., Emerick, S. G., Frye, G. D., Crotty, K., et al. (1984). Behavioral differences between neonatal and adult 6-hydroxydopamine-treated rats to dopamine agonists: Relevance to neurological symptoms in clinical syndromes with reduced brain dopamine. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 231(2), 343–354.
Breese, G. R., Criswell, H. E., Duncan, G. E., & Mueller, R. A. (1990). A dopamine deficiency model of Lesch-Nyhan disease: The neonatal-6-OHDA-lesioned rat. Brain Research Bulletin, 25(3), 477–484.
Bruhl, H. H., Fielding, L., Joyce, M., Peters, W., & Wieseler, N. (1982). Thirty-month demonstration project for treatment of self-injurious behavior in severely retarded individuals. Monographs of the American Association on Mental Deficiency, 5, 191–275.
Brylewski, J., & Wiggs, L. (1999). Sleep problems and daytime challenging behaviour in a community-based sample of adults with intellectual disability. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 43(6), 504–512.
Buitelaar, J. K. (1993). Self-injurious behaviour in retarded children: Clinical phenomena and biological mechanisms. Acta Paedopsychiatrica, 56(2), 105–111.
Butler, M. G., Bittel, D. C., Kibiryeva, N., Talebizadeh, Z., & Thompson, T. (2004). Behavioral differences among subjects with Prader-Willi syndrome and type I or type II deletion and maternal disomy. Pediatrics, 113(3), 565–573.
Campbell, M., Anderson, L. T., Small, A. M., Adams, P., Gonzalez, N. M., & Ernst, M. (1993). Naltrexone in autistic children: Behavioral symptoms and attentional learning. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 32(6), 1283–1291.
Cancela, L. M., Artinian, J., & Fulginiti, S. (1988). Opioid influence on some aspects of stereotyped behavior induced by repeated amphetamine treatment. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 30(4), 899–904.
Canitano, R. (2006). Self injurious behavior in autism: Clinical aspects and treatment with risperidone. Journal of Neural Transmission, 113(3), 425–431.
Carr, J. E., Coriaty, S., Wilder, D. A., Gaunt, B. T., Dozier, C. L., Britton, L. N., et al. (2000). A review of “noncontingent” reinforcement as treatment for the aberrant behavior of individuals with developmental disabilities. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 21(5), 377–391.
Carr, E. G., & LeBlanc, L. A. (2003). Functional analysis of problem behavior. In W. Donahue, J. E. Fishers, & S. C. Hayes (Eds.), Cognitive behavior therapy: Applying empirically supported techniques in your practice. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Carr, J. E., Severtson, J. M., & Lepper, T. L. (2009). Noncontingent reinforcement is an empirically supported treatment for problem behavior exhibited by individuals with developmental disabilities. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 30(1), 44–57.
Carr, E. G., & Smith, C. E. (1995). Biological setting events for self-injury. Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews, 1(2), 94–98.
Carr, E. G., Smith, C. E., Giacin, T. A., Whelan, B. M., & Pancari, J. (2003). Menstrual discomfort as a biological setting event for severe problem behavior: Assessment and intervention. American Journal of Mental Retardation, 108(2), 117–133.
Carroll, M. N., & Lim, R. K. (1960). Observations on the neuropharmacology of morphine and morphinelike analgesia. Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Therapie, 125, 383–403.
Cassidy, S. B. (1997). Prader-Willi syndrome. Journal of Medical Genetics, 34(11), 917–923.
Cassidy, S. B., & Driscoll, D. J. (2009). Prader-Willi syndrome. European Journal of Human Genetics, 17(1), 3–13.
Cassidy, S. B., Schwartz, S., Miller, J. L., & Driscoll, D. J. (2012). Prader-Willi syndrome. Genetics in Medicine, 14(1), 10–26.
Clarke, S., Dunlap, G., & Vaughn, B. (1999). Family-centered, assessment-based intervention to improve behavior during an early morning routine. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 1(4), 235–241.
Codling, M., & MacDonald, N. (2009). Epilepsy: Implications for people with profound intellectual and multiple disabilities. In J. Pawlyn & S. Carnaby (Eds.), Profound intellectual and multiple disabilities: Nursing complex needs (pp. 134–146). Hoboken: Wiley.
Coffey, M. J. (2013). Resolution of self-injury with phenytoin in a man with autism and intellectual disability: The role of frontal lobe seizures and catatonia. Journal of ECT, 29(1), 12–13.
Cohen, S. A., & Underwood, M. T. (1994). The use of clozapine in a mentally retarded and aggressive population. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 55(10), 440–444.
Collins, M. S., & Cornish, K. (2002). A survey of the prevalence of stereotypy, self-injury and aggression in children and young adults with Cri du Chat syndrome. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 46(2), 133–140.
Consoli, A., Cohen, J., Bodeau, N., Guinchat, V., Wachtel, L., & Cohen, D. (2013). Electroconvulsive therapy in adolescents with intellectual disability and severe self-injurious behavior and aggression: A retrospective study. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 22(1), 55–62.
Conti, F., & Manzoni, T. (1994). The neurotransmitters and postsynaptic actions of callosally projecting neurons. Behavioural Brain Research, 64(1), 37–53.
Cooper, A. F., & Fowlie, H. C. (1973). Control of gross self-mutilation with lithium carbonate. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 122(568), 370–371.
Cooper, J. O., Heron, T. E., & Heward, W. L. (2007). Applied behavior analysis. New Jersey: Pearson Education Inc.
Cooper, S. A., Smiley, E., Allan, L. M., Jackson, A., Finlayson, J., Mantry, D., et al. (2009). Adults with intellectual disabilities: Prevalence, incidence and remission of self-injurious behaviour, and related factors. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 53(3), 200–216.
Cornish, K. M., Bramble, D., Munir, F., & Pigram, J. (1999). Cognitive functioning in children with typical cri du chat (5p-) syndrome. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 41(4), 263–266.
Courtemanche, A., Schroeder, S., Sheldon, J., Sherman, J., & Fowler, A. (2012). Observing signs of pain in relation to self-injurious behaviour among individuals with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 56(5), 501–515.
Crawford, H. (2009). Dysphagia and people with profound intellectual and multiple disabilities. In J. Pawlyn & S. Carnaby (Eds.), Profound intellectual and multiple disabilities: Nursing complex needs (pp. 236–258). Hoboken: Wiley.
Crockett, C. M., Sackett, G. P., Sandman, C. A., Chicz-DeMet, A., & Bentson, K. L. (2007). Beta-endorphin levels in longtailed and pigtailed macaques vary by abnormal behavior rating and sex. Peptides, 28(10), 1987–1997.
