Abstract
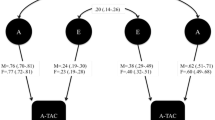
A genetically informed cross-lagged model was applied to twin data to explore etiological links between autistic-like traits and affective problems in early childhood. The sample comprised 310 same-sex twin pairs (143 monozygotic and 167 dizygotic; 53 % male). Autistic-like traits and affective problems were assessed at ages 2 and 3 using parent ratings. Both constructs were related within and across age (r = 0.30–0.53) and showed moderate stability (r = 0.45–0.54). Autistic-like traits and affective problems showed genetic and environmental influences at both ages. Whereas at age 2, the covariance between autistic-like traits and affective problems was entirely due to environmental influences (shared and nonshared), at age 3, genetic factors also contributed to the covariance between constructs. The stability paths, but not the cross-lagged paths, were significant, indicating that there is stability in both autistic-like traits and affective problems but they do not mutually influence each other across age. Stability effects were due to genetic, shared, and nonshared environmental influences. Substantial novel genetic and nonshared environmental influences emerge at age 3 and suggest change in the etiology of these constructs over time. During early childhood, autistic-like traits tend to occur alongside affective problems and partly overlapping genetic and environmental influences explain this association.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T. M., & Rescorla, L. A. (2000). Manual for the ASEBA Preschool Forms & Profiles. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, & Families.
American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed., ). Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing.
Baird, G., Simonoff, E., Pickles, A., Chandler, S., Loucas, T., Meldrum, D., & Charman, T. (2006). Prevalence of disorders of the autism spectrum in a population cohort of children in south Thames: the special needs and autism project (SNAP). Lancet, 368, 210–215. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69041-7.
Bolton, P. F., Pickles, A., Murphy, M., & Rutter, M. (1998). Autism, affective and other psychiatric disorders: patterns of familial aggregation. Psychological Medicine, 28, 385–395. doi:10.1017/S0033291797006004.
Boomsma, D. I., Van Beijsterveldt, C. E. M., & Hudziak, J. J. (2005). Genetic and environmental influences on anxious/depression during childhood: a study from The Netherlands twin register. Brain and Behavior, 4, 466–481.
Burt, S. A., McGue, M., Krueger, R. F., & Iacono, W. G. (2005). How are parent-child conflict and childhood externalizing symptoms related over time? Results from a genetically informative cross-lagged study. Development and Psychopathology, 17, 145–165. doi:10.1017/S095457940505008X.
Colvert, E., Tick, B., McEwen, F., Stewart, C., Curran, S. R., Woodhouse, E.,... Bolton, P. (2015). Heritability of autism spectrum disorder in a UK population-based twin sample. JAMA Psychiatry. doi 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.3028
Curran, S., Dworzynski, K., Happé, F., Ronald, A., Allison, C., Baron-Cohen, S.,... Bolton, P. F. (2011). No major effect of twinning on autistic traits. Autism Research, 4, 377–382. doi: 10.1002/aur.207
Dekker, M. C., Ferdinand, R. F., Van Lang, N. D., Bongers, I. L., Van Der Ende, J., & Verhulst, F. C. (2007). Developmental trajectories of depressive symptoms from early childhood to late adolescence: gender differences and adult outcome. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 48, 657–666. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2007.01742.x.
Evans, D. M., & Martin, N. G. (2000). The validity of twin studies. Genescreen, 1, 77–79.
Gau, J. S., Silberg, J. L., Erickson, M. T., & Hewitt, J. K. (1992). Childhood behavior problems: a comparison of twin and non-twin samples. Acta Geneticae Medicae Et Gemellologiae: Twin Research, 41, 53–63.
Hallett, V., Ronald, A., Rijsdijk, F., & Happé, F. (2010). Association of autistic-like and internalizing traits during childhood: a longitudinal twin study. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 167, 809–817. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2009.09070990.
Hollingshead, A. B. (1975). The four-factor index of social status. Yale University, New Haven, CT: Unpublished manuscript.
Holmboe, K., Rijsdijk, F. V., Hallett, V., Happé, F., Plomin, R., & Ronald, A. (2014). Strong genetic influences on the stability of autistic traits in childhood. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 53, 221–230. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2013.11.001.
Kim, J. A., Szatmari, P., Bryson, S. E., Streiner, D. L., & Wilson, F. J. (2000). The prevalence of anxiety and mood problems among children with autism and Asperger syndrome. Autism, 4, 117–132. doi:10.1177/1362361300004002002.
