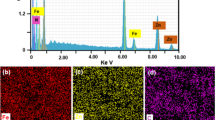
Abstract
ZnO and hematite (Fe2O3) nanoparticles (NPs) have been used as electrocatalysts or electron mediators for the modification of gold (Au) electrode for the detection of toxic compounds, i.e., para-nitrophenol (PNP). A comparison of the two types of NPs reveals higher efficiency for ZnO NPs. Electrochemical response measured by three different techniques, i.e., normal cyclic voltammetry (CV), differential pulse voltammetry (DPV), and amperometry, has been used to determine the sensitivity and detection limit of the system. The order of sensitivity varies in the order: amperometry > DPV > normal CV response, both for ZnO and α-Fe2O3 NPs. While, the order of detection limit for α-Fe2O3 NPs varies as DPV > normal CV > amperometry and for ZnO NPs, the order is normal CV > DPV > amperometry, suggesting that amperometry is the best among all the techniques for detection applications. Based on the electrochemical response, it is proposed that the electrochemical reaction of PNP proceeds via two-step mechanism. In the first step, irreversible reduction of PNP to para-hydroxy nitrophenol takes place with the gain of four electrons and in the second step, reversible redox reaction occurs by the exchange of two electrons, from hydroxy nitrophenol to nitrosophenol and vice versa.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guo X, Wang Z, Zhou S (2004) The separation and determination of nitrophenol isomers by high-performance capillary zone electrophoresis. Talanta 64:135–139
Podeh MRH, Bhattacharya SK, Qu M (1995) Effects of nitrophenols on acetate utilizing methanogenic systems. Water Res 29:391–399
L-Kochany E (1991) Degradation of aqueous nitrophenols and nitrobenzene by means of fenton reaction. Chemosphere 22:529–536
Yin H, Zhou Y, Ai S, Liu X, Zhu L, Lu L (2010) Electrochemical oxidative determination of 4-nitrophenol based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with a hydroxyapatite nanopowder. Microchim Acta 169:87–92
Castillo M, Domingues R, Alpendurada MF, Barcelo D (1997) Persistence of selected pesticides and their phenolic transformation products in natural waters using off-line liquid solid extraction followed by liquid chromatographic techniques. Anal Chim Acta 353:133–142
Niazi A, Yazdanipour A (2007) Spectrophotometric simultaneous determination of nitrophenol isomers by orthogonal signal correction and partial least squares. J Hazard Mater 146:421–427
Padilla-Sánchez JA, Plaza-Bolaňos P, Romero-González R, Garrido-Frenich A, Vidal JLM (2010) Application of a quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe-based method for the simultaneous extraction of chlorophenols, alkylphenols, nitrophenols and cresols in agricultural soils, analyzed by using gas chromatography–triple quadrupole-mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1217:5724–5731
Zhang W, Wilson CR (2008) Indirect fluorescent determination of selected nitro-aromatic and pharmaceutical compounds via UV-photolysis of 2-phenylbenzimidazole-5-sulfonate. Talanta 74:1400–1407
Abaker M, Dar GN, Umar A, Zaidi SA, Ibrahim AA, Baskoutas S, Al-Hajry A (2012) CuO nanocubes based highly-sensitive 4-nitrophenol chemical sensor. Sci Adv Mater 4:893–900
Li J, Kuang D, Feng Y, Zhang F, Xu Z, Liu M (2012) A graphene oxide-based electrochemical sensor for sensitive determination of 4-nitrophenol. J Hazard Mater 201:250–259
Bodewig F, Valenta P, Nurnberg H (1982) Trace determination of As(II) and As(V) in natural waters by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry. Fres Z Anal Chem 311:187–191
Lindsay AE, O’ Hare D (2006) The development of an electrochemical sensor for the determination of cyanide in physiological solutions. Anal Chim Acta 558:158–163
Gil EP, Ostapczuk P (1994) Potentiometric stripping determination of mercury(II), selenium(IV), copper(II) and lead(II) at a gold film electrode in water samples. Anal Chim Acta 293:55–65
Wu Y, Wu A (2000) Taguchi methods for robust design. ASME, New York
