Abstract
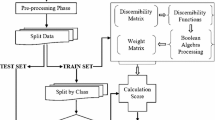
We propose in this paper a rough set based classification technique for real world Web services. The set of Web service quality attributes is reduced to a core set, which represents the most relevant set of attributes. Such reduction is achieved through the analysis of the QWS dataset using rough set theory. The core set is then used during the training phase to derive a minimal set of decision rules. These rules are applied during the classification phase to classify real world Web services into one of four categories: Platinum, Gold, Silver, and Bronze. Our experimental results show that the use of rough set theory to classify QWS services allows to have better classification accuracy results compared to other classification techniques, which have been recently applied on QWS.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Masri, E., & Mahmoud, Q. H. (2007). QoS-based discovery and ranking of Web services. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks (pp. 529–534).
Cong, R., Wang, X., Li, K., & Yang, N. (2010). New method for discretization of continuous attributes in rough set theory. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 21(2), 250–253.
Costa, E., Lorena, A., Carvalho, A., & Freitas, A. (2007). A Review of Performance Evaluation Measures for Hierarchical Classifiers, Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence AAAI, (pp. 1–6).
Crasso, M., Zunino, A., & Campo, M. (2008). AWSC: an approach to Web service classification based on machine learning techniques. Inteligencia Artificial Revista Iberoamericana de Inteligencia Artificial, 12(37), 25–36.
Dong, X., & Fuyun, L. (2010). Research and application of CT image mining based on rough sets theory and association rules. In Proceedings of the Computer Science and Information Technology (pp. 392–394).
Group of Logic in Poland. RSES, http://logic.mimuw.edu.pl/~rses.
Heß, A., Johnston, E., & Kushmerick, N. (2004). ASSAM: A tool for semi automatically annotating semantic web services. In Proceedings of the International Semantic Web Conference (pp. 320–334).
Iosif, E., & Potamianos, A. (2010). Unsupervised semantic similarity computation between terms using Web documents. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 22(11), 1637–1647.
Komorowski, J., Polkowski, L., & Skowron, A. (1999). Rough sets: A tutorial, rough fuzzy hybridization (pp. 3–98). Singapore: Springer Verlag.
Li, J., Xu, W., Tu, W., Wang, X., Zhang, W., & Wen, J. (2001). Rough set application in customer classification. Advanced Materials Research, 267, 46–49.
Li, Y., Feng, T., Zhang, S., & Li, Z. (2010). A generalized model of covering rough sets and its application in medical diagnosis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics (pp. 145–150).
Liu, J., Hu, Q., & Yu, D. (2008). A comparative study on rough set based class imbalance learning. International Journal of Knowledge-Based Systems, 21(8), 753–763.
Mohanty, R., Ravi, V., & Patra, M. R. (2010). Web services classification using intelligent techniques. Expert Systems with Applications, 37, 5484–5490.
Oldham, N., Thomas, C., Sheth, A., & Verma K. (2004). METEOR-S: Web service annotation framework with machine learning classification. In Semantic Web services and Web process composition, Vol. 3387 of LNCS, (pp. 137–146).
Parathaláin, N., & Shen, Q. (2010). On rough sets, their recent extensions and applications. Knowledge Engineering Review, 25(4), 365–395.
Pawlak, Z. (1982). Rough sets. International Journal of Computer and Information Sciences, 11, 341–356.
Pawlak, Z. (1991). Rough sets. Theoretical aspect of reasoning about data. Springer, 229 pages.
Pawlak, Z., Grzymala-Busse, J., Slowinski, R., & Ziarko, W. (1995). Rough sets. Communications of the ACM, 38(11), 89–95.
Pawlak, Z., Grzymala-Busse, J., Slowinski, R., & Ziarko, W. (2007). Rudiments of rough sets. Information Sciences, 177(1), 3–27.
Plebani, P., & Pernici, B. (2009). URBE: Web service retrieval based on similarity evaluation. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 21(11), 1629–1642.
Segev, A., & Toch, E. (2009). Context-based matching and ranking of Web services for composition. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2(3), 210–222.
Shannon, C. (1948). The mathematical theory of communication. Bell System Technical Journal, 27, 379–423.
Swiniarski, R., & Skowron, A. (2003). Rough set methods in feature selection and recognition. Pattern Recognition Letters, 24(6), 833–849.
Witten, I., Frank, E., & Hall, M. (2011). Data mining: Practical machine learning tools and techniques. Elsevier
Zhong, N., & Slowron, A. (2001). Rough sets based knowledge discovery process. International Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science, 11(3), 603–619.
Zhu, H., & Zhang, B. (2008). Research on the dependency among the non-functional properties of web services. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Knowledge Acquisition and Modeling (pp. 273–277).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Own, H.S., Yahyaoui, H. Rough set based classification of real world Web services. Inf Syst Front 17, 1301–1311 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-014-9496-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-014-9496-3