Lainhart, J. E., & Folstein, S. E. (1994). Affective disorders in people with autism: a review of published cases. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 24, 587–601. doi:10.1007/BF02172140.
Lake, J. K., Perry, A., & Lunsky, Y. (2014). Mental health services for individuals with high functioning autism spectrum disorder. Autism Research and Treatment, 2014, 502420. doi:10.1155/2014/502420.
Larsson, H., Viding, E., Rijsdijk, F. V., & Plomin, R. (2008). Relationships between parental negativity and child antisocial behavior over time: a bidirectional effects model in a longitudinal genetically informative design. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 36, 633–645. doi:10.1007/s10802-007-9151-2.
Lau, J. F., & Eley, T. C. (2006). Changes in genetic and environmental influences on depressive symptoms across adolescence and young adulthood. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 189, 422–427. doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.105.018721.
Lee, S. H., Ripke, S., Neale, B. M., Faraone, S. V., Purcell, S. M., Perlis, R. H.,... Wray, N. R. (2013). Genetic relationship between five psychiatric disorders estimated from genome-wide SNPs. Nature Genetics, 45, 984–994. doi: 10.1038/ng.2711
Lundstrom, S., Chang, Z., Kerekes, N., Gumpert, C. H., Rastam, M., Gillberg, C.,... Anckarsater, H. (2011). Autistic-like traits and their association with mental health problems in two nationwide twin cohorts of children and adults. Psychological Medicine, 41, 2423–2433. doi: 10.1017/S0033291711000377
Lundstrom, S., Chang, Z., Rastam, M., Gillberg, C., Larsson, H., Anckarsater, H., & Lichtenstein, P. (2012). Autism spectrum disorders and autistic like traits: similar etiology in the extreme end and the normal variation. Archives of Genetic Psychiatry, 69, 46–52. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.144.
Man, K. C., Tong, H. Y., Wong, L. L., Chan, E. W., Simonoff, E., & Wong, I. K. (2015). Exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors during pregnancy and risk of autism spectrum disorder in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 4982-4989. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.11.020.
McGue, M., & Bouchard, T. J. (1984). Adjustment of twin data for the effects of age and sex. Behavior Genetics, 14, 325–343. doi:10.1007/BF01080045.
Muratori, F., Narzisi, A., Tancredi, R., Cosenza, A., Calugi, S., Saviozzi, I., &... Calderoni, S. (2011). The CBCL 1.5–5 and the identification of preschoolers with autism in Italy. Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences, 20, 329–338. doi:10.1017/S204579601100045X
Najman, J. M., Williams, G. M., Nikles, J., Spence, S., Bor, W., O'Callaghan, M.,... Shuttlewood, G. J. (2001). Bias influencing maternal reports of child behaviour and emotional state. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 36, 186–194.
Narzisi, A., Calderoni, S., Maestro, S., Calugi, S., Mottes, E., & Muratori, F. (2013). Child behavior checklist 1½–5 as a tool to identify toddlers with autism spectrum disorders: a case-control study. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 34, 1179–1189. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2012.12.020.
Neale, M. C., Boker, S. M., Xie, G., & Maes, H. H. (2006). Mx: Statistical modeling (7th ed.) [Computer software]. Richmond, VA: Department of Psychiatry, Virginia Commonwealth University
Nivard, M. G., Dolan, C. V., Kendler, K. S., Kan, K. J., Willemsen, G., van Beijsterveldt, C. E.,... Boomsma, D. I. (2014). Stability in symptoms of anxiety and depression as a function of genotype and environment: a longitudinal twin study from ages 3 to 63 years. Psychological Medicine, 1-11. doi: 10.1017/S003329171400213X
Pickles, A., Rowe, R., Simonoff, E., Foley, D., Rutter, M., & Silberg, J. (2001). Child psychiatric symptoms and psychosocial impairment: relationship and prognostic significance. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 179, 230–235. doi:10.1192/bjp.179.3.230.
Piven, J., Gayle, J., Chase, G. A., Fink, B., Landa, R., Wzorek, M. M., & Folstein, S. E. (1990). A family history study of neuropsychiatric disorders in the adult siblings of autistic individuals. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 29, 177–183. doi:10.1097/00004583-199003000-00004.
Piven, J., Chase, G. A., Landa, R., Wzorek, M., Gayle, J., Cloud, D., & Folstein, S. (1991). Psychiatric disorders in the parents of autistic individuals. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 30, 471–478. doi:10.1097/00004583-199105000-00019.
Plomin, R., Haworth, C. M., & Davis, O. S. (2009). Common disorders are quantitative traits. Nature Reviews Genetics, 10, 872–878. doi:10.1038/nrg2670.
