Abstract
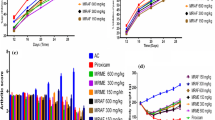
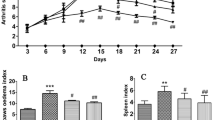
Clematis orientalis Linn has long been used as ethnopharmacy for the treatment of arthritis. This study is intended to evaluate the curative efficacy of Clematis orientalis in treating polyarthritis in rats. Aqueous ethanolic extract and fractions (hexane, butanol and aqueous) were administered orally at 200 mg/kg for 28 days after CFA immunization. Paw swelling, paw diameter, arthritic score, body weight, hematological parameters, radiographic and histological analysis of ankle joints were evaluated. Moreover, levels of various inflammatory markers through RT-PCR and ELISA were measured. DPPH and reducing power assays were used to appraise antioxidant capacity. Qualitative phytochemical analysis, determination of total phenolic and flavonoid contents were also carried out. Aqueous ethanolic extract and fractions significantly (p < 0.001) reduced paw volume, paw thickness and arthritic score and considerably prevented decrease in body weight along with anomalous alterations in hematological parameters in comparison with arthritic control. X-ray and histological examination revealed no significant structural changes in ankle joints of treated rats. Expression levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, COX-2 and NF-Kβ were significantly (p < 0.05–0.001) suppressed as well as noteworthy increase in the levels of IL-4 and IL-10 among treated animals has been detected. Overproduction of TNF-α and PGE2 was substantially prevented in animals given different treatments. Aqueous ethanol extract and its fractions demonstrated significant and concentration-dependent antioxidant potential. In general, among fractions aqueous fraction exhibited a greater anti-arthritic effect. Phytochemical analysis of aqueous fraction confirmed the presence of flavonoids and glycosides, 215.29 mgGAE/ml phenolic content and 633.03 μgQE/ml flavonoid content. Thus, we suggest Clematis orientalis as a potent strategy for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas Q, Khan SW, Khatoon S, Hussain SA, Hassan SN, Hussain A, Qureshi R, Hussain I (2014) Floristic biodiversıty and traditional uses of medicinal plants of Haramosh Valley Central Karakoram National Park of Gilgit district, Gilgit-Baltistan. Pak J Bio Env Sci 5:75–86
Alamgeer Uttra AM, Hasan UH (2017) Anti-arthritic activity of aqueous-methanolic extract and various fractions of Berberis orthobotrys Bien ex Aitch. BMC Complement Altern Med 17:371
Alamgeer Hasan UH, Uttra AM, Rasool S (2015) Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo anti-arthritic potential of Berberis calliobotrys. Bangladesh J Pharmacol 10:807–819
Alamgeer Niazi SG, Uttra AM, Qaiser MN, Ahsan H (2017) Appraisal of anti-arthritic and nephroprotective potential of Cuscuta reflexa. Pharm Biol 55:792–798
Amaeze OU, Ayoola GA, Sofidiya MO, Adepoju-Bello AA, Adegoke AO, Coker HAB (2011) Evaluation of antioxidant activity of tetracarpidium conophorum (M¨ull. Arg) Hutch and Dalziel Leaves. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/976701
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS, Medsger TA, Mitchell DM, Neustadt DH, Pinals RS, Schaller JG, Sharp JT, Wilder Ronald L, Hunder GG (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthr Rheum 31:315–324
Arulpriya P, Lalitha P, Hemalatha S (2010) In vitro antioxidant testing of the extracts of Samanea saman (Jacq.) Merr. Der Chem Sin 1:73–79
Bischoff SC (2008) Quercetin: potentials in the prevention and therapy of disease. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 11:733–740
Chaouche TM, Haddouchi F, Ksouri R, Atik-Bekkara F (2014) Evaluation of antioxidant activity of hydromethanolic extracts of some medicinal species from South Algeria. J Chin Med Assoc 77:302–307
Connolly KM, Stecher VJ, Danis E, Pruden DJ, LaBrie T (1988) Alteration of interleukin-1 activity and the acute phase response in adjuvant arthritic rats treated with disease modifying antirheumatic drugs. Agents Actions 25:94–105
Fattahi MJ, Mirshafiey A (2012) Prostaglandins and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/239310