Liu J, Chen Y, Guo Y, Yang F, Cheng F (2013) Electrochemical sensor for o-nitrophenol based on β-cyclodextrin functionalized graphene nanosheets. J Nanomater 2013
Tang Y, Huang R, Liu C, Yang LS, Lu ZZ, Luo S (2013) Electrochemical detection of 4-nitrophenol based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with reduced graphene oxide/Au nanoparticle composite. Anal Methods 5:5508–5514
Chu L, Han L, Zhang X (2011) Electrochemical simultaneous determination of nitrophenol isomers at nano-gold modified glassy carbon electrode. J Appl Electrochem 41:687–694
Niaz A, Fischer J, Barek J, Yosypchuk B, Sirajuddin, Bhanger MI (2009) Voltammetric determination of 4-nitrophenol using a novel type of silver amalgam paste electrode. Electroanalysis 21:1786–1791
Casella IG, Contursi M (2007) The electrochemical reduction of nitrophenols on silver globular particles electrodeposited under pulsed potential conditions. J Electrochem Soc 154:D697–D702
Sun W, Yang MX, Jiang Q, Jiao K (2008) Direct electrocatalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol at room temperature ionic liquid modified electrode. Chin Chem Lett 19:1156–1158
Xiong H-M (2013) ZnO nanoparticles applied to bioimaging and drug delivery. Adv Mater 25:5329–5335
Xu G, Yang L, Zhong M, Li C, Lu X, Kan X (2013) Selective recognition and electrochemical detection of p-nitrophenol based on a macroporous imprinted polymer containing gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 180:1461–1469
Li S, Du D, Huang J, Tu H, Yang Y, Zhang A (2013) One-step electrodeposition of a molecularly imprinting chitosan/phenyltrimethoxysilane/AuNPs hybrid film and its application in the selective determination of p-nitrophenol. Analyst 138:2761–2768
Yi Q, Yu W (2009) Electrocatalytic activity of a novel titanium-supported nanoporous gold catalyst for glucose oxidation. Microchim Acta 165:381–386
Kurniawan F, Tsakov V, Mirsky VM (2006) Gold nanoparticles in nonenzymatic electrochemical detection of sugars. Electroanalysis 18:1937–1942
Wang J, Thomas DF, Chen A (2008) Nonenzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on nanoporous PtPb networks. Anal Chem 80:997–1004
Sun Y, Buck H, Mallouk TE (2001) Combinatorial discovery of alloy electrocatalysts for amperometric glucose sensors. Anal Chem 73:1599–1604
Umar A, Hahn YB (2010) Metal oxide nanostructures and their applications. American Scientific Publisher, US
Baskoutas S, Bester G (2011) Transition in the optical emission polarization of ZnO nanorods. J Phys Chem C 115:15862–15867
Chrissanthopoulos A, Baskoutas S, Bouropoulos N, Dracopoulos V, Poulopoulos P, Yannopoulos SN (2011) Synthesis and characterization of ZnO/NiO p–n heterojunctions: ZnO nanorods grown on NiO thin film by thermal evaporation. Photonic Nanostruct 9:132–139
Baskoutas S, Bester G (2010) Conventional optics from unconventional electronics in ZnO quantum dots. J Phys Chem C 114:9301–9307
Fu YY, Wang RM, Xu J, Chen J, Yan Y, Narlikar AV, Zhang H (2003) Synthesis of large arrays of aligned a-Fe2O3 nanowires. Chem Phys Lett 379:373–379
Archibald DD, Mann S (1993) Template mineralization of self assembled anisotropic lipid microstructures. Nature 364:430–433
Wang S-B, Min Y-L, Yu S-H (2007) Synthesis and magnetic properties of uniform hematite nanocubes. J Phys Chem C 111:3551–3554
Cao X, Wang N (2011) A novel non-enzymatic glucose sensor modified with Fe2O3 nanowire arrays. Analyst 136:4241–4246
Adekunle AS, Agboola BO, Pillay J, Ozoemena KI (2010) Electrocatalytic detection of dopamine at single-walled carbon nanotubes–iron(III) oxide nanoparticles platform. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 148:93–102
Jiang L-C, Zhang W-D (2010) A highly sensitive nonenzymatic glucose sensor based on CuO nanoparticles-modified carbon nanotube electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 25:1402–1407
Yu C, Guo J, Gu H (2010) Electrocatalytical oxidation of nitrite and its determination based on Au@Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Electroanalysis 22:1005–1011
