Abstract
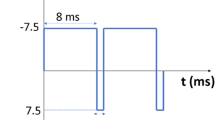
Amorphous Ni–P coating generates great internal stress in the process of electrodeposition due to hydrogen evolution and internal chaotic structure, thus forming surface micro-cracks and decreasing the corrosion resistance. In this study, the amorphous Ni–P coating with three-dimensional (3D) morphology was electrodeposited using a solution containing the crystal modifier induced by laser irradiation. The results show that with increasing temperature and electrochemical deposition (ECD) time, the impact of the crystal modifier on the surface morphology became more significant. The roughness (Rz) value of the coating prepared by ECD (ECDed, 10 min) was 0.76 μm, whereas that of the coating prepared by laser-assisted ECD (LECD) (LECDed, 20 μJ, 10 min) was 2.97 μm. Meanwhile, the coating immediately exhibited hydrophobic properties, and the contact angle (CA, water) reached 112° ± 2°. After electrochemical corrosion, the surface was still hydrophobic, and the CA was 113° ± 2° when the laser single pulse energy was 20 μJ. The results of Tafel analysis and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy indicated that hydrophobic surfaces with a 3D microstructure have better corrosion resistance. This is because that the 3D surface morphology replaces the cracks to improve corrosion mode.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suryanarayana C, Koch C (2000) Nanocrystalline materials-current research and future directions. Hyperfine Interact 130:5–44. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011026900989
Kumar K, SwygenhovDen HV, Suresh S (2003) Mechanical behavior of nanocrystalline metals and alloys. Acta Mater 51:743–5774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2003.08.032
Trudeau M, Ying J (1996) Nanocrystalline materials in catalysis and electrocatalysis: structure tailoring and surface reactivity. Nanostructured Mater 7:245–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/0965-9773(95)00308-8
Gleiter H (1989) Nanocrystalline Materials. Progress in Materials Science, vol 33. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 223–315
Gutfleisch O, WiIlard MA, Brück E, Sankar CCH (2011) Magnetic materials and devices for the 21st century: stronger, lighter, and more energy efficient. Adv Mater 23:821–842. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201002180
Inoue A, Takeuchi A, Makino A, Masumoto T (1996) Soft and hard magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Fe-MB (M= Zr, Nd) base alloys containing intergranular amorphous phase. Sci Rep Res Inst Tohoku Univ Ser A Phys Chem Metall 42:143–156
Zhang H, Fornell J, Feng Y, Golvano I, Baró MD, Pellicer E, Sort J (2019) Inducing surface nanoporosity on Fe-based metallic glass matrix composites by selective dealloying. Mater Char 153:46–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2019.04.025
Tan C, Zhu H, Kuang T, Shi J, Liu H, Liu Z (2017) Laser cladding AI-based amorphous-nanocrystalline composite coatings on AZ80 magnesium alloy under water cooling condition. J Alloy Compd 690:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.08.082
Wang S, Zhang Z, Gong Y, Nie G (2017) Microstructures and corrosion resistance of Fe-based amorphous/nanocrystalline coating fabricated by laser cladding. J Alloy Compd 728:1116–1123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.08.251
Bekish YN, Poznyak S, Tsybulskaya L, Gaevskaya T (2010) Electrodeposited Ni-B alloy coatings: structure, corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. Electrochim Acta 55:2223–2231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2009.11.069
Zhang ZY, Jiang YJ, Huang L, Nie X, Liu G (2017) Experiment study of laser thermal enhanced electrochemical deposition. Microsyst Technol 23:1695–1701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2759-1
Zouari I, Pierre C, Lapicque F, Calvo M (1993) Maskless zinc electrodeposition assisted by a pulsed laser beam. J Appl Electrochem 23:863–872. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00251021
Yu ZL, Meng XD, Hu Y, Yin M, Yang PX, Li HB (2017) Pulsed laser irradiation-assisted electrodeposition of germanium in ionic liquid: from amorphous film to polycrystalline branched structures. Mater Res Bull 93:208–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.05.008
Cho CH, Shin HS, Chua CN (2013) Selective electrodeposition of copper on stainless steel using laser irradiation. Surf Coat Technol 222:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2013.01.046
Wu YC, Zhang ZZ, Xu K, Lu JZ, Wang AB, Dai XR, Zhu H (2021) A study on the formation conditions of amorphous nickel-phosphorus (Ni-P)alloy by laser-assisted electrodeposition. Appl Surf Sci 535:14707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147707
Wu YC, Xu K, Zhang ZZ, Guo S, Dai XR, Gao J, Zhu H (2021) Study on application of laser in maskless localized electrodeposition and surface quality enhancement. Opt Laser Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2021.107383
Wu YC, Zhang ZZ, Xu K, Lu JZ, Dai XR, Zhu H, Yang S (2021) Effect of laser single pulse energy on micro-structural, mechanical and corrosion properties of amorphous Ni-Fe-P alloy prepared by laser-assisted electrodeposition. Surf Interfaces. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2020.100811
Daly BP, Barry FJ (2003) Electrochemical nickel-phosphorus alloy formation. Int Mater Rev 48:326–338. https://doi.org/10.1179/095066003225008482
Pillai AM, Rajendra A, Sharma AK (2012) Electrodeposited nickel-phosphorous (Ni-P) alloy coating: an in-depth study of its preparation, properties, and structural transitions. J Coat Technol Res 9:785–797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-012-9411-0
Armstrong R, Fleischmann M, Thirsk H (1966) Anodic behaviour of mercury in hydroxide ion solutions. J Electroanal Chem 11:208–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0728(66)80083-9
