Abstract
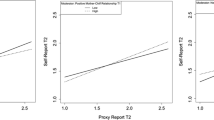
In light of evidence suggesting that maternal adaptation may impact early child emotional development, this study investigated the interactive effects of maternal psychosocial maladjustment and maternal sensitivity on child internalizing symptoms, with the aim of investigating the potentially protective function of maternal sensitivity. Families (N = 71 to 106 across measures, with gender spread almost evenly: number of boys = 31 to 51 across measures) took part in four assessments between child ages 1 and 3 years. Mothers completed measures of parental stress, psychological distress, and marital satisfaction when their children were between 12 and 15 months. A composite score of maternal psychosocial maladjustment was derived from these measures. Maternal sensitivity was rated by trained observers at 12 months following a home visit. Child internalizing symptoms were assessed by both parents when the child was 2 and 3 years old. Hierarchical regressions revealed that increased maternal psychosocial maladjustment was related to more internalizing symptoms in children, however only among children of less sensitive mothers. In contrast, children of more sensitive mothers appeared to be protected. This was observed with maternal reports at 2 years, and both maternal and paternal reports at 3 years. These results suggest that young children may be differentially affected by their parents’ emotional adjustment, while highlighting the pivotal protective role of maternal sensitivity in this process.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abidin, R. R. (1995). Parenting stress index: professional manual (3rd ed.). Odessa: Psychological Assessment Resources.
Achenbach, T. M., & Rescorla, L. A. (2000). Manual for the ASEBA preschool forms and profiles. Burlington: University of Vermont Department of Psychiatry.
Ainsworth, M. D. S., Bell, S. M., & Stayton, D. J. (1974). Infant-mother attachment and social development. In M. P. Richards (Ed.), The introduction of the child into a social world (pp. 99–135). London: Cambridge University Press.
Alink, L. R. A., Cicchetti, D., Kim, J., & Rogosch, F. (2009a). Mediating and moderating processes in the relation between maltreatment and psychopathology: mother- child relationship quality and emotion regulation. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 37, 831–843. doi:10.1007/s10802-009-9314-4.
Alink, L. R. A., Mesman, J., Van Zeijl, J., Stolk, M. N., Juffer, F., Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., & Koot, H. M. (2009b). Maternal sensitivity moderates the relation between negative discipline and aggression in early childhood. Social Development, 18, 99–120. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9507.2008.00478.x.
Bailey, W. T. (1994). A longitudinal study of fathers’ involvement with young children: infancy to age 5 years. The Journal of Genetic Psychology, 155, 331–339. doi:10.1080/00221325.1994.9914783.
Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., Van IJzendoorn, M. H., & Juffer, F. (2003). Less is more: meta-analyses of sensitivity and attachment interventions in early childhood. Psychological Bulletin, 129, 195–215. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.129.2.195.
Barker, E. D., Jaffee, S. R., Uher, R., & Maughan, B. (2011). The contribution of prenatal and postnatal maternal anxiety and depression to child maladjustment. Depression and Anxiety, 28, 696–702. doi:10.1002/da.20856.
Behrens, K. Y., Parker, A. C., & Kulkofsky, S. (2014). Stability of maternal sensitivity across time and contexts with Q‐sort measures. Infant and Child Development, 23, 532–541. doi:10.1002/icd.1835.
Bernier, A., Carlson, S. M., Deschênes, M., & Matte-Gagné, C. (2012). Social factors in the development of early executive functioning: a closer look at the caregiving environment. Developmental Science, 15, 12–24. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7687.2011.01093.x.
Birmaher, B., Ryan, N. D., Williamson, D. E., Brent, D. A., Kaufman, J., Dahl, R. E., & Nelson, B. (1996). Childhood and adolescent depression: a review of the past 10 years. Part I. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 35, 1427–1439. doi:10.1097/00004583-199611000-00011.
Bittner, A., Egger, H. L., Erkanli, A., Costello, J. E., Foley, D. L., & Angold, A. (2007). What do childhood anxiety disorders predict? Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 48, 1174–1183.
Bordeleau, S., Bernier, A., & Carrier, J. (2012). Maternal sensitivity and children’s behavior problems: examining the moderating role of infant sleep duration. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 41, 471–481. doi:10.1080/15374416.2012.686101.
Bornstein, M. H. (2002). Parenting infants. In M. H. Bornstein (Ed.), Handbook of parenting: Vol. 1. Children and parenting (2nd ed., pp 3–43). Mahwah: Erlbaum.