Khan SB, Rahman MM, Akhtar K, Asiri AM, Rub MA (2014) Nitrophenol chemi-sensor and active solar photocatalyst based on spinel hetaerolite nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 9(1):e85290. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0085290
Hu YF, Zhang ZH, Zhang HB, Luo LJ, Yao SZ (2012) Sensitive and selective imprinted electrochemical sensor for p-nitrophenol based on ZnO nanoparticles/carbon nanotubes doped chitosan film. Thin Solid Films 520:5314–5321
Mehta SK, Singh K, Umar A, Chaudhary GR, Singh S (2011) Well-crystalline-Fe2O3 nanoparticles for hydrazine chemical sensor application. Sci Adv Mater 3:962–967
Mehta SK, Singh K, Umar A, Chaudhary GR, Singh S (2012) Ultra-high sensitive hydrazine chemical sensor based on low-temperature grown ZnO nanoparticles. Electrochim Acta 69:128–133
Takeuchi ES, Murray RW (1985) Metalloporphyrin containing carbon paste electrodes. J Electroanal Chem 189:49–57
Yaghoubian H, Karimi-Maleh H, Khalilzadeh MA, Karimi F (2009) Electrochemical detection of carbidopa using a ferrocene-modified carbon nanotube paste electrode. J Serb Chem Soc 74:1443–1453
Soderberg JN, Co AC, Sirk AHC, Birss VI (2006) Impact of porous electrode properties on the electrochemical transfer coefficient. J Phys Chem B 110:10401–10410
Nicholson RS, Shain I (1964) Theory of stationary electrode polarography single scan and cyclic methods applied to reversible, irreversible, and kinetic systems. Anal Chem 36:706–723
Yogeswaran U, Chen S-M (2008) A review on the electrochemical sensors and biosensors composed of nanowires as sensing material. Sensors 8:290–313
Liu Z, Du J, Qiu C, Huang L, Ma H, Shen D, Ding Y (2009) Electrochemical sensor for detection of p-nitrophenol based on nanoporous gold. Electrochem Commun 11:1365–1368
Ndlovu T, Arotiba OA, Krause RW, Mamba BB (2010) Electrochemical detection of o-nitrophenol on a poly(propyleneimine)-gold nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode. Int J Electrochem Sci 5:1179–1186
Umar A, Rahman MM, Hahn Y-B (2009) Ultra-sensitive hydrazine chemical sensor based on high-aspect ratio ZnO nanowires. Talanta 77:1376–1380
Topoglidis E, Cass AEG, O’Regan B, Durrant JR (2001) Immobilisation and bioelectrochemistry of proteins on nanoporous TiO2 and ZnO films. J Electroanal Chem 517:20–27
Arcinte A, Mahosenaho M, Pinteala M, Sesay A-M, Virtanen V (2011) Electrochemical oxidation of p-nitrophenol using graphene-modified electrodes, and a comparison to the performance of MWNT-based electrodes. Microchim Acta 174:337–343
Roy AC, Nisha VS, Dhand C, Ali MA, Malhotra BD (2013) Molecularly imprinted polyaniline-polyvinyl sulphonic acid composite based sensor for para-nitrophenol detection. Anal Chim Acta 777:63–71
Zhang WB, Chang JL, Chen JH, Xu F, Wang F, Jiang K, Gao ZY (2012) Graphene–Au composite sensor for electrochemical detection of para-nitrophenol. Res Chem Intermed 38:2443–2455
Acknowledgments
KS and SKM are thankful to Council of Scientific and industrial research (CSIR), India for their financial assistance and fellowships. KS is thankful to Central Instrumental Laboratory (CIL), Panjab University, Chandigarh, India for TEM and XRD measurements. We also thank DST, Govt. of India for financial support under PURSE Grant Phase-II to Panjab University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10800_2014_762_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 1 (DOCX 382 kb) Appendix A. Supplementary data Supplementary data associated with this article can be found in the online version
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, K., Kaur, A., Umar, A. et al. A comparison on the performance of zinc oxide and hematite nanoparticles for highly selective and sensitive detection of para-nitrophenol. J Appl Electrochem 45, 253–261 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-014-0762-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-014-0762-3