Crossland, S., Burns, M., Leach, C., & Quinn, P. (2005). Needs assessment in forensic learning disability. Medicine, Science and the Law, 45(2), 147–153.
Czapinski, P., Blaszczyk, B., & Czuczwar, S. J. (2005). Mechanisms of action of antiepileptic drugs. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 5(1), 3–14.
Davanzo, P. A., Belin, T. R., Widawski, M. H., & King, B. H. (1998). Paroxetine treatment of aggression and self-injury in persons with mental retardation. American Journal of Mental Retardation, 102(5), 427–437.
Davanzo, P. A., & King, B. H. (1996). Open trial lamotrigine in the treatment of self-injurious behavior in an adolescent with profound mental retardation. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology, 6(4), 273–279.
Davis, K. V., Sprague, R. L., & Werry, J. S. (1969). Stereotyped behavior and activity level in severe retardates: The effect of drugs. American Journal of Mental Deficiency, 73(5), 721–727.
de Winter, C. F., Jansen, A. A., & Evenhuis, H. M. (2011). Physical conditions and challenging behaviour in people with intellectual disability: A systematic review. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 55(7), 675–698.
Deb, S., Thomas, M., & Bright, C. (2001). Mental disorder in adults with intellectual disability. 2: The rate of behaviour disorders among a community-based population aged between 16 and 64 years. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 45(6), 506–514.
DeLeon, I. G., Fisher, W. W., & Marhefka, J. M. (2004). Decreasing self-injurious behavior associated with awakening in a child with autism and developmental delays. Behavioral Interventions, 19(2), 111–119.
Didden, R., Korzilius, H., & Curfs, L. M. (2007). Skin-picking in individuals with Prader-Willi syndrome: Prevalence, functional assessment, and its comorbidity with compulsive and self-injurious behaviours. Journal of Applied Research in Intellectual Disabilities, 20(5), 409–419.
Dooley, P., Wilczenski, F. L., & Torem, C. (2001). Using an activity schedule to smooth school transitions. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 3(1), 57–61.
Dove, D., Warren, Z., McPheeters, M. L., Taylor, J. L., Sathe, N. A., & Veenstra-VanderWeele, J. (2012). Medications for adolescents and young adults with autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review. Pediatrics, 130(4), 717–726.
Duerden, E. G., Oatley, H. K., Mak-Fan, K. M., McGrath, P. A., Taylor, M. J., Szatmari, P., et al. (2012). Risk factors associated with self-injurious behaviors in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 42(11), 2460–2470.
Duker, P. C. (1975). Use of aversive shock therapy on a retarded girl with self destructive behaviors. Zeitschrift für Klinische Psychologie, 4(1), 38–47.
Duncan, D., Matson, J. L., Bamburg, J. W., Cherry, K. E., & Buckley, T. (1999). The relationship of self-injurious behavior and aggression to social skills in persons with severe and profound learning disability. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 20(6), 441–448.
Dykens, E. M., Cassidy, S. B., & King, B. H. (1999). Maladaptive behavior differences in Prader-Willi syndrome due to paternal deletion versus maternal uniparental disomy. American Journal on Mental Retardation, 104(1), 67–77.
Eidelberg, E., & Erspamer, R. (1975). Dopaminergic mechanisms of opiate actions in brain. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 192(1), 50–57.
Engel, J., & Berggren, U. (1980). Effects of lithium on behaviour and central monoamines. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 280, S133–S143.
Ernst, M. (2000). Commentary: Considerations on the characterization and treatment of self-injurious behavior. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 30(5), 447–450.
Espie, C. A., Watkins, J., Curtice, L., Espie, A., Duncan, R., Ryan, J. A., et al. (2003). Psychopathology in people with epilepsy and intellectual disability; an investigation of potential explanatory variables. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 74(11), 1485–1492.
Farber, J. M. (1987). Psychopharmacology of self-injurious behavior in the mentally retarded. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 26(3), 296–302.
Fatemi, S. H., Folsom, T. D., Reutiman, T. J., & Thuras, P. D. (2009). Expression of GABA(B) receptors is altered in brains of subjects with autism. Cerebellum, 8(1), 64–69.
Fisher, W. W., Groff, R. A., & Roane, H. S. (2011). Applied behavior analysis. In W. W. Fisher, C. C. Piazza, & H. S. Roane (Eds.), Handbook of applied behavior analysis (pp. 3–16). New York: Guilford Press.
Fontenot, M. B., Musso, M. W., McFatter, R. M., & Anderson, G. M. (2009). Dose-finding study of fluoxetine and venlafaxine for the treatment of self-injurious and stereotypic behavior in rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). Journal of the American Association for Laboratory Animal Science, 48(2), 176–184.
Fontenot, M. B., Padgett, E. E, I. I. I., Dupuy, A. M., Lynch, C. R., De Petrillo, P. B., & Higley, J. D. (2005). The effects of fluoxetine and buspirone on self-injurious and stereotypic behavior in adult male rhesus macaques. Comparative Medicine, 55(1), 67–74.
Garber, H. J., McGonigle, J. J., Slomka, G. T., & Monteverde, E. (1992). Clomipramine treatment of stereotypic behaviors and self-injury in patients with developmental disabilities. Journal of the Amercian Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 31(6), 1157–1160.
Glick, I. D., Murray, S. R., Vasudevan, P., Marder, S. R., & Hu, R. J. (2001). Treatment with atypical antipsychotics: New indications and new populations. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 35(3), 187–191.
Goldstein, M. (1989). Dopaminergic mechanisms in self-inflicting biting behavior. Psychopharmacology Bulletin, 25(3), 349–352.
Goldstein, M., Anderson, L. T., Reuben, R., & Dancis, J. (1985). Self-mutilation in Lesch-Nyhan disease is caused by dopaminergic denervation. Lancet, 1(8424), 338–339.
Gossler, A., Schalamon, J., Huber-Zeyringer, A., & Hollwarth, M. E. (2007). Gastroesophageal reflux and behavior in neurologically impaired children. Journal of Pediatric Surgery, 42(9), 1486–1490.
Granger, P., Biton, B., Faure, C., Vige, X., Depoortere, H., Graham, D., et al. (1995). Modulation of the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor by the antiepileptic drugs carbamazepine and phenytoin. Molecular Pharmacology, 47(6), 1189–1196.
Greenberg, A., & Coleman, M. (1973). Depressed whole blood serotonin levels associated with behavioral abnormalities in the de Lange syndrome. Pediatrics, 52(5), 720–724.
Gualtieri, C. T. (1989). The differential diagnosis of self-injurious behavior in mentally retarded people. Psychopharmacology Bulletin, 25(3), 358–363.
Gualtieri, C. T., & Schroeder, S. R. (1989). Pharmacotherapy for self-injurious behavior: Preliminary tests of the D1 hypothesis. Psychopharmacology Bulletin, 25(3), 364–371.