Bornstein, M. H. (2006). Parenting science and practice. In W. Damon, R. M. Lerner (Series Eds.) & I. E. Sigel, K. A. Renninger (Vol. Eds.) Handbook of child psychology: Vol. 4. Child psychology and practice (6th ed., pp. 893–949). New York: Wiley.
Bronfenbrenner, U. (1979). Contexts of child rearing: problems and prospects. American Psychologist, 34, 844–850.
Calkins, S. D. (2004). Early attachment processes and the development of self regulation. In R. F. Baumeister & K. D. Vohs (Eds.), Handbook of self regulation: research, theory and applications (pp. 324–339). New York: Guilford Press.
Campbell, S. B., Brownell, C. A., Hungerford, A., Spieker, S. J., Mohan, R., & Blessing, J. S. (2004). The course of maternal depressive symptoms and maternal sensitivity as predictors of attachment security at 36 months. Development and Psychopathology, 16, 231–252. doi:10.1017/S0954579404044499.
Campbell, S. B., Matestic, P., von Stauffenberg, C., Mohan, R., & Kirchner, T. (2007). Trajectories of maternal depressive symptoms, maternal sensitivity, and children’s functioning at school entry. Developmental Psychology, 43, 1202–1215. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.43.5.1202.
Cicchetti, D., & Toth, S. L. (1991). A developmental perspective on internalizing and externalizing disorders. In D. Cicchetti & S. L. Toth (Eds.), Rochester symposium on developmental psychopathology, Vol 16: internalizing and externalizing expressions of dysfunction (pp. 1–19). NJ: Erlbaum.
Ciciolla, L., Gerstein, E. D., & Crnic, K. A. (2014). Reciprocity among maternal distress, child behavior, and parenting: transactional processes and early childhood risk. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 43, 751–764. doi:10.1080/15374416.2013.812038.
Colder, C. R., Lochman, J. E., & Wells, K. C. (1997). The moderating effects of children’s fear and activity level on relations between parenting practices and childhood symptomatology. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 25, 251–263. doi:10.1023/a:1025704217619.
Cole, P. M., Martin, S. E., & Dennis, T. A. (2004). Emotion regulation as a scientific construct: challenges and directions for child development research. Child Development, 75, 317–333.
Collins, W. A., Maccoby, E. E., Steinberg, L., Hetherington, E. M., & Bornstein, M. H. (2000). Contemporary research on parenting: the case for nature and nurture. American Psychologist, 55, 218–232. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.55.2.218.
Connell, A. M., & Goodman, S. H. (2002). The association between psychopathology in fathers versus mothers and children’s internalizing and externalizing behavior problems: a meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 128, 746–773. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.128.5.746.
Côté, S. M., Boivin, M., Liu, X., Nagin, D. S., Zoccolillo, M., & Tremblay, R. E. (2009). Depression and anxiety symptoms: onset, developmental course and risk factors during early childhood. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 50, 1201–1208. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2009.02099.x.
Cummings, E. M., Goeke-Morey, M. C., & Papp, L. M. (2003). Children’s responses to everyday marital conflict tactics in the home. Child Development, 74, 1918–1929. doi:10.1046/j.1467-8624.2003.00646.x.
Davies, P. T., Winter, M., & Cicchetti, D. (2006). The implications of emotional security theory for understanding and treating childhood psychopathology. Development and Psychopathology, 18, 707–735. doi:10.1017/S0954579406060354.
De Wolff, M. S., & Van IJzendoorn, M. H. (1997). Sensitivity and attachment: a meta-analysis on parental antecedents of infant attachment. Child Development, 68, 571–591.
Eley, T. C. (1999). Behavioral genetics as a tool for developmental psychology: anxiety and depression in children and adolescents. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 2, 21–36. doi:10.1023/A:1021863324202.
Elgar, F. J., McGrath, P. J., Waschbusch, D. A., Stewart, S. H., & Curtis, L. J. (2003). Mutual influences on maternal depression and child adjustment problems. Clinical Psychology Review, 24, 441–459. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2004.02.002.
Field, T. (2010). Postpartum depression effects on early interactions, parenting, and safety practices: a review. Infant Behavior and Development, 33, 1–6.
Gershoff, E. T. (2002). Corporal punishment by parents and associated child behaviors and experiences: a meta-analytic and theoretical review. Psychological Bulletin, 128, 539–579. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.128.4.539.