Posthuma, D., & Polderman, T. J. (2013). What have we learned from recent twin studies about the etiology of neurodevelopmental disorders? Current Opinion in Neurology, 26, 111–121. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e32835f19c3.
Price, T. S., Freeman, B., Craig, L., Ebersole, L., & Plomin, R. (2000). Infant zygosity can be assigned by parent questionnaire data. Twin Research, 3, 129–133. doi:10.1375/twin.3.3.129.
Rijsdijk, F., & Sham, P. (2002). Analytic approaches to twin data using structural equation models. Bioinformatics, 3, 119–133.
Robinson, E. B., Koenen, K. C., McCormick, M. C., Munir, K., Hallett, V., Happé, F.,... Ronald, A. (2011). Evidence that autistic traits show the same etiology in the general population and at the quantitative extremes (5 %, 2.5 %, and 1 %). Archives of Genetic Psychiatry, 68, 1113–1121. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.119
Ronald, A., & Hoekstra, R. A. (2011). Autism spectrum disorders and autistic traits: a decade of new twin studies. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics, 156B, 255–274. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.31159.
Ronald, A., Happé, F., Bolton, P., Butcher, L. M., Price, T. S., Wheelwright, S.,... Plomin, R. (2006). Genetic heterogeneity between the three components of the autism spectrum: a twin study. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 45, 691–699. doi: 10.1097/01.chi.0000215325.13058.9d
Ronald, A., Simonoff, E., Kuntsi, J., Asherson, P., & Plomin, R. (2008). Evidence for overlapping genetic influences on autistic and ADHD behaviours in a community twin sample. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 49, 535–542.
Ronald, A., Edelson, L. R., Asherson, P., & Saudino, K. J. (2010). Exploring the relationship between autistic-like traits and ADHD behaviors in early childhood: findings from a community twin study of 2-year-olds. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 38, 185–196. doi:10.1007/s10802-009-9366-5.
Sikora, D. M., Hall, T. A., Hartley, S. L., Gerrard-Morris, A. E., & Cagle, S. (2008). Does parent report of behavior differ across ADOS-G classifications: analysis of scores from the CBCL and GARS. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38, 440–448. doi:10.1007/s10803-007-0407-z.
Simonoff, E., Pickles, A., Charman, T., Chandler, S., Loucas, T., & Baird, G. (2008). Psychiatric disorders in children with autism spectrum disorders: prevalence, comorbidity, and associated factors in a population-derived sample. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 47, 921–929. doi:10.1097/CHI.0b013e318179964f.
Smoller, J. W., Craddock, N., Kendler, K., Lee, P. H., Neale, B. M., Nurnberger, J. I.,... Sullivan, P. F. (2013). Identification of risk loci with shared effects on five major psychiatric disorders: a genome-wide analysis. Lancet, 381, 1371–1379. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)62129-1
St Pourcain, B. Skuse, D. H. Mandy, W. P. Wang, K. Hakonarson, H. Timpson, N. J.,... Smith, G. D. (2014). Variability in the common genetic architecture of social-communication spectrum phenotypes during childhood and adolescence. Molecular Autism, 5, 18. doi: 10.1186/2040-2392-5-18
Stilp, R. H., Gernsbacher, M. A., Schweigert, E. K., Arneson, C. L., & Goldsmith, H. H. (2010). Genetic variance for autism screening items in an unselected sample of toddler-age twins. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 49, 267–276. doi:10.1097/00004583-201003000-00010.
Waszczuk, M. A., Zavos, H. M., Gregory, A. M., & Eley, T. C. (2014). The phenotypic and genetic structure of depression and anxiety disorder symptoms in childhood, adolescence, and young adulthood. JAMA Psychiatry, 71, 905–916. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.655.
Yang, J., Lee, S. H., Goddard, M. E., & Visscher, P. M. (2011). GCTA: a tool for genome-wide complex trait analysis. American Journal of Human Genetics, 88, 76–82. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.11.011.
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by grants R01 HD068435 and R01 MH062375 from the National Institutes of Health to Dr. Saudino.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Compliance with Ethical Standards
ᅟ
Conflict of Interest
There are no conflicts of interest to report.
Additional information
Lauren Micalizzi and Angelica Ronald joint first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Micalizzi, L., Ronald, A. & Saudino, K.J. A Genetically Informed Cross-Lagged Analysis of Autistic-Like Traits and Affective Problems in Early Childhood. J Abnorm Child Psychol 44, 937–947 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-015-0088-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-015-0088-6