Abstract
Background
The pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) remains unclear. C66, a derivative of curcumin, reportedly exerts anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic and anti-apoptotic effects by targeting the JNK pathway. However, the effect of C66 against IBD is not clear. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effect of C66 against IBD.
Methods
C57BL/6J mice were treated with 2.5% DSS for 7 days, and then administered water for 3 days to develop the IBD mouse model. A mouse intestinal epithelial cell line, MODE-K, stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was used as the in vitro model. The therapeutic effects of C66 were evaluated and the pharmacological mechanisms were explored.
Results
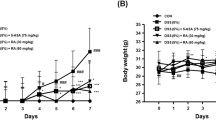
Compared to the model group, C66 treatment significantly reduced colitis-associated damage, including a decrease in disease activity index (DAI), a higher body weight and longer colon. In addition, the infiltration of distal inflammatory cells, loss of crypt tissues, and destruction of epithelial cells were reduced in C66-treated group. In addition, C66 treatment reduced fibrotic areas and inflammatory responses in the colon tissues, leading to increased epithelial cell proliferation and decreased apoptosis in colon. Furthermore, C66 treatment decreased the levels of p-JNK and p-P65, indicating that C66 inhibits the activation of the JNK and NF-κB signaling pathways induced by DSS in colon tissues. Finally, in vitro data show that C66 inhibited LPS-induced inflammation and apoptosis in small intestinal epithelial cells.
Conclusions
The curcumin analog C66 exhibits its anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting the DSS-induced activation of JNK/NF-κB signaling pathways. C66 may be a potential candidate for the treatment of IBD.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Bax:
-
BCL2-Associated X protein
- Bcl-2:
-
B-cell lymphoma-2
- Col-1:
-
Type 1 collagen
- i.p.:
-
Intraperitoneal
- IBD:
-
Inflammatory bowel disease
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- IL-12:
-
Interleukin 12
- IL-17:
-
Interleukin 17
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin 1β
- IL-22:
-
Interleukin 22
- IL-23:
-
Interleukin 23
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin 6
- INF-γ:
-
γ Interferon
- IκB-α:
-
Inhibitor of NF-κB-α
- JNK:
-
C Jun N-terminal kinase
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa-B
- NLRP3:
-
NLR family pyrin domain containing 3
- P38:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- STAT3:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor-β
- Th17:
-
T helper cell 17
- Timp-1:
-
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
References
Adhikari N, Charles N, Lehmann U, Hall JL (2006) Transcription factor and kinase-mediated signaling in atherosclerosis and vascular injury. Curr Atheroscler Rep 8:252–260
Anand P, Kunnumakkara AB, Newman RA, Aggarwal BB (2007) Bioavailability of curcumin: problems and promises. Mol Pharm 4:807–818
Bos S, Laukens D (2020) Metabolic modulation during intestinal fibrosis. J Dig Dis 21:319–325
Bruck R, Ashkenazi M, Weiss S, Goldiner I, Shapiro H, Aeed H, Genina O, Helpern Z, Pines M (2007) Prevention of liver cirrhosis in rats by curcumin. Liver Int 27:373–383
Eckburg PB, Bik EM, Bernstein CN, Purdom E, Dethlefsen L, Sargent M, Gill SR, Nelson KE, Relman DA (2005) Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 308:1635–1638
Feng J, Xiao B, Chen W, Ding T, Chen L, Yu P, Xu F, Zhang H, Liu Z, Liang G (2015) Synthesis and anti-inflammatory evaluation of novel c66 analogs for the treatment of lps-induced acute lung injury. Chem Biol Drug Des 86:753–763
Feuerstein JD, Moss AC, Farraye FA (2019) Ulcerative colitis. Mayo Clin Proc 94:1357–1373
Gong Z, Zhao S, Zhou J, Yan J, Wang L, Du X, Li H, Chen Y, Cai W, Wu J (2018) Curcumin alleviates dss-induced colitis via inhibiting nlrp3 inflammsome activation and il-1beta Production. Mol Immunol 104:11–19
Grynberg K, Ma FY, Nikolic-Paterson DJ (2017) The Jnk signaling pathway in renal fibrosis. Front Physiol 8:829
Guan Q (2019) A comprehensive review and update on the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. J Immunol Res 2019:7247238
Hommes D, Van Den Blink B, Plasse T, Bartelsman J, Xu C, Macpherson B, Tytgat G, Peppelenbosch M, Van Deventer S (2002) Inhibition of stress-activated map kinases induces clinical improvement in moderate to severe Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 122:7–14
Kaplan GG (2015) The global burden of Ibd: from 2015 to 2025. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 12:720–727