Goeke-Morey, M. C., Cummings, E. M., & Papp, L. M. (2007). Children and marital conflict resolution: implications for emotional security and adjustment. Journal of Family Psychology, 21, 744–753. doi:10.1037/0893-3200.21.4.744.
Goodman, S. H., Rouse, M. H., Connell, A. M., Broth, M. R., Hall, C. M., & Heyward, D. (2011). Maternal depression and child psychopathology: a meta-analytic review. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 14, 1–27. doi:10.1007/s10567-010-0080-1.
Gotlib, I. H., Joormann, J., Minor, K. L., & Hallmayer, J. (2008). HPA axis reactivity: a mechanism underlying the associations among 5-HTTLPR, stress, and depression. Biological Psychiatry, 63, 847–851. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.10.008.
Grant, K.-A., McMahon, C., Reilly, N., & Austin, M.-P. (2010a). Maternal sensitivity moderates the impact of prenatal anxiety disorder on infant mental development. Early Human Development, 86, 551–556. doi:10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2010.07.004.
Grant, K.-A., McMahon, C., Reilly, N., & Austin, M.-P. (2010b). Maternal sensitivity moderates the impact of prenatal anxiety disorder on infant responses to the still-face procedure. Infant Behavior and Development, 33, 453–462. doi:10.1016/j.infbeh.2010.05.001.
Gravener, J. A., Rogosch, F. A., Oshri, A., Narayan, A. J., Cicchetti, D., & Toth, S. L. (2012). The relations among maternal depressive disorder, maternal expressed emotion, and toddler behavior problems and attachment. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 40, 803–813. doi:10.1007/s10802-011-9598-z.
Groh, A. M., Roisman, G. I., Van IJzendoorn, M. H., Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., & Fearon, R. P. (2012). The significance of insecure and disorganized attachment for children’s internalizing symptoms: a meta-analytic study. Child Development, 83, 591–610. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8624.2011.01711.x.
Grossmann, K. E., & Grossmann, K. (1991). Attachment quality as an organizer of emotional and behavioral responses in a longitudinal perspective. In C. M. Parkes, J. Stevenson-Hinde, & P. Marris (Eds.), Attachment across the life cycle (pp. 93–114). New York: Travistock/Routledge.
Hammen, C., & Rudolph, K. D. (2003). Childhood mood disorders. Child Psychopathology, 2, 233–278.
Handal, P. J., Tschannen, T., & Searight, H. R. (1998). The relationship of child adjustment to husbands’ and wives’ marital distress, perceived family conflict, and mothers’ occupational status. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 29, 113–126. doi:10.1023/A:1025083915840.
Harachi, T. W., Fleming, C. B., White, H. R., Ensminger, M. E., Abbott, R. D., Catalano, R. F., & Haggerty, K. P. (2006). Aggressive behavior among girls and boys during middle childhood: predictors and sequelae of trajectory group membership. Aggressive Behavior, 32, 279–293. doi:10.1002/ab.20125.
Ilfeld, F. W. (1976). Further validation of a psychiatric symptom index in a normal population. Psychological Reports, 39, 1215–1228.
Ilfeld, F. W. (1978). Psychologic status of community residents along major demographic dimensions. Archives of General Psychiatry, 35, 716–724.
Kaitz, M., Maytal, H. R., Devor, N., Bergman, L., & Mankuta, D. (2010). Maternal anxiety, mother-infant interactions, and infants’ response to challenge. Infant Behavior and Development, 33, 136–148. doi:10.1016/j.infbeh.2009.12.003.
Kopp, C. B. (1982). Antecedents of self-regulation: a developmental perspective. Developmental Psychology, 18, 199–214.
Koss, K. J., George, M. R. W., Cummings, E. M., Davies, P. T., El-Sheikh, M., & Cicchetti, D. (2014). Asymmetry in children’s salivary cortisol and alpha-amylase in the context of marital conflict: links to children’s emotional security and adjustment. Developmental Psychobiology, 56, 836–849. doi:10.1002/dev.21156.
Leerkes, E. M., Blankson, A. N., & O’Brien, M. (2009). Differential effects of maternal sensitivity to infant distress and nondistress on social-emotional functioning. Child Development, 80, 762–775.
Lemelin, J.-P., Tarabulsy, G. M., & Provost, M. A. (2006). Predicting preschool cognitive development from infant temperament, maternal sensitivity, and psycho-social risk. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 52, 779–806.
