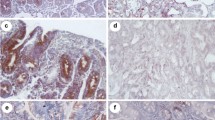
Abstract
Celiac Disease (CeD) is a chronic immune-mediated enteropathy, in which dietary gluten induces an inflammatory reaction, predominantly in the duodenum. Propolis is a resinous hive product, collected by honeybees from various plant sources. Propolis is well-known for its anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and immunomodulatory effects, due to its major compounds, polyphenols and flavonoids. The aim of our study was to assess the ex vivo effect of ethanolic extract of propolis (EEP) upon the activity and expression of iNOS, along with IFN-γ and IL-10 production in Algerian Celiac patients. In this context, PBMCs isolated from peripheral blood of Celiac patients and healthy controls were cultured with different concentrations of EEP. NO production was measured using the Griess method, whereas quantitation of IFN-γ and IL-10 levels was performed by ELISA. Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression, NFκB and pSTAT-3 activity were analyzed by immunofluorescence assay. Our results showed that PBMCs from Celiac patients produced high levels of NO and IFN-γ compared with healthy controls (HC). Interestingly, EEP reduced significantly, NO and IFN-γ levels and significantly increased IL-10 levels at a concentration of 50 µg/mL. Importantly, EEP downmodulated the iNOS expression as well as the activity of NFκB and pSTAT-3 transcription factors. Altogether, our results highlight the immunomodulatory effect of propolis on NO pathway and on pro-inflammatory cytokines. Therefore, we suggest that propolis may constitute a potential candidate to modulate inflammation during Celiac Disease and has a potential therapeutic value.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arroul-Lammali A, Rahal F, Chetouane R, Djeraba Z, Medjeber O, Ladjouze-Rezig A, Touil-Boukoffa C (2017) Ex vivo all-trans retinoic acid modulates NO production and regulates IL-6 effect during rheumatoid arthritis: a study in Algerian patients. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 39:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1080/08923973.2017.1285919
Bankova VS, Castro SLd, Marcucci MC (2000) Propolis: recent advances in chemistry and plant origin. Apidologie 31:3–15
Bankova V et al (2016) Standard methods for Apis mellifera propolis research. J Apic Res. https://doi.org/10.1080/00218839.2016.1222661
Beckett CG, Dell’Olio D, Shidrawi RG, Rosen-Bronson S, Ciclitira PJ (1999) Gluten-induced nitric oxide and pro-inflammatory cytokine release by cultured coeliac small intestinal biopsies. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 11:529–535
Belguendouz H et al (2011) Interferon-gamma and nitric oxide production during Behcet uveitis: immunomodulatory effect of interleukin-10. J Interferon Cytokine Res 31:643–651. https://doi.org/10.1089/jir.2010.0148
Belkhelfa M et al (2014) IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha are involved during Alzheimer disease progression and correlate with nitric oxide production: a study in Algerian patients. J Interferon Cytokine Res 34:839–847. https://doi.org/10.1089/jir.2013.0085
Bianchi ML, Bardella MT (2008) Bone in celiac disease. Osteoporos Int 19:1705–1716. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-008-0624-0
Bjorck S, Lindehammer SR, Fex M, Agardh D (2015) Serum cytokine pattern in young children with screening detected coeliac disease. Clin Exp Immunol 179:230–235. https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.12454
Blonska M, Bronikowska J, Pietsz G, Czuba ZP, Scheller S, Krol W (2004) Effects of ethanol extract of propolis (EEP) and its flavones on inducible gene expression in J774A.1 macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol 91:25–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2003.11.011
Boufadi YM et al (2014) Characterization and antioxidant properties of six Algerian propolis extracts: ethyl acetate extracts inhibit myeloperoxidase activity. Int J Mol Sci 15:2327–2345. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15022327
Brasier AR (2010) The nuclear factor-kappaB-interleukin-6 signalling pathway mediating vascular inflammation. Cardiovasc Res 86:211–218. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvq076
Cheikna Z et al. (2010) Polyphenols Content, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Ampelocissus grantii (Baker) Planch. (Vitaceae): A Medicinal Plant from Burkina Faso vol 6. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijp.2010.880.887
Christel Quettier-Deleu BG, Dine Thierry, Cazin Jean-Claude, Bailleul François, Brunet Claude, Luyckx Michel, Vasseur Jacques, Cazin Micheline, Trotin Francis (2000) Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activities of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) hulls and flour. J Ethnopharmacol 72:35–42
Cottica S, Sawaya A, N Eberlin M, Franco S, Zeoula L, Visentainer J (2011) Antioxidant activity and composition of propolis obtained by different methods of extraction vol 22. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0103-50532011000500016
de Sousa JR, de Sousa RPM, de Souza Aarao TL, Dias LB Jr, Oliveira Carneiro FR, Simoes Quaresma JA (2017) Response of iNOS and its relationship with IL-22 and STAT3 in macrophage activity in the polar forms of leprosy. Acta Trop 171:74–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2017.03.016
Dey P, Panga V, Raghunathan S (2016) PLoS One. A cytokine signalling network for the regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in rheumatoid arthritis 11:e0161306. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0161306