Khor B, Gardet A, Xavier RJ (2011) Genetics and pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 474:307–317
Kim TW, Shin JS, Chung KS, Lee YG, Baek NI, Lee KT (2019) Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Koreanaside a, a Lignan Isolated from the Flower of Forsythia Koreana, against Lps-Induced Macrophage Activation and Dss-Induced Colitis Mice: The Crucial Role of Ap-1, Nf-Kappab, and Jak/Stat Signaling. Cells 8:1
Korn T, Bettelli E, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK (2009) Il-17 and Th17 cells. Annu Rev Immunol 27:485–517
Lawrence T (2009) The nuclear factor Nf-Kappab pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1:a001651
Li X, Zhu R, Jiang H, Yin Q, Gu J, Chen J, Ji X, Wu X, Fu H, Wang H, Tang X, Gao Y, Wang B, Ji Y, Chen H (2022) Autophagy enhanced by curcumin ameliorates inflammation in atherogenesis via the Tfeb-P300-Brd4 axis. Acta Pharm Sin B 12:2280–2299
Liang G, Zhou H, Wang Y, Gurley EC, Feng B, Chen L, Xiao J, Yang S, Li X (2009) Inhibition of Lps-induced production of inflammatory factors in the macrophages by mono-carbonyl analogues of curcumin. J Cell Mol Med 13:3370–3379
Lin AN, Li YQ, Zhong MX, Liu J, Dai Q, Zhu W, Zhang YL (2016) Expressions of inflammatory cytokines in intestinal mucosa and their prognostic value in patients with ulcerative colitis. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 36:1712–1717
Liu Z, Huang XR, Chen HY, Penninger JM, Lan HY (2012) Loss of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 enhances Tgf-beta/Smad-mediated renal fibrosis and Nf-kappab-driven renal inflammation in a mouse model of obstructive nephropathy. Lab Invest 92:650–661
Liu C, He L, Wang J, Wang Q, Sun C, Li Y, Jia K, Wang J, Xu T, Ming R, Wang Q, Lin N (2020a) Anti-angiogenic effect of shikonin in rheumatoid arthritis by downregulating pi3k/akt and mapks signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol 260:113039
Liu M, Ding J, Zhang H, Shen J, Hao Y, Zhang X, Qi W, Luo X, Zhang T, Wang N (2020b) Lactobacillus casei Lh23 modulates the immune response and ameliorates Dss-induced colitis via suppressing Jnk/P-38 signal pathways and enhancing histone H3k9 acetylation. Food Funct 11:5473–5485
Luhrs H, Gerke T, Muller JG, Melcher R, Schauber J, Boxberge F, Scheppach W, Menzel T (2002) Butyrate inhibits Nf-kappab activation in lamina propria macrophages of patients with ulcerative colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol 37:458–466
Mak WY, Zhao M, Ng SC, Burisch J (2020) The epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: east meets west. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 35:380–389
Mitsuyama K, Suzuki A, Tomiyasu N, Tsuruta O, Kitazaki S, Takeda T, Satoh Y, Bennett BL, Toyonaga A, Sata M (2006) Pro-inflammatory signaling by Jun-N-terminal kinase in inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Mol Med 17:449–455
Moschen AR, Tilg H, Raine T (2019) Il-12, Il-23 and Il-17 in Ibd: immunobiology and therapeutic targeting. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16:185–196
Neurath MF (2014) Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol 14:329–342
Neurath MF, Pettersson S, Meyer Zum Buschenfelde KH, Strober W (1996) Local administration of antisense phosphorothioate oligonucleotides to the P65 subunit of nf-kappa b abrogates established experimental colitis in mice. Nat Med 2:998–1004
Pan Y, Wang Y, Cai L, Cai Y, Hu J, Yu C, Li J, Feng Z, Yang S, Li X, Liang G (2012) Inhibition of high glucose-induced inflammatory response and macrophage infiltration by a novel curcumin derivative prevents renal injury in diabetic rats. Br J Pharmacol 166:1169–1182
Pan Y, Zhang X, Wang Y, Cai L, Ren L, Tang L, Wang J, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Liu Q, Li X, Liang G (2013) Targeting Jnk by a new curcumin analog to inhibit Nf-Kb-mediated expression of cell adhesion molecules attenuates renal macrophage infiltration and injury in diabetic mice. PLoS ONE 8:e79084
Pan Y, Huang Y, Wang Z, Fang Q, Sun Y, Tong C, Peng K, Wang Y, Miao L, Cai L, Zhao Y, Liang G (2014a) Inhibition of Mapk-mediated ace expression by compound c66 prevents stz-induced diabetic nephropathy. J Cell Mol Med 18:231–241
Pan Y, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Peng K, Li W, Wang Y, Zhang J, Zhou S, Liu Q, Li X, Cai L, Liang G (2014b) Inhibition of Jnk phosphorylation by a novel curcumin analog prevents high glucose-induced inflammation and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes and the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes 63:3497–3511
Pizarro TT, Cominelli F (2007) Cytokine therapy for Crohn’s disease: advances in translational research. Annu Rev Med 58:433–444