Manning, L.G., Davies, P.T., & Cicchetti, D. (2014). Interparental violence and childhood adjustment: How and why maternal sensitivity is a protective factor. Child Development, 85, doi:10.1111/cdev.12279.
McCloskey, L. A., Figueredo, A. J., & Koss, M. P. (1995). The effects of systemic family violence on children’s mental health. Child Development, 66, 1239–1261. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8624.1995.tb00933.x.
McLeod, B. D., Weisz, J. R., & Wood, J. J. (2007). Examining the association between parenting and childhood anxiety: a meta-analysis. Clinical Psychology Review, 27, 155–172.
McMahon, C. A., Barnett, B., Kowalenko, N. M., & Tennant, C. C. (2006). Maternal attachment state of mind moderates the impact of postnatal depression on infant attachment. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 47, 660–669. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2005.01547.x.
Mezulis, A. H., Hyde, J. S., & Clark, R. (2004). Father involvement moderates the effect of maternal depression during a child’s infancy on child behavior problems in kindergarten. Journal of Family Psychology, 18, 575–588. doi:10.1037/0893-3200.18.4.575.
Miranda, J. K., de la Osa, N., Granero, R., & Ezpeleta, L. (2013). Multiple mediators of the relationships among maternal childhood abuse, intimate partner violence, and offspring psychopathology. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 28, 2941–2965. doi:10.1177/0886260513488686.
Moffitt, T. E., Caspi, A., Harrington, H., Milne, B. J., Melchior, M., Goldberg, D., & Poulton, R. (2007). Generalized anxiety disorder and depression: childhood risk factors in a birth cohort followed to age 32. Psychological Medicine, 37, 441–452.
Moss, E., Dubois-Comtois, K., Cyr, C., Tarabulsy, G. M., St-Laurent, D., & Bernier, A. (2011). Efficacy of a home-visiting intervention aimed at improving maternal sensitivity, child attachment, and behavioral outcomes for maltreated children: a randomized control trial. Development and Psychopathology, 23, 195–210. doi:10.1017/S0954579410000738.
Mouton-Simien, P., McCain, A. P., & Kelly, M. L. (1997). The development of the toddler behavior screening inventory. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 25, 59–64.
Okun, A., Stein, R. E., Bauman, L. J., & Silver, E. J. (1996). Content validity of the psychiatric symptom index CES-depression scale, and state-trait anxiety inventory from the perspective of DSM-IV. Psychological Reports, 79, 1059–1069.
Pederson, D. R., & Moran, G. (1995). A categorical description of infant–mother relationship in the home and its relation to Q-sort measures of infant–mother interaction. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 60, 111–145.
Pluess, M., Velders, F. P., Belsky, J., Van IJzendoorn, M. H., Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., Jaddoe, V. W. V., & Tiemeier, H. (2011). Serotonin transporter polymorphism moderates effects of prenatal maternal anxiety on infant negative emotionality. Biological Psychiatry, 69, 520–525. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.10.006.
Preacher, K.J., Curran, P.J., & Bauer, D.J. (2006). Probing interactions in multiple linear regression, latent curve analysis, and hierarchical linear modeling: interactive calculation tools for simple intercepts, simple slopes, and regions of significance. http://www.quantpsy.org.
Préville, M., Potvin, L., & Boyer, R. (1995). The structure of psychological distress. Psychological Reports, 77, 275–293.
Richman, N. (1977). Is a behavior checklist for preschool useful? In P. J. Graham (Ed.), Epidemiological approaches to child psychiatry (pp. 125–136). London: Academic.
Richmond, M. K., & Stocker, C. M. (2006). Associations between family cohesion and adolescent siblings’ externalizing behavior. Journal of Family Psychology, 20, 663–669. doi:10.1037/0893-3200.20.4.663.
Rochette, E., & Bernier, A. (2014). Parenting, family socioeconomic status, and child executive functioning: a longitudinal study. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 60, 431–460.
Sabourin, S., Valois, P., & Lussier, Y. (2005). Development and validation of a brief version of the dyadic adjustment scale with a nonparametric item analysis model. Psychological Assessment, 17, 15–27.
Sakakibara, B. M., Miller, W. C., Orenczuk, S. G., & Wolfe, D. L. (2009). A systematic review of depression and anxiety measures used with individuals with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord, 47, 841–851.
