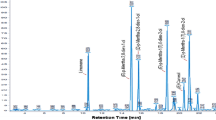
Abstract
The topical application of essential oils is considered an effective treatment for skin diseases. Cymbopogon distans (Nees ex Steud.) Wats (Poaceae) is a promising aromatic grass widespread in the Himalayan temperate zone. Therefore, using in-vitro and in-vivo bioassays, we examined the chemical and pharmacological characteristics of essential oil hydro-distilled from C. distans coded as CDA-01, specifically concerning skin inflammation. Characterization using GC-FID and GC–MS provided a chemical fingerprint for CDA-01, enabling the identification of 54 compounds; amongst them, citral (34.3%), geranyl acetate (21.2%), and geraniol (16.4%) were the most abundant. To examine the anti-inflammatory potential, CDA-01 treatment on LPS-stimulated macrophage cells in addition to 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) generated cutaneous inflammatory reaction in the mouse ear was assessed through quantification of the inflammatory markers. Consequently, CDA-01 demonstrated protection against inflammation caused by LPS by lowering the pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6 and TNF-α) level in HaCaT cells with negligible cytotoxicity. Consistent with the in-vitro findings, CDA-01 treatment reduced pro-inflammatory mediators (TNF-, IL-6, and NO) and lipid peroxidation in an in-vivo investigation. Subcutaneous inflammation in TPA-treated mice ears was similarly decreased, as evidenced by the histological and morphological studies. As a result of our findings, it is possible that CDA-01 could be an effective treatment for skin inflammation disorders.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data and materials for this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abraham A, Roga G (2014) Topical steroid-damaged skin. Indian J Dermatol 59:456–459. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5154.139872
Bakkali F, Averbeck S, Averbeck D, Idaomar M (2008) Biological effects of essential oils–a review. Food Chem Toxicol 46:446–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2007.09.106
Cashman JN (1996) The mechanisms of action of NSAIDs in analgesia. Drugs 52:13–23. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199600525-00004
Chen L, Lu H (2009) Analysis of the chemical constituents of essential oil from Hubei Cymbopogon distans by GC-MS. Chin J Hosp Pharm 15:1290–1291
Chen J, Jiang Q-D, Chai Y-P, Zhang H, Peng P, Yang X-X (2016) Natural terpenes as penetration enhancers for transdermal drug delivery. Molecules 21:1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21121709
De Vry CG, Valdez M, Lazarov M, Muhr E, Buelow R, Fong T, Iyer S (2005) Topical application of a novel immunomodulatory peptide, RDP58, reduces skin inflammation in the phorbol ester-induced dermatitis model. J Invest Dermatol 125:473–481. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23831.x
Elias PM, Wood LC, Feingold KR (1999) Epidermal pathogenesis of inflammatory dermatoses. Am J Contact Dermat 10:119–126
Fuchs J, Zollner T, Kaufmann R, Podda M (2001) Redox-modulated pathways in inflammatory skin diseases. Free Radic Biol Med 30:337–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0891-5849(00)00482-2
Herrmann F, Romero MR, Blazquez AG, Kaufmann D, Ashour ML, Kahl S, Marin JJ, Efferth T, Wink M (2011) Diversity of pharmacological properties in Chinese and European medicinal plants: cytotoxicity, antiviral and antitrypanosomal screening of 82 herbal drugs. Diversity 3:547–580. https://doi.org/10.3390/d3040547
Koziol A, Stryjewska A, Librowski T, Salat K, Gawel M, Moniczewski A, Lochynski S (2014) An overview of the pharmacological properties and potential applications of natural monoterpenes. Mini Rev Med Chem 14:1156–1168. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389557514666141127145820
Kumar A, Agarwal K, Singh M, Saxena A, Yadav P, Maurya AK, Yadav A, Tandon S, Chanda D, Bawankule DU (2018) Essential oil from waste leaves of Curcuma longa L. alleviates skin inflammation. Inflammopharmacology 26:1245–1255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-0447-3
Kundu JK, Shin YK, Surh Y-J (2006) Resveratrol modulates phorbol ester-induced pro-inflammatory signal transduction pathways in mouse skin in vivo: NF-κB and AP-1 as prime targets. Biochem Pharmacol 72:1506–1515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2006.08.005
Lee C-H, Hwang ST-Y (2012) Pathophysiology of chemokines and chemokine receptors in dermatological science: a focus on psoriasis and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Dermatol Sin 30:128–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsi.2012.08.004
Lohani H, Bhandari U, Gwari G, Haider SZ, Sah S, Chauhan NK (2015) Intraspecific chemical variability in essential oil of Cymbopogon distans (Nees ex Steud.) W. Watson from Uttarakhand Himalaya (India). Indian J Nat Prod Resour 6:122–126. http://op.niscair.res.in/index.php/IJNPR/article/view/6017
Loza-Tavera H (1999) Monoterpenes in essential oils. Chem Higher Plant Bioeng. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-4729-7_5
Mathela C, Melkani A, Joshi P, Mathela D, Pant A, Dev V (1987) Aromatic grasses of Kumaon Himalaya: distribution, chemotaxonomy, nutritive value and economic importance. J Econ Taxon Bot 11:337–343. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines3010006
Mathela C, Melkani A, Pant A, Pande C (1988) Chemical variations in Cymbopogon distans and their chemosystematic implications. Biochem Syst Ecol 16:161–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-1978(88)90090-7
