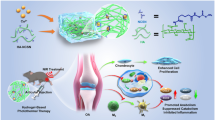
Abstract
In this study, we evaluated the hypothesis that immunonanosomes carrying the drug [5-(p-Fluorophenyl)-2-ureido]thiophene-3-carboxamide (TPCA-1) will help in reducing nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB)-associated inflammation in porcine chondrocytes against tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α)-induced stress. The nanosomes were tagged with monoclonal anti-type II collagen (MabCII) antibody to specifically target the exposed type II collagen in cartilage matrix. TPCA-1 at a concentration of 10 µM significantly reduced expression of the matrix-degrading enzyme, Matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13) and blocked the p65 nuclear translocation. In comparison to the TPCA-1 solution alone, the TPCA-1 nanosomes were found to be more effective in reducing the cellular toxicity, oxidative stress and inflammation in chondrocytes treated with TNF-α. In addition, TPCA-1 nanosomes were more effective in reducing the gene expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha (HIF-2α) that in turn is associated with the regulation of MMP-13 gene. TPCA-1 nanosomes significantly reduced expression of both these genes. The data also showed that TPCA-1 did not attenuate the down-regulated gene expression levels of anabolic genes aggrecan (ACAN) and collagen type II alpha (COL2A1). In conclusion, this study showed that TPCA-1 nanosomes carrying a dose of 10 µM TPCA-1 can effectively increase the survival of cultured porcine chondrocytes against TNF-α-induced stress. The findings of this study could be used to develop nanosome-based drug delivery systems (DDSs) for animal model of OA. Moreover, the approach presented here can be further utilized in other studies for targeted delivery of the drug of interest at a cellular level.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbarzadeh A et al (2013) Liposome: classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res Lett 8:102. https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276x-8-102
Blanco FJ, Lotz M (1995) IL-1-induced nitric oxide inhibits chondrocyte proliferation via PGE2. Exp Cell Res 218:319–325. https://doi.org/10.1006/excr.1995.1161
Blanco FJ, Ochs RL, Schwarz H, Lotz M (1995) Chondrocyte apoptosis induced by nitric oxide. Am J Pathol 146:75–85
Cho H, Stuart JM, Magid R, Danila DC, Hunsaker T, Pinkhassik E, Hasty KA (2014) Theranostic immunoliposomes for osteoarthritis. Nanomedicine 10:619–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2013.09.004
Cho H, Pinkhassik E, David V, Stuart JM, Hasty KA (2015a) Detection of early cartilage damage using targeted nanosomes in a post-traumatic osteoarthritis mouse model. Nanomedicine 11:939–946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2015.01.011
Cho H, Walker A, Williams J, Hasty KA (2015b) Study of osteoarthritis treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs: cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor and steroids. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/595273
Friedmann-Morvinski D, Narasimamurthy R, Xia Y, Myskiw C, Soda Y, Verma IM (2016) Targeting NF-kappaB in glioblastoma: a therapeutic approach. Sci Adv 2:e1501292. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1501292
Goldring MB et al (2011) Roles of inflammatory and anabolic cytokines in cartilage metabolism: signals and multiple effectors converge upon MMP-13 regulation in osteoarthritis. Eur Cell Mater 21:202–220
Greene MA, Loeser RF (2015) Aging-related inflammation in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil 23:1966–1971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2015.01.008
Harisa GI, Badran MM, Alanazi FK, Attia SM (2017) An overview of nanosomes delivery mechanisms: trafficking, orders, barriers and cellular effects. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46(4):669–679. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2017.1354301
Hua S, Wu SY (2013) The use of lipid-based nanocarriers for targeted pain therapies. Front Pharmacol 4:143. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2013.00143
Jasin HE, Noyori K, Takagi T, Taurog JD (1993) Characteristics of anti-type II collagen antibody binding to articular cartilage. Arthritis Rheum 36:651–659
Jeng C-C et al (2011) Dynamic probing of nanoparticle stability in vivo: a liposomal model assessed using in situ microdialysis and optical imaging. J Nanomaterials 2011:8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/932719
Johnson CI, Argyle DJ, Clements DN (2016) In vitro models for the study of osteoarthritis. Vet J 209:40–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tvjl.2015.07.011
Kaja S, Payne AJ, Naumchuk Y, Koulen P (2017) Quantification of lactate dehydrogenase for cell viability testing using cell lines and primary cultured astrocytes. Curr Protoc Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1002/cptx.21
Kishore N et al (2003) A selective IKK-2 inhibitor blocks NF-kappa B-dependent gene expression in interleukin-1 beta-stimulated synovial fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 278:32861–32871. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m211439200
Li H, Wang D, Yuan Y, Min J (2017) New insights on the MMP-13 regulatory network in the pathogenesis of early osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 19:248. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-017-1454-2
Lieberthal J, Sambamurthy N, Scanzello CR (2015) Inflammation in joint injury and post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil 23:1825–1834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2015.08.015
