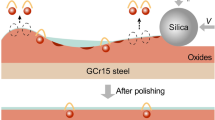
Abstract
Potassium persulfate was used as an effective oxidizer for chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) of GCr15 steel. The effects of pH, potassium persulfate content and chelating agents on the CMP performance of GCr15 steel were investigated, and the surface films formed in the potassium persulfate-based slurries were characterized accordingly. It is revealed experimentally that, with pH increasing from 2.0 to 9.0, the material removal rate (MRR) is independent of pH while the surface roughness Ra decreases. At pH 8.0, as the potassium persulfate content increases, the MRR linearly increases with a slope of 48 nm min−1 mM−1, but the surface quality continues to deteriorate accompanied with the black Fe3O4 residue due to the severe corrosion by persulfate. In particular, Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions are continuously produced by oxidation of persulfate, and a significant part of Fe2+ and Fe3+ further reacts with OH− to form a non-uniform and rough surface film which primarily consists of Fe3O4. After adding an appropriate chelating agent EDTA, the Ra reaches 1.7 nm without any black residue due to the chelation reactions between iron ions and EDTA. The findings suggest that a nano-precision surface finish of bearing steel could be achieved at weakly alkaline pH with persulfate-based slurries.
Graphic abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yin F, Hua L, Mao H, Han X (2013) Constitutive modeling for flow behavior of GCr15 steel under hot compression experiments. Mater Des 43:393–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2012.07.009
Sihag N, Kala P, Pandey PM (2015) Chemo Assisted Magnetic Abrasive Finishing: Experimental Investigations. Procedia CIRP 26:539–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2014.07.067
Komata H, Iwanaga Y, Ueda T, Ueda K, Mitamura N (2015) In: Beswick J (ed) Enhanced performance of rolling bearings by improving the resistance of rolling elements to surface degradation. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, pp 272–290. https://doi.org/10.1520/STP158020140085
Chi X, Suo XH (2011) Study on float polishing of metal nanometer surface. Adv Mater Res 154–155:1757–1760. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.154-155.1757
Li Y (2007) Microelectronic applications of chemical mechanical planarization. John Wiley & Sons Inc, Hoboken
Zhao D, Lu X (2013) Chemical mechanical polishing: theory and experiment. Friction 1(4):306–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40544-013-0035-x
Peng D-X (2014) Chemical mechanical polishing of steel substrate using aluminum nanoparticles abrasive slurry. Ind Lubr Tribol 66(1):124–130. https://doi.org/10.1108/ILT-10-2011-0078
Peng D-X (2014) Optimization of chemical mechanical polishing parameters on surface roughness of steel substrate with aluminum nanoparticles via Taguchi approach. Ind Lubr Tribol 66(6):685–690. https://doi.org/10.1108/ILT-07-2012-0063
Jiang L, He Y, Luo J (2015) Chemical mechanical polishing of steel substrate using colloidal silica-based slurries. Appl Surf Sci 330:487–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.01.016
Kao MJ, Hsu FC, Peng DX (2014) Synthesis and characterization of SiO2 nanoparticles and their efficacy in chemical mechanical polishing steel substrate. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2014:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/691967
House DA (1962) Kinetics and mechanism of oxidations by peroxydisulfate. Chem Rev 62(3):185–203. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr60217a001
Kanki T, Shirasu T, Takesako S, Sakamoto M, Asneil AA, Idani N, Kimura T, Nakamura T, Miyajima M (2008) On the elements of high throughput Cu-CMP slurries compatible with low step heights. In: 2008 international interconnect technology conference, 1–4 June 2008. pp 79–81. https://doi.org/10.1109/IITC.2008.4546931
Wei Z, Xinchun L, Yuhong L, Guoshun P, Jianbin L (2009) Effect of pH on material removal rate of Cu in abrasive-free polishing. J Electrochem Soc 156(3):H176–H180. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.3055985
Kanki T, Kimura T, Nakamura T (2013) Chemical and mechanical properties of Cu surface reaction layers in Cu-CMP to improve planarization. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 2(9):P375–P379. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.023309jss