Mathela C (1990) Himalayan Cymbopogon species: new chemical, morphological, anatomical and agronomical results. Proceedings of the 11th international congress of essential oils, fragrances and flavours. New Delhi, India, 12–16 November, 1989 Vol. 4 Chemistry-analysis and structure. Aspect Publishing
Maurya AK, Mohanty S, Pal A, Chanotiya CS, Bawankule DU (2018) The essential oil from Citrus limetta Risso peels alleviates skin inflammation: in-vitro and in-vivo study. J Ethnopharmacol 212:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2017.10.018
Moore RA, Tramer M, Carroll D, Wiffen PJ, McQuay H (1998) Quantitive systematic review of topically applied non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. BMJ 316:333–338. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.316.7128.333
Murphy J-E, Robert C, Kupper TS (2000) Interleukin-1 and cutaneous inflammation: a crucial link between innate and acquired immunity. J Invest Dermato 114:602–608. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1747.2000.00917.x
Newton K, Dixit VM (2012) Signaling in innate immunity and inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 4(3):6049. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a006049
Padalia RC, Verma RS, Chauhan A, Goswami P, Singh VR, Verma SK, Singh N, Kurmi A, Darokar MP, Saikia D (2018) p-Menthenols chemotype of Cymbopogon distans from India: composition, antibacterial and antifungal activity of the essential oil against pathogens. J Essent Oil Res 30:40–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/10412905.2017.1375035
Ross RG, Sathishkumar K, Naik AK, Bawankule DU, Sarkar SN, Mishra SK, Prakash VR (2004) Mechanisms of lipopolysaccharide-induced changes in effects of contractile agonists on pregnant rat myometrium. Am J Obstet Gynecol 190(2):532–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9378(03)00949-9
Sabat R, Wolk K, Loyal L, Döcke W-D, Ghoreschi K (2019) T cell pathology in skin inflammation. Semin Immunopathol 41(3):359–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-019-00742-7
Salmon J, Armstrong C, Ansel J (1994) The skin as an immune organ. West J Med 160(2):146–152
Singh S, Bhatt D, Singh MK, Sundaresan V, Tandon S, Padalia RC, Bawankule DU, Verma RS (2021) New insights into the chemical composition, pro-inflammatory cytokine inhibition profile of davana (Artemisia pallens Wall ex DC) essential oil and cis-davanone in primary macrophage cells. Chem Biodivers 18:e2100531. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.202100531
Singh S, Bhatt D, Singh MK, Maurya AK, Israr KM, Chauhan A, Padalia RC, Verma RS, Bawankule DU (2022) p-Menthadienols-rich essential oil from Cymbopogon martini ameliorates skin inflammation. Inflammopharmacology 30(3):895–905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-00954-8
Stanley PL, Steiner S, Havens M, Tramposch KM (1991) Mouse skin inflammation induced by multiple topical applications of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Skin Pharmacol 4(4):262–271. https://doi.org/10.1159/000210960
Varman RM, Singh S (2012) Investigation of effects of terpene skin penetration enhancers on stability and biological activity of lysozyme. AAPS PharmSciTech 13(4):1084–1090. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-012-9840-1
Wu JH, Cohen BA (2019) The stigma of skin disease. Curr Opin Pediatr 31(4):509–514. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOP.0000000000000792
Wu J-Y, Xie J-H, Chen Y-J, Fu X-Q, Wang R-J, Deng Y-Y, Wang S, Yu H-X, Liang C, Yu Z-L (2022) Amelioration of TPA-induced skin inflammation by the leaf extract of Vernonia amygdalina involves ERK/STAT3 (Ser727) signaling inhibition. Phytomedicine 102:154194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154194
Xue D, Song M, Chen N, Chen Y (1992) Studies on chemical ingredients of the essential oil of Cymbopogon distans (Nees) W. Wats. Chem J Chin Univ 13(12):1551–1552. http://www.cjcu.jlu.edu.cn/EN/Y1992/V13/I12/1551
Zhang JS, Zhao NN, Liu QZ, Liu ZL, Du SS, Zhou L, Deng ZW (2011) Repellent constituents of essential oil of Cymbopogon distans aerial parts against two stored-product insects. J Agric Food Chem 59:9910–9915. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf202266n
Acknowledgements
CSIR-CIMAP supported the present study financially under the Aroma Mission Project (HCP-0007). Additionally, the first author thanks the Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi, India, for the DST/INSPIRE Fellowship [IF170937]. The authors are appreciative of the Institute Director's gracious support as the work has progressed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DB: actual experimentation, recording of observation and manuscript preparation (biological activity). SS: actual experimentation, recording of observation, analysis and manuscript preparation (chemistry). MKS: analysis and manuscript preparation. AKM: histopathological analysis. AC: maintenance of plant in the field and botanical authentication. RCP: extraction and analysis. RSV: planning, analysis and manuscript preparation. DUB: planning, analysis and manuscript preparation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have claimed no conflict of interest in the content of this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatt, D., Singh, S., Singh, M.K. et al. Acyclic monoterpenoid-rich essential oil of Cymbopogon distans mitigates skin inflammation: a chemico-pharmacological study. Inflammopharmacol 32, 509–521 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01302-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01302-0