Guptill, J. T., Booker, A. B., Gibbs, T. T., Kemper, T. L., Bauman, M. L., & Blatt, G. J. (2007). [3H]-flunitrazepam-labeled benzodiazepine binding sites in the hippocampal formation in autism: A multiple concentration autoradiographic study. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37(5), 911–920.
Hammock, R., Levine, W. R., & Schroeder, S. R. (2001). Brief report: Effects of clozapine on self-injurious behavior of two risperidone nonresponders with mental retardation. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 31(1), 109–113.
Hanley, H. G., Stahl, S. M., & Freedman, D. X. (1977). Hyperserotonemia and amine metabolites in autistic and retarded children. Archives of General Psychiatry, 34(5), 521–531.
Hardan, A. Y., Minshew, N. J., & Keshavan, M. S. (2000). Corpus callosum size in autism. Neurology, 55(7), 1033–1036.
Hassiotis, A., Parkes, C., Jones, L., Fitzgerald, B., & Romeo, R. (2008). Individual characteristics and service expenditure on challenging behaviour for adults with intellectual disabilities. Journal of Applied Research in Intellectual Disabilities, 21(5), 438–445.
Hedges, D., Jeppson, K., & Whitehead, P. (2003). Antipsychotic medication and seizures: A review. Drugs Today, 39(7), 551–557.
Hellings, J. A., & Warnock, J. K. (1994). Self-injurious behavior and serotonin in Prader-Willi syndrome. Psychopharmacology Bulletin, 30(2), 245–250.
Hellings, J. A., Weckbaugh, M., Nickel, E. J., Cain, S. E., Zarcone, J. R., Reese, R. M., et al. (2005). A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of valproate for aggression in youth with pervasive developmental disorders. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology, 15(4), 682–692.
Hollander, E., Wasserman, S., Swanson, E. N., Chaplin, W., Schapiro, M. L., Zagursky, K., et al. (2006). A double-blind placebo-controlled pilot study of olanzapine in childhood/adolescent pervasive developmental disorder. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology, 16(5), 541–548.
Holson, R. R., Scallet, A. C., Ali, S. F., Sullivan, P., & Gough, B. (1988). Adrenocortical, beta-endorphin and behavioral responses to graded stressors in differentially reared rats. Physiology & Behavior, 42(2), 125–130.
Horner, R. H., Day, H. M., & Day, J. R. (1997). Using neutralizing routines to reduce problem behaviors. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 30(4), 601–614.
Horner, R. H., Day, H. M., Sprague, J. R., & O’Brien, M. (1991). Interspersed requests: A nonaversive procedure for reducing aggression and self-injury during instruction. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 24(2), 265–278.
Horsthemke, B., & Wagstaff, J. (2008). Mechanisms of imprinting of the Prader-Willi/Angelman region. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 146A(16), 2041–2052.
Hurwitz, S., & Minshawi, N. (2012). Methods of defining and observing behaviors. In J. L. Matson (Ed.), Functional assessment for challenging behaviors (pp. 91–103). New York: Springer Science + Business Media LLC.
Iwata, B. A., Dorsey, M. F., Slifer, K. J., & Bauman, K. E. (1994a). Toward a functional analysis of self-injury. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 27(2), 197–209.
Iwata, B. A., Pace, G. M., Dorsey, M. F., & Zarcone, J. R. (1994b). The functions of self-injurious behavior: An experimental-epidemiological analysis. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 27(2), 215–240.
Iwata, B. A., Pace, G. M., Kalsher, M. J., & Cowdery, G. E. (1990a). Experimental analysis and extinction of self-injurious escape behavior. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 23(1), 11–27.
Iwata, B. A., Vollmer, T. R., & Zarcone, J. R. (1990b). The experimental (functional) analysis of behavior disorders: Methodology, applications, and limitations. In A. C. Repp (Ed.), Perspectives on the use of nonaversive and aversive interventions for persons with developmental disabilities (pp. 301–330). Illinois: Sycamore Publishing Company.
Jankovic, J., Caskey, T. C., Stout, J. T., & Butler, I. J. (1988). Lesch-Nyhan syndrome: A study of motor behavior and cerebrospinal fluid neurotransmitters. Annals of Neurology, 23(5), 466–469.
Janowsky, D. S., Barnhill, L. J., & Davis, J. M. (2003). Olanzapine for self-injurious, aggressive, and disruptive behaviors in intellectually disabled adults: A retrospective, open-label, naturalistic trial. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 64(10), 1258–1265.
Janowsky, D. S., Barnhill, L. J., Shetty, M., & Davis, J. M. (2005). Minimally effective doses of conventional antipsychotic medications used to treat aggression, self-injurious and destructive behaviors in mentally retarded adults. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology, 25(1), 19–25.
Jennett, H., Hagopian, L. P., & Beaulieu, L. (2011). Analysis of heart rate and self-injury with and without restraint in an individual with autism. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 5(3), 1110–1118.
Jinnah, H. A., Gage, F. H., & Friedmann, T. (1990). Animal models of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. Brain Research Bulletin, 25(3), 467–475.
Jinnah, H. A., Vissar, J. E., Harris, J. C., Verdu, A., Larovere, L., Ceballos-Piscot, I., et al. (2006). Delineation of the motor disorder of Lesch-Nyhan disease. Brain, 129(5), 1201–1217.
Jordan, I., Robertson, D., Catani, M., Craig, M., & Murphy, D. (2012). Aripiprazole in the treatment of challenging behaviour in adults with autism spectrum disorder. Psychopharmacology (Berl), 223(3), 357–360.
Kaplan, G. B., & Leite-Morris, B. S. (2002). Introduction to neuronal signaling pathways. In G. B. Kaplan & R. P. Hammer (Eds.), Brain circuitry and signaling in psychiatry (pp. 31–62). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing Inc.
Kelley, M. E., LaRue, R. H., Roane, H. S., & Gadaire, D. M. (2011). Indirect behavioral assessments: Interviews and rating scales. In W. W. Fisher, C. C. Piazza, & H. S. Roane (Eds.), Handbook of applied behavior analysis (pp. 182–205). New York: Guilford Press.
Kemp, A. S., Fillmore, P. T., Lenjavi, M. R., Lyon, M., Chicz-Demet, A., Touchette, P. E., et al. (2008). Temporal patterns of self-injurious behavior correlate with stress hormone levels in the developmentally disabled. Psychiatry Research, 157(1), 181–189.
Kern, L., Gallagher, P., Starosta, K., Hickman, W., & George, M. (2006). Longitudinal outcomes of functional behavioral assessment-based intervention. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 8(2), 67–78.