Podolsky DK (2002) Inflammatory bowel disease. N Engl J Med 347:417–429
Rana SV, Sharma S, Kaur J, Prasad KK, Sinha SK, Kochhar R, Malik A, Morya RK (2014) Relationship of cytokines, oxidative stress and Gi motility with bacterial overgrowth in ulcerative colitis patients. J Crohns Colitis 8:859–865
Ren BC, Zhang YF, Liu SS, Cheng XJ, Yang X, Cui XG, Zhao XR, Zhao H, Hao MF, Li MD, Tie YY, Qu L, Li XY (2020) Curcumin alleviates oxidative stress and inhibits apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy via sirt1-foxo1 and pi3k-akt signalling pathways. J Cell Mol Med 24:12355–12367
Rogler G, Singh A, Kavanaugh A, Rubin DT (2021) Extraintestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease: current concepts, treatment, and implications for disease management. Gastroenterology 161:1118–1132
Roy PK, Rashid F, Bragg J, Ibdah JA (2008) Role of the Jnk signal transduction pathway in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 14:200–202
Salim SY, Soderholm JD (2011) Importance of disrupted intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis 17:362–381
Shih DQ, Targan SR (2008) Immunopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 14:390–400
Van Der Sluis M, De Koning BA, De Bruijn AC, Velcich A, Meijerink JP, Van Goudoever JB, Buller HA, Dekker J, Van Seuningen I, Renes IB, Einerhand AW (2006) Muc2-Deficient mice spontaneously develop colitis, indicating that muc2 is critical for colonic protection. Gastroenterology 131:117–129
Waetzig GH, Seegert D, Rosenstiel P, Nikolaus S, Schreiber S (2002) P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is activated and linked to Tnf-alpha signaling in inflammatory bowel disease. J Immunol 168:5342–5351
Wang Y, Zhou S, Sun W, Mcclung K, Pan Y, Liang G, Tan Y, Zhao Y, Liu Q, Sun J, Cai L (2014) Inhibition of Jnk by novel curcumin analog c66 prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy with a preservation of cardiac metallothionein expression. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 306:E1239-1247
Wang Y, Wang Y, Luo M, Wu H, Kong L, Xin Y, Cui W, Zhao Y, Wang J, Liang G, Miao L, Cai L (2015) Novel curcumin analog c66 prevents diabetic nephropathy via jnk pathway with the involvement of p300/cbp-mediated histone acetylation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1852:34–46
Wehkamp J, Harder J, Weichenthal M, Mueller O, Herrlinger KR, Fellermann K, Schroeder JM, Stange EF (2003) Inducible and constitutive beta-defensins are differentially expressed in crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 9:215–223
Ye L, Chen X, Wang M, Jin L, Zhuang Z, Yang D, Guan X, Samorodov AV, Pavlov VN, Chattipakorn N, Feng J, Wang Y, Luo W, Liang G (2021a) Curcumin analogue c66 attenuates obesity-induced myocardial injury by inhibiting jnk-mediated inflammation. Biomed Pharmacother 143:112121
Ye L, Hu X, Hu X, Yin S, Chen J, He H, Hong S, Yang B, Singh KK, Feng J, Wang Y, Luo W, Liang G (2021b) Curcumin analogue c66 attenuates obesity-induced renal injury by inhibiting chronic inflammation. Biomed Pharmacother 137:111418
Yu P, Dong L, Zhang Y, Chen W, Xu S, Wang Z, Shan X, Zhou J, Liu Z, Liang G (2015) Design, synthesis and biological activity of novel asymmetric c66 analogs as anti-inflammatory agents for the treatment of acute lung injury. Eur J Med Chem 94:436–446
Zhang YZ, Li YY (2014) Inflammatory bowel disease: pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 20:91–99
Zhu H, Wang X, Wang X, Liu B, Yuan Y, Zuo X (2020) Curcumin attenuates inflammation and cell apoptosis through regulating nf-kappab and jak2/stat3 signaling pathway against acute kidney injury. Cell Cycle 19:1941–1951
Funding
This study was supported by Key Research Project of Wenzhou City (ZY2021021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CH, YW and LH contributed to the literature search and study design. CH, YC, LZ, ML and JY carried out the experiments. CH, FH and YW contributed to data collection and analysis. CH, LH and YW participated in the drafting of the manuscript. CH and YW revised the manuscript. All authors contributed significantly and approved the submission of this manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10787_2022_1085_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary file 1 (DOCX 20 KB) Supplemental information includes three tables. All the other data are available from the authors on request.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, C., Chen, Y., Zhang, L. et al. Curcumin analog C66 alleviates inflammatory colitis by inhibiting the activation of NF-κB. Inflammopharmacol 30, 2167–2179 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-01085-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-01085-w