Ranaweera CK, Baradanahalli NK, Popuri R, Seo J, Babu SV (2019) Ammonium persulfate and potassium oleate containing silica dispersions for chemical mechanical polishing for cobalt interconnect applications. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 8(5):P3001–P3008. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0021905jss
Tamilmani S, Huang W, Raghavan S, Small R (2002) Potential-pH diagrams of interest to chemical mechanical planarization of copper. J Electrochem Soc 149(12):G638–G642. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1516224
Beverskog B, Puigdomenech I (1996) Revised pourbaix diagrams for iron at 25–300 °C. Corros Sci 38(12):2121–2135. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-938X(96)00067-4
Liu X, Liu Y, Liang Y, Liu H, Zhao Z, Gao B (2011) Effect of slurry components on chemical mechanical polishing of copper at low down pressure and a chemical kinetics model. Thin Solid Films 520(1):400–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2011.06.050
Mufti N, Atma T, Fuad A, Sutadji E (2014) Synthesis and characterization of black, red and yellow nanoparticles pigments from the iron sand. AIP Conf Proc 1617(1):165–169. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4897129
Blesa MA, Borghi EB, Maroto AJG, Regazzoni AE (1984) Adsorption of EDTA and iron—EDTA complexes on magnetite and the mechanism of dissolution of magnetite by EDTA. J Colloid Interface Sci 98(2):295–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9797(84)90155-3
Gorantla VRK, Goia D, Matijević E, Babu SV (2005) Role of amine and carboxyl functional groups of complexing agents in slurries for chemical mechanical polishing of copper. J Electrochem Soc 152(12):G912–G916. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2083287
Kim YJ, Kwon OJ, Kang MC, Kim JJ (2011) Effects of the functional groups of complexing agents and Cu oxide formation on Cu dissolution behaviors in Cu CMP process. J Electrochem Soc 158(2):H190–H196. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.3522811
Martell AE, Motekaitis RJ, Chen D, Hancock RD, McManus D (1996) Selection of new Fe(III)/Fe(II) chelating agents as catalysts for the oxidation of hydrogen sulfide to sulfur by air. Can J Chem 74(10):1872–1879. https://doi.org/10.1139/v96-210
Wu H, Jiang L, Liu J, Deng C, Huang H, Qian L (2020) Efficient chemical mechanical polishing of AISI 52100 bearing steel with TiSol-NH4 dispersion-based slurries. Tribol Lett 68(1):34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-020-1274-4
Wu W, Hao WK, Liu ZY, Li XG, Du CW, Liao WJ (2015) Corrosion behavior of E690 high-strength steel in alternating wet-dry marine environment with different pH values. J Mater Eng Perform 24(12):4636–4646. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1781-x
Hussain I, Zhang Y, Huang S, Du X (2012) Degradation of p-chloroaniline by persulfate activated with zero-valent iron. Chem Eng J 203:269–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.06.120
Bremner DH, Burgess AE, Houllemare D, Namkung K-C (2006) Phenol degradation using hydroxyl radicals generated from zero-valent iron and hydrogen peroxide. Appl Catal B 63(1):15–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2005.09.005
Beyaz S, Kockar H, Tanrisever T (2009) Simple synthesis of superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles and ion effect on magnetic fluids. J Optoelectron Adv Mater Symp 1(3):447–450
Li H, Wan J, Ma Y, Huang M, Wang Y, Chen Y (2014) New insights into the role of zero-valent iron surface oxidation layers in persulfate oxidation of dibutyl phthalate solutions. Chem Eng J 250:137–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.03.092
Christian GD, Dasgupta PK, Schug KA (2013) Analytical chemistry, 7th edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Kissi M, Bouklah M, Hammouti B, Benkaddour M (2006) Establishment of equivalent circuits from electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study of corrosion inhibition of steel by pyrazine in sulphuric acidic solution. Appl Surf Sci 252(12):4190–4197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2005.06.035
Song Y, Shan D, Chen R, Han E-H (2009) Investigation of surface oxide film on magnesium lithium alloy. J Alloys Compd 484(1):585–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.04.137