King, B. H. (1993). Self-injury by people with mental retardation: A compulsive behavior hypothesis. American Journal of Mental Retardation, 98(1), 93–112.
King, B. H. (2000). Pharmacological treatment of mood disturbances, aggression, and self-injury in persons with pervasive developmental disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 30(5), 439–445.
King, B. H., Cromwell, H. C., Lee, H. T., Behrstock, S. P., Schmanke, T., & Maidment, N. T. (1998). Dopaminergic and glutamatergic interactions in the expression of self-injurious behavior. Developmental Neuroscience, 20(2–3), 180–187.
Knapp, M., Comas-Herrera, A., Astin, J., Beecham, J., & Pendaries, C. (2005). Intellectual disability, challenging behaviour and cost in care accommodation: What are the links? Health and Social Care in the Community, 13(4), 297–306.
Kraemer, G. W., & Clarke, A. S. (1990). The behavioral neurobiology of self-injurious behavior in rhesus monkeys. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 14, S141–S168.
La Malfa, G. P., Bertelli, M., Ricca, V., Mannucci, E., & Cabras, P. L. (1997). Fluvoxamine and mental retardation: Clinical use. Italian Journal of Intellective Impairment, 10, 3–6.
Lakin, K. C., Hill, B. K., Hauber, F. A., Bruininks, R. H., & Heal, L. W. (1983). New admissions and readmissions to a national sample of public residential facilities. American Journal of Mental Deficiency, 88, 13–20.
Le Vann, L. J. (1971). Clinical comparison of haloperidol with chlorpromazine in mentally retarded children. American Journal of Mental Deficiency, 75(6), 719–723.
Leboyer, M., Bouvard, M. P., Launay, J. M., Recasens, C., Plumet, M. H., Waller-Perotte, D., et al. (1993). Opiate hypothesis in infantile autism? Therapeutic trials with naltrexone. L’Encephale, 19(2), 95–102.
Lecavalier, L., Leone, S., & Wiltz, J. (2006). The impact of behaviour problems on caregiver stress in young people with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 50(3), 172–183.
Leite-Morris, K. A., Fukudome, E. Y., & Kaplan, G. B. (2002). Opiate-induced motor stimulation is regulated by gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptors found in the ventral tegmental area in mice. Neuroscience Letters, 317(3), 119–122.
Lejeune, J., Lafourcade, J., Berger, R., Vialatte, J., Boeswillwald, M., Seringe, P., et al. (1963). 3 cases of partial deletion of the short arm of a 5 chromosome. Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Seances de l’Academie des Sciences, 257, 3098–3102.
Lequia, J., Machalicek, W., & Rispoli, M. J. (2012). Effects of activity schedules on challenging behavior exhibited in children with autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 6(1), 480–492.
Lewis, M. H., Bodfish, J. W., Powell, S. B., Parker, D. E., & Golden, R. N. (1996). Clomipramine treatment for self-injurious behavior of individuals with mental retardation: A double-blind comparison with placebo. American Journal of Mental Retardation, 100(6), 654–665.
Lewis, M. H., Gluck, J. P., Beauchamp, A. J., Keresztury, M. F., & Mailman, R. B. (1990). Long-term effects of early social isolation in Macaca mulatta: Changes in dopamine receptor function following apomorphine challenge. Brain Research, 513(1), 67–73.
Lindauer, S. E., DeLeon, I. G., & Fisher, W. W. (1999). Decreasing signs of negative affect and correlated self-injury in an individual with mental retardation and mood disturbances. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 32(1), 103–106.
Lindberg, J. S., Iwata, B. A., Roscoe, E. M., Worsdell, A. S., & Hanley, G. P. (2003). Treatment efficacy of noncontingent reinforcement during brief and extended application. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 36(1), 1–19.
Lloyd, K. G., Hornykiewicz, O., Davidson, L., Shannak, K., Farley, I., Goldstein, M., et al. (1981). Biochemical evidence of dysfunction of brain neurotransmitters in the Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. The New England Journal of Medicine, 305(19), 1106–1111.
Loh, H. H., Brase, D. A., Sampath-Khanna, S., Mar, J. B., Way, E. L., & Li, C. H. (1976). Beta-endorphin in vitro inhibition of striatal dopamine release. Nature, 264(5586), 567–568.
Lotan, M., Ljunggren, E. A., Johnsen, T. B., Defrin, R., Pick, C. G., & Strand, L. I. (2009). A modified version of the non-communicating children pain checklist-revised, adapted to adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: Sensitivity to pain and internal consistency. The Journal of Pain, 10(4), 398–407.
Luiselli, J. K. (1992). Assessment and treatment of self-injury in a deaf-blind child. Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities, 4(3), 219–226.
Luiselli, J. K., Cochran, M. L., & Huber, S. A. (2005). Effects of otitis media on a child with autism receiving behavioral intervention for self-injury. Child & Family Behavior Therapy, 27(2), 51–56.
MacLean, W. E., Tervo, R. C., Hoch, J., Tervo, M., & Symons, F. J. (2010). Self-injury among a community cohort of young children at risk for intellectual and developmental disabilities. The Journal of Pediatrics, 157(6), 979–983.
Magee, S. K., & Ellis, J. (2000). Extinction effects during the assessment of multiple problem behaviors. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 33(3), 313–316.
Major, C. A., Kelly, B. J., Novak, M. A., Davenport, M. D., Stonemetz, K. M., & Meyer, J. S. (2009). The anxiogenic drug FG7142 increases self-injurious behavior in male rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). Life Sciences, 85(21–22), 753–758.
Mandell, D. S. (2008). Psychiatric hospitalization among children with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38(6), 1059–1065.
Marcus, R. N., Owen, R., Kamen, L., Manos, G., McQuade, R. D., Carson, W. H., et al. (2009). A placebo-controlled, fixed-dose study of aripiprazole in children and adolescents with irritability associated with autistic disorder. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 48(11), 1110–1119.
Marholin, D, I. I., Touchette, P. E., & Stewart, R. M. (1979). Withdrawal of chronic chlorpromazine medication: An experimental analysis. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 12(2), 159–171.
Matson, J. L., Bamburg, J. W., Mayville, E. A., & Khan, I. (1999). Seizure disorders in people with intellectual disability: An analysis of differences in social functioning, adaptive functioning and maladaptive behaviours. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 43(6), 531–539.
Matson, J. L., & LoVullo, S. V. (2008). A review of behavioral treatments for self-injurious behaviors of persons with autism spectrum disorders. Behavior Modification, 32(1), 61–76.
Matthews, T., Weston, N., Baxter, H., Felce, D., & Kerr, M. (2008). A general practice-based prevalence study of epilepsy among adults with intellectual disabilities and of its association with psychiatric disorder, behaviour disturbance and career stress. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 52(2), 163–173.