Sameroff, A. J. (1983). Developmental systems: Contexts and evolution. In P. Mussen (Ed.), Handbook of child psychology (Vol. 1, pp. 237–294). New York: Wiley.
Sameroff, A., Gutman, L. M., & Peck, S. C. (2003). Adaptation among youth facing multiple risks: Prospective research findings. In Resilience and vulnerability: adaptation in the context of childhood adversities (pp. 364–391). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Spangler, G., Johann, M., Ronai, Z., & Zimmermann, P. (2009). Genetic and environmental influence on attachment disorganization. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 50, 952–961.
Spanier, G. B. (1976). Measuring dyadic adjustment: new scales for assessing the quality of marriage and similar dyads. Journal of Marriage and Family, 38, 15–28. doi:10.2307/350547.
Sroufe, L. A. (1995). Emotional development: the organization of emotional life in the early years. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Sroufe, L. A. (2005). Attachment and development: a prospective, longitudinal study from birth to adulthood. Attachment and Human Development, 7, 349–367.
Sroufe, L. A., & Rutter, M. (1984). The domain of developmental psychopathology. Child Development, 55, 17–29.
Tarabulsy, G. M., Provost, M. A., Larose, S., Moss, E., Lemelin, J.-P., Moran, G., & Pederson, D. R. (2008). Similarities and differences in mothers’ and observers’ ratings of infant security on the Attachment Q-Sort. Infant Behavior and Development, 31, 10–22.
Teti, D. M., Nakagawa, M., Das, R., & Wirth, O. (1991). Security of attachment between preschoolers and their mothers: relations among social interaction, parenting stress, and mother’s sorts of the attachment Q-Set. Developmental Psychology, 27, 440–447. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.27.3.440.
Tietjen, A. M., & Bradley, C. F. (1985). Social support and maternal psychosocial adjustment during the transition to parenthood. Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science/Revue Canadienne des Sciences du Comportement, 17, 109–121. doi:10.1037/h0080136.
van Doesum, K. T., Hosman, C. M., Riksen-Walraven, J. M., & Hoefnagels, C. (2007). Correlates of depressed mothers’ sensitivity toward their infants: the role of maternal, child, and contextual characteristics. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 46, 747–756. doi:10.1097/CHI.0b013e318040b272.
Van IJzendoorn, M. H., Vereijken, C. M. J. L., Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., & Riksen-Walraven, J. M. (2004). Assessing attachment security with the attachment Q-sort: meta-analytic evidence for the validity of the observer AQS. Child Development, 75, 1188–1213. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8624.2004.00733.x.
Weissman, M. M., Wickramaratne, P., Nomura, Y., Warner, V., Verdeli, H., Pilowsky, D. J., & Bruder, G. (2005). Families at high and low risk for depression - A 3-generation study. Archives of General Psychiatry, 62, 29–36.
Wetter, E. K., & El-Sheikh, M. (2012). Trajectories of children’s internalizing symptoms: the role of maternal internalizing symptoms, respiratory sinus arrhythmia and child sex. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 53, 168–177. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2011.02470.x.
Wilens, T. E., Biederman, J., Brown, S., Monuteaux, M., Prince, J., & Spencer, T. J. (2002). Patterns of psychopathology and dysfunction in clinically referred preschoolers. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics, 23(Suppl), S31–S36.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Émilie Rochette, Nadine Marzougui, Natasha Ballen, Natasha Whipple, Isabelle Demers, Jessica Laranjo, Véronique Jarry-Boileau, Marie Deschênes, Célia Matte-Gagné, Stéphanie Bordeleau, Marie-Ève Bélanger, Christine Gagné, Sarah Hertz, Marie-Soleil Sirois, Émilie Tétreault, and Rachel Perrier for help with data collection. Special thanks go to the participating families of the Grandir Ensemble project who generously opened their homes to us.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The authors declared that they had no conflicts of interest with respect to their authorship or the publication of this article.
Funding
The research described in this article was supported by grants from the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada (410-2010-1366), the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (MOP-119390), and the Fonds Québécois de Recherche sur la Société et la Culture (2012-RP-144923) to Annie Bernier.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouvette-Turcot, AA., Bernier, A. & Leblanc, É. Maternal Psychosocial Maladjustment and Child Internalizing Symptoms: Investigating the Modulating Role of Maternal Sensitivity. J Abnorm Child Psychol 45, 157–170 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-016-0154-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-016-0154-8