Song Y, Shan D, Chen R, Zhang F, Han E-H (2009) Biodegradable behaviors of AZ31 magnesium alloy in simulated body fluid. Mater Sci Eng C 29(3):1039–1045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2008.08.026
Fernández Macía L, Petrova M, Hubin A (2015) ORP-EIS to study the time evolution of the [Fe(CN)6]3-/[Fe(CN)6]4- reaction due to adsorption at the electrochemical interface. J Electroanal Chem 737:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2014.10.032
Liu C, Bi Q, Leyland A, Matthews A (2003) An electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study of the corrosion behaviour of PVD coated steels in 0.5 N NaCl aqueous solution: Part II.: EIS interpretation of corrosion behaviour. Corros Sci 45(6):1257–1273. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-938X(02)00214-7
Yamashita T, Hayes P (2008) Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials. Appl Surf Sci 254(8):2441–2449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.09.063
Zhu H, Cao F, Zuo D, Zhu L, Jin D, Yao K (2008) A new hydrothermal blackening technology for Fe3O4 coatings of carbon steel. Appl Surf Sci 254(18):5905–5909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.03.184
Hawn DD, DeKoven BM (1987) Deconvolution as a correction for photoelectron inelastic energy losses in the core level XPS spectra of iron oxides. Surf Interface Anal 10(2–3):63–74. https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.740100203
Stoch J, Gablankowska-Kukucz J (1991) The effect of carbonate contaminations on the XPS O 1s band structure in metal oxides. Surf Interface Anal 17(3):165–167. https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.740170308
Horváth D, Toth L, Guczi L (2000) Gold nanoparticles: effect of treatment on structure and catalytic activity of Au/Fe2O3 catalyst prepared by co-precipitation. Catal Lett 67(2):117–128. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019073723384
Cheng F-Y, Su C-H, Yang Y-S, Yeh C-S, Tsai C-Y, Wu C-L, Wu M-T, Shieh D-B (2005) Characterization of aqueous dispersions of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Biomaterials 26(7):729–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.03.016
Lin T-C, Seshadri G, Kelber JA (1997) A consistent method for quantitative XPS peak analysis of thin oxide films on clean polycrystalline iron surfaces. Appl Surf Sci 119(1):83–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-4332(97)00167-0
Allen GC, Curtis MT, Hooper AJ, Tucker PM (1974) X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy of iron–oxygen systems. J Chem Soc Dalton Trans 14:1525–1530. https://doi.org/10.1039/DT9740001525
Qin Z, Luo Q, Zhang Q, Wu Z, Liu L, Shen B, Hu W (2018) Improving corrosion resistance of nickel-aluminum bronzes by surface modification with chromium ion implantation. Surf Coat Technol 334:402–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.11.066
López GP, Castner DG, Ratner BD (1991) XPS O 1s binding energies for polymers containing hydroxyl, ether, ketone and ester groups. Surf Interface Anal 17(5):267–272. https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.740170508
Kaplun M, Sandström M, Boström D, Shchukarev A, Persson P (2005) Crystal structures and spectroscopic properties of palladium complexes isolated from Pd–EDTA solutions. Inorg Chim Acta 358(3):527–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2004.09.027
Atzei D, De Filippo D, Rossi A, Caminiti R (1993) X-ray photoelectron spectra of dinitrogen chelating ligands with some transition metals. Spectrochim Acta Part A 49(12):1779–1785. https://doi.org/10.1016/0584-8539(93)80246-7
Ihnfeldt R, Talbot JB (2008) Effect of CMP slurry chemistry on copper nanohardness. J Electrochem Soc 155(6):H412–H420. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2903293
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51975488, 51991373 and 51605396), National Key R&D Program of China (2020YFA0711001 and 2018YFB2000400), Science Challenge Project (TZ2018006), and Laboratory of Precision Manufacturing Technology CAEP (ZD17005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, T., Jiang, L., Liu, J. et al. Potassium persulfate as an effective oxidizer for chemical mechanical polishing of GCr15 bearing steel. J Appl Electrochem 51, 803–814 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-021-01540-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-021-01540-6