McDonough, M., Hillery, J., & Kennedy, N. (2000). Olanzapine for chronic, stereotypic self-injurious behaviour: A pilot study in seven adults with intellectual disability. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 44(6), 677–684.
McDougle, C. J. (2013). Sounding a wake-up call: Improving the lives of adults with autism. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 52(6), 566–568.
McDougle, C. J., Naylor, S. T., Cohen, D. J., Aghajanian, G. K., Heninger, G. R., & Price, L. H. (1996a). Effects of tryptophan depletion in drug-free adults with autistic disorder. Archives of General Psychiatry, 53(11), 993–1000.
McDougle, C. J., Naylor, S. T., Cohen, D. J., Volkmar, F. R., Heninger, G. R., & Price, L. H. (1996b). A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of fluvoxamine in adults with autistic disorder. Archives of General Psychiatry, 53(11), 1001–1008.
McElroy, S. L., Keck, P. E., Pope, H. G., & Hudson, J. I. (1989). Valproate in psychiatric disorders: Literature review and clinical guidelines. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 50, S23–S29.
McManaman, J., & Tam, D. A. (1999). Gabapentin for self-injurious behavior in Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. Pediatric Neurology, 20(5), 381–382.
McNally, G. P., & Akil, H. (2002). Endogenous opioid peptides and their receptors: Overview and function in pain modulation. In K. L. Davis, D. Charney, J. T. Coyle, & C. Nemeroff (Eds.), Neuropsychopharmacology: The fifth generation of progress (pp. 35–46). New York: Lippincott Williams Wilkins.
Mesibov, G. B., Browder, D. M., & Kirkland, C. (2002). Using individualized schedules as a component of positive behavioral support for students with developmental disabilities. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 4(2), 73–79.
Micev, V., & Lynch, D. M. (1974). Effect of lithium on disturbed severely mentally retarded patients. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 125(584), 110.
Miller, D. T., Adam, M. P., Aradhya, S., Biesecker, L. G., Brothman, A. R., Carter, N. P., et al. (2010). Consensus statement: Chromosomal microarray is a first-tier clinical diagnostic test for individuals with developmental disabilities or congenital anomalies. American Journal of Human Genetics, 86(5), 749–764.
Miyamoto, S., Duncan, G. E., Goff, D. C., & Lieberman, J. A. (2002). Therapeutics of schizophrenia. In K. L. Davis, D. Charney, J. T. Coyle, & C. Nemeroff (Eds.), Neuropsychopharmacology: The fifth generation of progress (pp. 777–797). Philidelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Mizuno, T. I., & Yugari, Y. (1974). Letter: Self mutilation in Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. Lancet, 1(7860), 761.
Mizuno, T., & Yugari, Y. (1975). Prophylactic effect of L-5-hydroxytryptophan on self-mutilation in the Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. Neuropadiatrie, 6(1), 13–23.
Moreno-Fuenmayor, H., Borjas, L., Arrieta, A., Valera, V., & Socorro-Candanoza, L. (1996). Plasma excitatory amino acids in autism. Investigacion Clinica, 37(2), 113–128.
Morgan, J. R., Storch, E. A., Woods, D. W., Bodzin, D., Lewin, A. B., & Murphy, T. K. (2010). A preliminary analysis of the phenomenology of skin-picking in Prader-Willi syndrome. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 41(4), 448–463.
Mori, T., Ito, S., Kita, T., Narita, M., Suzuki, T., Matsubayashi, K., et al. (2007). Oxidative stress in methamphetamine-induced self-injurious behavior in mice. Behavioural Pharmacology, 18(3), 239–249.
Mori, T., Ito, S., Kita, T., & Sawaguchi, T. (2004). Effects of dopamine- and serotonin-related compounds on methamphetamine-induced self-injurious behavior in mice. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences, 96(4), 459–464.
Muehlmann, A. M., Brown, B. D., & Devine, D. P. (2008). Pemoline (2-amino-5-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4-one)-induced self-injurious behavior: A rodent model of pharmacotherapeutic efficacy. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 324(1), 214–223.
Muehlmann, A. M., & Devine, D. P. (2008). Glutamate-mediated neuroplasticity in an animal model of self-injurious behaviour. Behavioural Brain Research, 189(1), 32–40.
Muehlmann, A. M., Kies, S. D., Turner, C. A., Wolfman, S., Lewis, M. H., & Devine, D. P. (2012). Self-injurious behaviour: Limbic dysregulation and stress effects in an animal model. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 56(5), 490–500.
Muehlmann, A. M., Wilkinson, J. A., & Devine, D. P. (2011). Individual differences in vulnerability for self-injurious behavior: Studies using an animal model. Behavioural Brain Research, 217(1), 148–154.
Novak, M. A. (2003). Self-injurious behavior in rhesus monkeys: New insights into its etiology, physiology, and treatment. American Journal of Primatology, 59(1), 3–19.
Nyhan, W. L. (1972). Behavioral phenotypes in organic genetic disease: Presidential address to the Society for Pediatric Research, May 1, 1971. Pediatric Research, 6(1), 1–9.
Nyhan, W. L. (1973). The Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. Annual Review of Medicine, 24, 41–60.
Nyhan, W. L. (1997). The recognition of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome as an inborn error of purine metabolism. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease, 20(2), 171–178.
Nyhan, W. L., Johnson, H. G., Kaufman, I. A., & Jones, K. L. (1980). Serotonergic approaches to the modification of behavior in the Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. Applied Research in Mental Retardation, 1(1), 25–40.
Oblak, A., Gibbs, T. T., & Blatt, G. J. (2009). Decreased GABAA receptors and benzodiazepine binding sites in the anterior cingulate cortex in autism. Autism Research, 2(4), 205–219.
Oliver, C., Sloneem, J., Hall, S., & Arron, K. (2009). Self-injurious behaviour in Cornelia de Lange syndrome: 1. Prevalence and phenomenology. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 53(7), 575–589.
Oltras, C. M., Mora, F., & Vives, F. (1987). Beta-endorphin and ACTH in plasma: Effects of physical and psychological stress. Life Sciences, 40(17), 1683–1686.
Orr, R. (1993). Age-related changes in stress experienced by families with a child who has developmental delays. Mental Retardation, 31(3), 171–176.
Osman, O. T., & Loschen, E. L. (1992). Self-injurious behavior in the developmentally disabled: Pharmacologic treatment. Psychopharmacology Bulletin, 28(4), 439–449.
Overhauser, J., Huang, X., Gersh, M., Wilson, W., McMahon, J., Bengtsson, U., et al. (1994). Molecular and phenotypic mapping of the short arm of chromosome 5: Sublocalization of the critical region for the cri-du-chat syndrome. Human Molecular Genetics, 3(2), 247–252.