Ghasemzadeh A, Ghasemzadeh N (2011) Flavonoids and phenolic acids: role and biochemical activity in plants and human. J Med Plant Res 5:6697–6703
Goekoop-Ruiterman YP, de Vries-Bouwstra JK, Allaart CF, van Zeben D, Kerstens PJ, Hazes JM, Zwinderman AH, Ronday HK, Han KH, Westedt ML, Gerards AH, van Groenendael JH, Lems WF, van Krugten MV, Breedveld FC, Dijkmans BA (2005) Clinical and radiographic outcomes of four different treatment strategies in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (the BeSt study): a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 52:3381–3390
Gomaa A, Elshenawy M, Afifi N, Mohammed E, Thabit R (2009) Enhancement of the anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effects of theophylline by a low dose of a nitric oxide donor or non-specific nitric oxide synthase inhibitor. British J Pharmacol 158:1835–1847
Gorman CL, Cope AP (2008) Immune-mediated pathways in chronic inflammatory arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 22:221–238
Han W, Xiong Y, Li Y, Fang W, Ma Y, Liu L, Li F, Zhu X (2013) Anti-arthritic effects of clematichinenoside (AR-6) on PI3 K/Akt signaling pathway and TNF-α associated with collagen-induced arthritis. Pharm Biol 51(1):13–22
Hasan UH, Alamgeer (2018) anti-arthritic efficacy of Clematis orientalis. Bangladesh J Pharmacol 13:142–148
Irmler I, Bräuer R (2007) Paradoxical role of interferon-gamma in arthritis. Rheumatol 66:591–594
Ishtiaq M, Mumtaz AS, Hussain T, Ghani A (2012) Medicinal plant diversity in the flora of Leepa Valley, Muzaffarabad (AJK). Pak Afr J Biotechnol 11:3087–3098
Jin F (2012) The pharmaceutical potential of compounds from Tasmanian Clematis species
Kavitha KS, Satish S (2013) Evaluation of antimicrobial and antioxidant activities from Toona ciliata Roemer. J Anal Sci Technol 4:23
Klareskog L, Catrina A, Paget S (2009) Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 373:659–672
Kroes BH, van den Berg AJ, Quarles van Ufford HC, Van Dijk H, Labadie RP (1992) Anti-inflammatory activity of gallic acid. Planta Med 58:499–504
Li Y, Yao J, Han C, Yang J, Chaudhry M, Wang S, Liu H, Yin Y (2016) Quercetin, inflammation and immunity. Nutrients 8(3):167
Liang N, Kitts DD (2016) Role of chlorogenic acids in controlling oxidative and inflammatory stress conditions. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8010016
Lin B, Zhang H, Zhao X, Rahman K, Wang Y, Maa X, Zheng C, Zhang Q, Han T, Lu-Ping Q (2013) Inhibitory effects of the root extract of Litsea cubeba (lour.) pers.on adjuvant arthritis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 147:327–334
Liu M, Ma W, Guan H, Li L, Wei B, Li P (2011) Effects of taurochenodeoxycholic acid on adjuvant arthritis in rats. Int J Immunopharmacol 11:2150–2158
Lü SW, Wang QS, Li GY, Sun S, Guo YY, Kuang HX (2015) The treatment of rheumatoid arthritis using Chinese medicinal plants: from pharmacology to potential molecular mechanisms. J Ethnopharmacol 176:177–206
Makrov SS (2001) NF-κB in rheumatoid arthritis: a pivotal regulator of inflammation, hyperplasia, and tissue destruction. Arthritis Res 3:200–206
Manach C, Scalbert A, Morand C, Remesy C, Jimenez L (2004) Polyphenols: food sources and bioavailability. Am J Clin Nutr 79:727–747
NRC (1996) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. National Academy Press, Washington DC
Pan T, Cheng T, Jia Y, Li P, Li F (2017) Anti-rheumatoid arthritis effects of traditional Chinese herb couple in adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 205:1–7
Perveen K, Hanif F, Jawed H, Simjee SU (2013) Protective efficacy of N-(2-Hydroxyphenyl) acetamide against adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/635143
Perveen K, Hanif F, Jawed H, Jamall S, Simjee SU (2014) N-(2-hydroxy phenyl) acetamide: a novel suppressor of Toll-like receptors (TLR-2 and TLR-4) in adjuvant-induced arthritic rats. Mol Cell Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2082-7
Pitsiou G, Kyriazis G, Hatzizisi O, Argyropoulou P, Mavrofridis E, Patakas D (2002) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha serum levels, weight loss and tissue oxygen at ionin chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Med 96:594–598