Maguire O, Collins C, O’Loughlin K, Miecznikowski J, Minderman H (2011) Quantifying nuclear p65 as a parameter for NF-kappaB activation: correlation between imagestream cytometry, microscopy, and Western blot. Cytometry A 79:461–469. https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.a.21068
Nan J et al (2014) TPCA-1 is a direct dual inhibitor of STAT3 and NF-kappaB and regresses mutant EGFR-associated human non-small cell lung cancers. Mol Cancer Ther 13:617–629. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-13-0464
Podolin PL et al (2005) Attenuation of murine collagen-induced arthritis by a novel, potent, selective small molecule inhibitor of IkappaB Kinase 2, TPCA-1 (2-[(aminocarbonyl)amino]-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-thiophenecarboxamide), occurs via reduction of proinflammatory cytokines and antigen-induced T cell proliferation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:373–381. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.104.074484
Prince DE, Greisberg JK (2015) Nitric oxide-associated chondrocyte apoptosis in trauma patients after high-energy lower extremity intra-articular fractures. J Orthop Traumatol 16:335–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10195-015-0350-2
Ricciotti E, FitzGerald GA (2011) Prostaglandins and inflammation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31:986–1000. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.207449
Rigoglou S, Papavassiliou AG (2013) The NF-kappaB signalling pathway in osteoarthritis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 45:2580–2584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2013.08.018
Rivard J, James A, Wegner G, Reagan K (2014) Modulating the tumor necrosis factor-α induced inflammatory response in human colonic epithelial cells by inhibiting NF-κB signaling (CCR5P.258). J Immunol 192:181.112
Ryu JH, Shin Y, Huh YH, Yang S, Chun CH, Chun JS (2012) Hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha regulates Fas-mediated chondrocyte apoptosis during osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. Cell Death Differ 19:440–450. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2011.111
Saito T, Kawaguchi H (2010) HIF-2alpha as a possible therapeutic target of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil 18:1552–1556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2010.10.006
Schnyder A, Huwyler J (2005) Drug transport to brain with targeted liposomes. NeuroRx 2:99–107. https://doi.org/10.1602/neurorx.2.1.99
Schuerwegh AJ, Dombrecht EJ, Stevens WJ, Van Offel JF, Bridts CH, De Clerck LS (2003) Influence of pro-inflammatory (IL-1 alpha, IL-6, TNF-alpha, IFN-gamma) and anti-inflammatory (IL-4) cytokines on chondrocyte function. Osteoarthr Cartil 11:681–687
Sercombe L, Veerati T, Moheimani F, Wu SY, Sood AK, Hua S (2015) Advances and challenges of liposome assisted drug delivery. Front Pharmacol 6:286. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2015.00286
TenBroek EM, Yunker L, Nies MF, Bendele AM (2016) Randomized controlled studies on the efficacy of antiarthritic agents in inhibiting cartilage degeneration and pain associated with progression of osteoarthritis in the rat. Arthritis Res Ther 18:24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-016-0921-5
Tilstra JS, Gaddy DF, Zhao J, Dave SH, Niedernhofer LJ, Plevy SE, Robbins PD (2014) Pharmacologic IKK/NF-kappaB inhibition causes antigen presenting cells to undergo TNFalpha dependent ROS-mediated programmed cell death. Sci Rep 4:3631. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep03631
Valovka T, Hottiger MO (2011) p65 controls NF-kappaB activity by regulating cellular localization of IkappaBbeta. Biochem J 434:253–263. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20101220
van der Kraan PM, van den Berg WB (2012) Chondrocyte hypertrophy and osteoarthritis: role in initiation and progression of cartilage degeneration? Osteoarthr Cartil 20:223–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2011.12.003
Wojdasiewicz P, Poniatowski LA, Szukiewicz D (2014) The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm 2014:561459. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/561459
Zhao Y, Feng G, Wang Y, Yue Y, Zhao W (2014) A key mediator, PTX3, of IKK/IkappaB/NF-kappaB exacerbates human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and dysfunction. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7:7699–7707
Zhong Z, Ji Q, Zhang JA (2010) Analysis of cationic liposomes by reversed-phase HPLC with evaporative light-scattering detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal 51:947–951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2009.10.001
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Arthritis Foundation (Discovery award; H. Cho) and Oxnard Foundation (Medical Research; H. Cho). This research also supported by a VA Merit Review award and VA Research Career Scientist Award (K. Hasty) from the Department of Veterans Affairs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FB and HC: designed and performed the experiments. FB and HC: performed the statistical analysis. FB and HC: wrote the manuscript. HC and KH: critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatti, F.U.R., Hasty, K.A. & Cho, H. Anti-inflammatory role of TPCA-1 encapsulated nanosomes in porcine chondrocytes against TNF-α stimulation. Inflammopharmacol 27, 1011–1019 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-0542-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-0542-5