Owen, R., Sikich, L., Marcus, R. N., Corey-Lisle, P., Manos, G., McQuade, R. D., et al. (2009). Aripiprazole in the treatment of irritability in children and adolescents with autistic disorder. Pediatrics, 124(6), 1533–1540.
Parikh, M. S., Kolevzon, A., & Hollander, E. (2008). Psychopharmacology of aggression in children and adolescents with autism: A critical review of efficacy and tolerability. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology, 18(2), 157–178.
Patel, N. C., Crismon, M. L., Hoagwood, K., Johnsrud, M. T., Rascati, K. L., Wilson, J. P., et al. (2005). Trends in the use of typical and atypical antipsychotics in children and adolescents. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 44(6), 548–556.
Peebles, K. A., & Price, T. J. (2012). Self-injurious behaviour in intellectual disability syndromes: Evidence for aberrant pain signalling as a contributing factor. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 56(5), 441–452.
Pfeffer, C. R., Jiang, H., & Domeshek, L. J. (1997). Buspirone treatment of psychiatrically hospitalized prepubertal children with symptoms of anxiety and moderately severe aggression. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology, 7(3), 145–155.
Piazza, C. C., Adelinis, J. D., Hanley, G. P., Goh, H., & Delia, M. D. (2000). An evaluation of the effects of matched stimuli on behaviors maintained by automatic reinforcement. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 33(1), 13–27.
Piazza, C. C., Fisher, W. W., & Kahng, S. W. (1996). Sleep patterns in children and young adults with mental retardation and severe behavior disorders. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 38(4), 335–344.
Politte, L. C., & McDougle, C. J. (2014). Atypical antipsychotics in the treatment of children and adolescents with pervasive developmental disorders. Psychopharmacology (Berl), 231(6), 1023–1036.
Posey, D. J., Stigler, K. A., Erickson, C. A., & McDougle, C. J. (2008). Antipsychotics in the treatment of autism. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 118(1), 6–14.
Potenza, M. N., Holmes, J. P., Kanes, S. J., & McDougle, C. J. (1999). Olanzapine treatment of children, adolescents, and adults with pervasive developmental disorders: An open-label pilot study. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology, 19(1), 37–44.
Privitera, M. D. (1997). Topiramate: A new antiepileptic drug. The Annals of Pharmacotherapy, 31(10), 1164–1173.
Quine, L. (1991). Sleep problems in children with mental handicap. Journal of Mental Deficiency Research, 35(4), 269–290.
Quine, S. (1993). Stressors experienced by relatives of patients in an innovative rehabilitation program. Health and Social Work, 18(2), 114–122.
Ratey, J. J., Sovner, R., Mikkelsen, E., & Chmielinski, H. E. (1989). Buspirone therapy for maladaptive behavior and anxiety in developmentally disabled persons. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 50(10), 382–384.
Reisberg, B., & Gershon, S. (1979). Side effects associated with lithium therapy. Archives of General Psychiatry, 36(8), 879–887.
Riblet, L. A., Taylor, D. P., Elson, M. S., & Stanton, H. C. (1982). Pharmacology and neurochemistry of buspirone. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 43(12), 11–16.
Richardson, J. S., & Zaleski, W. A. (1983). Naloxone and self-mutilation. Biological Psychiatry, 18(1), 99–101.
Richman, D. M., Barnard-Brak, L., Bosch, A., Thompson, S., Grubb, L., & Abby, L. (2013). Predictors of self-injurious behaviour exhibited by individuals with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 57(5), 429–439.
Ricketts, R. W., Goza, A. B., Ellis, C. R., Singh, Y. N., Chambers, S., Singh, N. N., et al. (1994). Clinical effects of buspirone on intractable self-injury in adults with mental retardation. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 33(2), 270–276.
Roach, E. S., Delgado, M., Anderson, L., Iannaccone, S. T., & Burns, D. K. (1996). Carbamazepine trial for Lesch-Nyhan self-mutilation. Journal of Child Neurology, 11(6), 476–478.
Roby-Brami, A., Bussel, B., Willer, J. C., & Le Bars, D. (1987). An electrophysiological investigation into the pain-relieving effects of heterotopic nociceptive stimuli: Probable involvement of a supraspinal loop. Brain, 110(6), 1497–1508.
Rohatgi, S., Clark, D., Kline, A. D., Jackson, L. G., Pie, J., Siu, V., et al. (2010). Facial diagnosis of mild and variant CdLS: Insights from a dysmorphologist survey. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 152A(7), 1641–1653.
Rojahn, J., Wilkins, J., Matson, J. L., & Boisjoli, J. (2010). A comparison of adults with intellectual disabilities with and without ASD on parallel measures of challenging behaviour: The behavior problems inventory-01 (BPI-01) and Autism spectrum disorders-behavior problems for intellectually disabled adults (ASD-BPA). Journal of Applied Research in Intellectual Disabilities, 23(2), 179–185.
Ruedrich, S., Swales, T. P., Fossaceca, C., Toliver, J., & Rutkowski, A. (1999). Effect of divalproex sodium on aggression and self-injurious behaviour in adults with intellectual disability: A retrospective review. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 43(2), 105–111.
Ruedrich, S. L., Swales, T. P., Rossvanes, C., Diana, L., Arkadiev, V., & Lim, K. (2008). Atypical antipsychotic medication improves aggression, but not self-injurious behaviour, in adults with intellectual disabilities. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 52(2), 132–140.
Saito, Y., & Takashima, S. (2000). Neurotransmitter changes in the pathophysiology of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. Brain and Development, 22, S122–S131.
Sampat, R., Fu, R., Larovere, L. E., Torres, R. J., Ceballos-Picot, I., Fischbach, M., et al. (2011). Mechanisms for phenotypic variation in Lesch-Nyhan disease and its variants. Human Genetics, 129(1), 71–78.
Sandman, C. A., Barron, J. L., Chicz-DeMet, A., & DeMet, E. M. (1990). Plasma B-endorphin levels in patients with self-injurious behavior and stereotypy. American Journal of Mental Retardation, 95(1), 84–92.
Sandman, C. A., Datta, P. C., Barron, J., Hoehler, F. K., Williams, C., & Swanson, J. M. (1983). Naloxone attenuates self-abusive behavior in developmentally disabled clients. Applied Research in Mental Retardation, 4(1), 5–11.
Sandman, C. A., Hetrick, W., Taylor, D. V., & Chicz-DeMet, A. (1997). Dissociation of POMC peptides after self-injury predicts responses to centrally acting opiate blockers. American Journal of Mental Retardation, 102(2), 182–199.
Sandman, C. A., Spence, M. A., & Smith, M. (1999). Proopiomelanocortin (POMC) disregulation and response to opiate blockers. Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews, 5(4), 314–321.