Rakesh T, Parashant T (2012) Effect of Cocculus hirsutus leaves extract on Freunds complete adjuvant and formaldehyde-induced arthritis. Int Res J Pharm 3:267–290
Rio DC, Ares M, Hannon GJ, Nilsen TW (2010) Purification of RNA using TRIzol (TRI reagent). Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2010(6):pdb.prot5439
Rosloniec EF, Latham K, Guedez YB (2002) Paradoxical roles of IFN-γ in models of Th1-mediated autoimmunity. Arthritis Res 4:333–336
Sahoo S, Ghosh G, Das D, Nayak S (2013) Phytochemical investigation and in vitro antioxidant activity of an indigenous medicinal plant Alpinia nigra B.L. Burtt Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 3:871–876
Schulze-Koops H, Kalden JR (2001) The balance of Th1/Th2 cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 15:677–691
Scott DL, Wolfe F, Huizinga TW (2010) Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 376:1094–1108
Shabbir A, Shahzad M, Ali A, Zia-ur-Rehman M (2014) Anti-arthritic activityof N0-[(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)methylidene]-2-(3,4-dimethyl-5,5-dioxidopyrazolo[4,3-c][1,2]benzothiazin-1(4H)-yl)acetohydrazide. Eur J Pharmacol 738:263–272
Shen L, Wang P, Guo J, Du G (2013) Anti-arthritic activity of ethanol extract of Fagopyrum cymosum with adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Pharm Biol 51:783–789
Sindhu G, Ratheesh M, Shyni GL, Nambisan B, Helen A (2012) Anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects of mucilage of Trigonella foenum graecum (Fenugreek) on adjuvant-induced arthritic rats. Int Immunopharmacol 12:205–211
Smolen JS, Steiner G (2003) Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2(6):473–488
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Koeller M, Weisman MH, Emery P (2007) New therapies for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 370:1861–1874
Srikanth G, Babu SM, Kavitha CHN, Rao MB, Vijaykumar N, Pradeep CH (2010) Studies on in vitro antioxidant activities of Carica papaya aqueous leaf extract. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci 1:59–65
Sukketsiri W, Chonpathompikunlert P, Tanasawet S, Choosri N, Wongtawatchai T (2016) Effects of apium graveolens extract on the oxidative stress in the liver of adjuvant-induced arthritic rats. Prev Nutr Food Sci 21:79–84
Sun X, Liu Y, Yang Y, Liu X, Xiang D (2016) Anti-arthritic effect of total saponins from Clematis henryi Oliv. on collagen-induced arthritis rats. Eur J Inflamm 14(2):71–77
Tayar JH, Suarez-Almazor ME (2010) New understanding and approaches to treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Brit Med Bull 94(1):201–214
Tracey K, Cerami AVH (1989) Cachectin/tumornecrosisfactor. Lancet 167:1122–1225
Tracey KJ, Wei H, Manogue KR, Fong Y, Hesse DD, Nguyen HT, Kuo GC, Beutler B, Cotran RS, Cerami A, Lowry SF (1988) Cachectin/tumornecrosisfactor induces cachexia, anemia, and inflammation. J Exper Med 167:1211–1227
Wanasundara PK, Shahidi F (1996) Optimization of hexametaphosphate- assisted extraction of flaxseed proteins using response surface methodology. J Food Sci 61:604–607
Woode E, Boakey-Gyasi E, Danquah CA, Anash C, Duwiejua M (2009) Anti-arthritic effects of Palisota hirsuta K. Schum. Leaf extract in Freund’s adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Int J Pharmacol 5:181–190
Yuting C, Rongliang Z, Zhongjian J, Yong J (1990) Flavonoids as superoxide scavengers and antioxidants. Free Rad Biol Med 9:19–21
Acknowledgement
The authors extend their appreciation to the deanship scientific research at King Saud University for funding this research through # (RG-1439-002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hasan, U.H., Alamgeer, Shahzad, M. et al. Inhibitory effects of Clematis orientalis aqueous ethanol extract and fractions on inflammatory markers in complete Freund's adjuvant-induced arthritis in Sprague–Dawley rats. Inflammopharmacol 27, 781–797 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-0543-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-0543-4