Ehsan R, Ali R, Amin I, Ali RKR, Saman H, Ali D (2019) Synergistic effect of a crystal modifier and screw dislocation step defects on the formation mechanism of nickel micro-nanocone. Mater Lett 245:68–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.02.093
Darband GB, Aliofkhazraei M, Dolati A, Rouhaghdam AS (2020) Electrocrystallization of Ni nanocones from chloride-based bath using crystal modifier by electrochemical methods. J Alloy Compd 818:152843
Chen Z, Tian FF, Hu AM, Li M (2013) A facile process for preparing superhydrophobic nickel films with stearic acid. Surf Coat Technol 231:99–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2012.01.053
Hang T, Hu AM, Ling HQ, Li M, Mao DL (2010) Super-hydrophobic nickel films with micro-nano hierarchical structure prepared by electrodeposition. Appl Surf Sci 256:2400–2404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.10.074
Tu ZM, An MZ, Hu H (2016) Modern Theory and Technology of Alloy Electrodeposition. National Defense Industry Press, Beijing
Yang Y, Gu HJ, Zhang QX, Zhang F, Li H (2021) Hollow Ni-p amorphous alloy nanospheres: an efficient catalyst for sugars hydrogenation to polyols. Catal Today 365:282–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2020.04.031
Bewick A, Fleischmann M, Thirsk H (1962) Kinetics of the electrocrystallization of thin fìlms of calomel. Trans Faraday Soc 58:2200–2216. https://doi.org/10.1039/TF9625802200
Lin CS, Lee CY, Chen FJ, Li WC (2008) Structural evolution and internal stress of nickel-phosphorus electrodeposits. J Electrochem Soc 152:C370–C375. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1901064
Bai A, Chuang PY, Hu CC (2003) The corrosion behavior of Ni–P deposits with high phosphorous contents in brine media. Mater Chem Phys 82:93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0254-0584(03)00193-7
Splinter SJ, Rofagha R, McIntyre NS, Erb U (1996) XPS characterization of the corrosion films formed on nanocrystalline Ni-P alloys in sulphuric acid. Surf Interface Anal 24:181–186. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9918(199603)24:3%3c181::AID-SIA92%3e3.0.CO;2-N
Królikowski A, Butkiewicz P (1993) Anodic behavior of NiP alloys studied by impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim Acta 38:1979–1983. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4686(93)80327-V
Wang XY, Lin ZB (2021) Robust, hydrophobic anti-corrosion coating prepared by PDMS modified epoxy composite with graphite nanoplatelets/nano-silica hybrid nanofillers. Surf Coat Technol 421:127440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127440
Chen HY, Fan HZ, Su N, Hong RY, Lu XS (2021) Highly hydrophobic polyaniline nanoparticles for anti-corrosion epoxy coatings. Chem Eng J 420:130540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130540
Ma K, Wang QBY (2021) Understanding the Impedance of CNOs-Graphene hybrid electrode through both experimental and simulated electrochemical impedance spectrum. Electrochim Acta 371:137839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2021.137839
Tanno M, Ogawa K, Shoji T (2010) Influence of asymmetric electrode geometry on an impedance spectrum of a plasma-sprayed thermal barrier coating system. Surf Coat Technol 204:2504–2509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2010.01.030
Moradi M, Ghiara G, Spotorno R, Xu D, Cristiani P (2022) Understanding biofilm impact on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analyses in microbial corrosion and microbial corrosion inhibition phenomena. Electrochim Acta 486:14803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2022.140803
Rouabhia F, Hamlaoui Y, Meroufel A, Pedraza F (2021) Corrosion properties of ceria-based coating electrodeposited from alkaline bath on electrogalvanized steel. J Appl Electrochem 51:567–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-020-01517-x
Zhang ZZ, Gu QM, Jiang W, Zhu H, Xu K, Ren YP, Xu C (2019) Achieving of bionic super-hydrophobicity by electrodepositing nano-Nipyramids on the picosecond laser-ablated micro-Cu-cone surface. Surf Coat Technol 363:170–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.02.037
Bhattacharya P, Gohil S, Mazher J, Ghosh S, Ayyub P (2008) Universal, geometry-driven hydrophobic behaviour of bare metal nanowire clusters. Nanotechonology 19:075709. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/19/7/075709
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52075227, 52105449, and 51905226), Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (2021K264B), Chinese Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Nos. 2018M640461 and 2019T120392), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20210755), and Natural Science Research Project of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (21KJB460014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Jian Gao: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing-original draft, Writing-review & editing. Yucheng Wu: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Writing-review & editing. Xueren Dai: Methodology, Investigation, Supervision, Validation, Writing-review & editing. Zhaoyang Zhang: Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Project administration, Validation, Writing-review & editing. Douyan Zhao: Investigation, Methodology. Hao Zhu: Funding acquisition, Formal analysis, Writing-review & editing. Kun Xu: Funding acquisition, Resources, Investigation. Yang Liu: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, J., Wu, Y., Dai, X. et al. Corrosion behavior of electrodeposited amorphous Ni–P coating by laser-induced crystal modifier. J Appl Electrochem 52, 1647–1658 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-022-01740-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-022-01740-8