Sandman, C. A., Touchette, P. E., Marion, S. D., & Chicz-DeMet, A. (2008). The role of proopiomelanocortin (POMC) in sequentially dependent self-injurious behavior. Developmental Psychobiology, 50(7), 680–689.
Sassi, R. B., & Soares, J. C. (2002). Neural circuitry and signaling in bipolar disorder. In G. B. Kaplan & R. P. Hammer (Eds.), Brain circuitry and signaling in psychiatry (pp. 179–200). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing Inc.
Scahill, L., Aman, M. G., McDougle, C. J., Arnold, L. E., McCracken, J. T., Handen, B., et al. (2009). Trial design challenges when combining medication and parent training in children with pervasive developmental disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39(5), 720–729.
Schain, R. J., & Freedman, D. X. (1961). Studies on 5-hydroxyindole metabolism in autistic and other mentally retarded children. The Journal of Pediatrics, 58, 315–320.
Schroeder, S. R., Oster-Granite, M. L., Berkson, G., Bodfish, J. W., Breese, G. R., Cataldo, M. F., et al. (2001). Self-injurious behavior: Gene–brain–behavior relationships. Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews, 7(1), 3–12.
Schroeder, S. R., Schroeder, C. S., Smith, B., & Dalldorf, J. (1978). Prevalence of self-injurious behaviors in a large state facility for the retarded: A three-year follow-up study. Journal of Autism and Childhood Schizophrenia, 8(3), 261–269.
Shakya, D. R., Shyangwa, P. M., Pandey, A. K., Subedi, S., & Yadav, S. (2010). Self injurious behavior in temporal lobe epilepsy. Journal of the Nepal Medical Association, 49(179), 239–242.
Shapira, N. A., Lessig, M. C., Murphy, T. K., Driscoll, D. J., & Goodman, W. K. (2002). Topiramate attenuates self-injurious behaviour in Prader-Willi syndrome. The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology, 5(2), 141–145.
Shinohe, A., Hashimoto, K., Nakamura, K., Tsujii, M., Iwata, Y., Tsuchiya, K. J., et al. (2006). Increased serum levels of glutamate in adult patients with autism. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 30(8), 1472–1477.
Siegel, M., Milligan, B., Robbins, D., & Prentice, G. (2012). Electroconvulsive therapy in an adolescent with autism and bipolar I disorder. The Journal of ECT, 28(4), 252–255.
Sigafoos, J., O’Reilly, M., Ma, C. H., Edrisinha, C., Cannella, H., & Lancioni, G. E. (2006). Effects of embedded instruction versus discrete-trial training on self-injury, correct responding, and mood in a child with autism. Journal of Intellectual and Developmental Disability, 31(4), 196–203.
Simeon, D., Stein, D. J., Gross, S., Islam, N., Schmeidler, J., & Hollander, E. (1997). A double-blind trial of fluoxetine in pathologic skin picking. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 58(8), 341–347.
Singh, N. N., & Aman, M. G. (1981). Effects of thioridazine dosage on the behavior of severely mentally retarded persons. American Journal of Mental Deficiency, 85(6), 580–587.
Skinner, B. F. (1938). The behavior of organisms: An experimental analysis. Oxford, England: Appleton-Century.
Smith, R. G. (2011). Developing antecedent interventions for problem behavior. In W. W. Fisher, C. C. Piazza, & H. S. Roane (Eds.), Handbook of applied behavior analysis (pp. 297–316). New York: Guilford Press.
Snyder, R., Turgay, A., Aman, M., Binder, C., Fisman, S., & Carroll, A. (2002). Effects of risperidone on conduct and disruptive behavior disorders in children with subaverage IQs. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 41(9), 1026–1036.
Sohanpal, S. K., Deb, S., Thomas, C., Soni, R., Lenotre, L., & Unwin, G. (2007). The effectiveness of antidepressant medication in the management of behaviour problems in adults with intellectual disabilities: A systematic review. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 51(10), 750–765.
Sovner, R. (1986). Limiting factors in the use of DSM-III criteria with mentally ill/mentally retarded persons. Psychopharmacology Bulletin, 22(4), 1055–1059.
Sovner, R., Fox, C. J., Lowry, M. J., & Lowry, M. A. (1993). Fluoxetine treatment of depression and associated self-injury in two adults with mental retardation. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 37(3), 301–311.
Sprague, J. R., & Horner, R. H. (1995). Functional assessment and intervention in community settings. Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews, 1(2), 89–93.
Sprague, R. L., & Werry, J. S. (1971). Methodology of psychopharmacological studies with the retarded. International Review of Research in Mental Retardation, 5, 147–219.
Stein, D. J., Keating, J., Zar, H. J., & Hollander, E. (1994). A survey of the phenomenology and pharmacotherapy of compulsive and impulsive-aggressive symptoms in Prader-Willi syndrome. The Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 6(1), 23–29.
Sterling-Turner, H. E., & Jordan, S. S. (2007). Interventions addressing transition difficulties for individuals with autism. Psychology in the Schools, 44(7), 681–690.
Stigler, K. A., Diener, J. T., Kohn, A. E., Li, L., Erickson, C. A., Posey, D. J., et al. (2009). Aripiprazole in pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified and Asperger’s disorder: A 14-week, prospective, open-label study. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology, 19(3), 265–274.
Stigler, K. A., Potenza, M. N., Posey, D. J., & McDougle, C. J. (2004). Weight gain associated with atypical antipsychotic use in children and adolescents: Prevalence, clinical relevance, and management. Pediatric Drugs, 6(1), 33–44.
Stout, R. J. (1990). Fluoxetine for the treatment of compulsive facial picking. American Journal of Psychiatry, 147(3), 370.
Stout, J. T., & Caskey, C. T. (1985). HPRT: Gene structure, expression, and mutation. Annual Review of Genetics, 19, 127–148.
Svendsen, C. N., Froimowitz, M., Hrbek, C., Campbell, A., Kula, N., Baldessarini, R. J., et al. (1988). Receptor affinity, neurochemistry and behavioral characteristics of the enantiomers of thioridazine: Evidence for different stereoselectivities at D1 and D2 receptors in rat brain. Neuropharmacology, 27(11), 1117–1124.
Symons, F. J., Butler, M. G., Sanders, M. D., Feurer, I. D., & Thompson, T. (1999). Self-injurious behavior and Prader-Willi syndrome: Behavioral forms and body locations. American Journal of Mental Retardation, 104(3), 260–269.
Symons, F. J., & Danov, S. E. (2005). A prospective clinical analysis of pain behavior and self-injurious behavior. Pain, 117(3), 473–477.
Tate, B. G., & Baroff, G. S. (1973). Aversive control of self-Injurious behavior in a psychotic boy. In J. M. Stedman, W. F. Patton, & K. F. Walton (Eds.), Clinical studies in behavior therapy with children, adolescents and their families (pp. 352–360). Springfield, IL: Charles C. Thomas Publisher.
Taylor, D. V., Rush, D., Hetrick, W. P., & Sandman, C. A. (1993). Self-injurious behavior within the menstrual cycle of women with mental retardation. American Journal of Mental Retardation, 97(6), 659–664.
Thompson, R. H., & Borrero, J. C. (2011). Direct observation. In W. W. Fisher, C. C. Piazza, & H. S. Roane (Eds.), Handbook of applied behavior analysis (pp. 191–205). New York: Guilford Press.
Tiefenbacher, S., Novak, M. A., Lutz, C. K., & Meyer, J. S. (2005). The physiology and neurochemistry of self-injurious behavior: A nonhuman primate model. Frontiers in Bioscience, 10, 1–11.
Tsiouris, J. A., Cohen, I. L., Patti, P. J., & Korosh, W. M. (2003). Treatment of previously undiagnosed psychiatric disorders in persons with developmental disabilities decreased or eliminated self-injurious behavior. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 64(9), 1081–1090.
Tyrer, S. P., Walsh, A., Edwards, D. E., Berney, T. P., & Stephens, D. A. (1984). Factors associated with a good response to lithium in aggressive mentally handicapped subjects. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 8(4), 751–755.
Van der Zee, S. P., Schretlen, E. D., & Monnens, L. A. (1968). Megaloblastic anaemia in the Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. Lancet, 1(7557), 1427.
Van Erp, A. M., & Miczek, K. A. (2000). Aggressive behavior, increased accumbal dopamine, and decreased cortical serotonin in rats. Journal of Neuroscience, 20(24), 9320–9325.
Vandenbergh, D. J., Persico, A. M., Hawkins, A. L., Griffin, C. A., Li, X., Jabs, E. W., et al. (1992). Human dopamine transporter gene (DAT1) maps to chromosome 5p15.3 and displays a VNTR. Genomics, 14(4), 1104–1106.
Veenstra-VanderWeele, J., & Anderson, G. M. (2011). The serotonin system in autism. In E. Hollander, A. Kolevzon, & J. T. Coyle (Eds.), Textbook of autism spectrum disorders (pp. 315–322). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing Inc.
Vestergaard, P., Amdisen, A., & Schou, M. (1980). Clinically significant side effects of lithium treatment: A survey of 237 patients in long-term treatment. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 62(3), 193–200.
Vollmer, T. R., Iwata, B. A., Zarcone, J. R., & Smith, R. G. (1993). The role of attention in the treatment of attention-maintained self-injurious behavior: Noncontingent reinforcement and differential reinforcement of other behavior. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 26(1), 9–21.
Vollmer, T. R., Marcus, B. A., & LeBlanc, L. (1994). Treatment of self-injury and hand mouthing following inconclusive functional analyses. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 27(2), 331–344.
Wachtel, L. E., Contrucci-Kuhn, S. A., Griffin, M., Thompson, A., Dhossche, D. M., & Reti, I. M. (2009). ECT for self-injury in an autistic boy. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 18(7), 458–463.
Wachtel, L. E., & Dhossche, D. M. (2010). Self-injury in autism as an alternate sign of catatonia: Implications for electroconvulsive therapy. Medical Hypotheses, 75(1), 111–114.
Wachtel, L. E., Griffin, M., & Reti, I. M. (2010). Electroconvulsive therapy in a man with autism experiencing severe depression, catatonia, and self-injury. The Journal of ECT, 26(1), 70–73.
Wallis, C. (2009). Respiratory health of people with profound intellectual and multiple disabilities. In J. Pawlyn & S. Carnaby (Eds.), Profound intellectual and multiple disabilities: Nursing complex needs (pp. 186–201). Hoboken: Wiley.
Walters, A. S., Barrett, R. P., Feinstein, C., Mercurio, A., & Hole, W. T. (1990). A case report of naltrexone treatment of self-injury and social withdrawal in autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 20(2), 169–176.
Watt-Smith, P. (2009). Dental care and oral health. In J. Pawlyn & S. Carnaby (Eds.), Profound intellectual and multiple disabilities: Nursing complex needs (pp. 202–235). Hoboken: Wiley.
West, S. A., Keck, P. E., & Mcelroy, S. L. (1995). Oral loading doses in the valproate treatment of adolescents with mixed bipolar disorder. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology, 5(3), 225–231.
Willemsen-Swinkels, S. H., Buitelaar, J. K., Nijhof, G. J., & van Engeland, H. (1995). Failure of naltrexone hydrochloride to reduce self-injurious and autistic behavior in mentally retarded adults. Double-blind placebo-controlled studies. Archives of General Psychiatry, 52(9), 766–773.
Willer, J. C., Dehen, H., & Cambier, J. (1981). Stress-induced analgesia in humans: Endogenous opioids and naloxone-reversible depression of pain reflexes. Science, 212(4495), 689–691.
Williams, K., Wheeler, D. M., Silove, N., & Hazell, P. (2010). Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, (8), CD004677. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004677.pub2.
Wilson, J. M., Young, A. B., & Kelley, W. N. (1983). Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency. The molecular basis of the clinical syndromes. The New England Journal of Medicine, 309(15), 900–910.
Wink, L. K., Erickson, C. A., & McDougle, C. J. (2010). Pharmacologic treatment of behavioral symptoms associated with autism and other pervasive developmental disorders. Current Treatment Options in Neurology, 12(6), 529–538.
Wolff, J. J., Hazlett, H. C., Lightbody, A. A., Reiss, A. L., & Piven, J. (2013). Repetitive and self-injurious behaviors: Associations with caudate volume in autism and fragile X syndrome. Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders, 5(1), 12.
Wong, D. F., Harris, J. C., Naidu, S., Yokoi, F., Marenco, S., Dannals, R. F., et al. (1996). Dopamine transporters are markedly reduced in Lesch-Nyhan disease in vivo. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 93(11), 5539–5543.
Zhang, W., & Bymaster, F. P. (1999). The in vivo effects of olanzapine and other antipsychotic agents on receptor occupancy and antagonism of dopamine D1, D2, D3, 5HT2A and muscarinic receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berl), 141(3), 267–278.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minshawi, N.F., Hurwitz, S., Morriss, D. et al. Multidisciplinary Assessment and Treatment of Self-Injurious Behavior in Autism Spectrum Disorder and Intellectual Disability: Integration of Psychological and Biological Theory and Approach. J Autism Dev Disord 45, 1541–1568 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-014-2307-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-014-2307-3