Djeraba Z, Boumedine K, Arroul-Lammali A, Otmani F, Belguendouz H, Touil-Boukoffa C (2014) Ex vivo immunomodulatory effect of all-trans-retinoic acid during Behcet’s disease: a study in Algerian patients. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 36:78–86. https://doi.org/10.3109/08923973.2013.873048
Driessler F, Venstrom K, Sabat R, Asadullah K, Schottelius AJ (2004) Molecular mechanisms of interleukin-10-mediated inhibition of NF-kappaB activity: a role for p50. Clin Exp Immunol 135:64–73
Esposito G et al (2007) Enteric glial-derived S100B protein stimulates nitric oxide production in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 133:918–925. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2007.06.009
Henshaw FR et al (2014) Topical application of the bee hive protectant propolis is well tolerated and improves human diabetic foot ulcer healing in a prospective feasibility study. J Diabetes Complic 28:850–857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2014.07.012
Holtmeier W, Caspary WF (2006) Celiac disease. Orphanet J Rare Dis 1:3. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1172-1-3
Horvath C, Darnell JJ (1997) The state of the STATs: recent developments in the study of signal transduction to the nucleus. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9:233–239
Ignarro LJ (2010) Nitric oxide: biology and pathobiology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Khayyal MT, el-Ghazaly MA, el-Khatib AS, Hatem AM, de Vries PJ, el-Shafei S, Khattab MM (2003) A clinical pharmacological study of the potential beneficial effects of a propolis food product as an adjuvant in asthmatic patients. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 17:93–102
Lahat N, Karban A, Gerstein R, Kinarty A, Lerner A (1999) Cytokine profile in Coeliac Disease. Scand J Immunol 49:441–446
Leon F, Sanchez L, Camarero C, Roy G (2005) Cytokine production by intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte subsets in celiac disease. Dig Dis Sci 50:593–600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-2480-5
Lirdprapamongkol K et al (2013) Chrysin overcomes TRAIL resistance of cancer cells through Mcl-1 downregulation by inhibiting STAT3 phosphorylation. Int J Oncol 43:329–337. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2013.1926
Mazzarella G (2015) Effector and suppressor T cells in celiac disease. World J Gastroenterol 21:7349–7356. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7349
Middleton SJ, Shorthouse M, Hunter JO (1993) Increased nitric oxide synthesis in ulcerative colitis. Lancet (London, England) 341:465–466
Mujica V et al (2017) The role of propolis in oxidative stress and lipid metabolism: a randomized controlled trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2017:4272940. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4272940
Murray IA, Daniels I, Coupland K, Smith JA, Long RG (2002) Increased activity and expression of iNOS in human duodenal enterocytes from patients with celiac disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 283:G319–326. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00324.2001
Murray IA, Bullimore DW, Long RG (2003) Fasting plasma nitric oxide products in coeliac disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 15:1091–1095. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.meg.0000085469.12407.0d
Musso A et al (2005) Signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 signaling pathway: an essential mediator of inflammatory bowel disease and other forms of intestinal inflammation. Inflamm Bowel Dis 11:91–98
Napetschnig J, Wu H (2013) Molecular basis of NF-kappaB signaling. Annu Rev Biophys 42:443–468. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biophys-083012-130338
Natarajan K, Singh S, Burke TR, Grunberger D, Aggarwal BB (1996) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester is a potent and specific inhibitor of activation of nuclear transcription factor NF-kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:9090–9095
Nilsen EM et al (1998) Gluten induces an intestinal cytokine response strongly dominated by interferon gamma in patients with celiac disease. Gastroenterology 115:551–563
Ningsih FN, Rifa’i M (2017) Propolis action in controlling activated T cell producing TNF-alfa and IFN-gamma in diabetic mice. Turk J Immunol 5. https://doi.org/10.25002/tji.2017.575
Orsatti CL, Missima F, Pagliarone AC, Sforcin JM (2010) Th1/Th2 cytokines’ expression and production by propolis-treated mice. J Ethnopharmacol 129:314–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2010.03.030
Orsi RO, SRC Funari, Soares AMVC, Calvi SA, Oliveira SL, Sforcin JM, Bankova V (2000) Immunomodulatory action of propolis on macrophage activation. J Venom Anim Toxins 6(2):205–219. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0104-79302000000200006
Pascual V, Dieli-Crimi R, Lopez-Palacios N, Bodas A, Medrano LM, Nunez C (2014) Inflammatory bowel disease and celiac disease: overlaps and differences. World J Gastroenterol 20:4846–4856. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.4846
Pautz A, Art J, Hahn S, Nowag S, Voss C, Kleinert H (2010) Regulation of the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Nitric Oxide 23:75–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2010.04.007
Rafa H et al (2013) IL-23/IL-17A axis correlates with the nitric oxide pathway in inflammatory bowel disease: immunomodulatory effect of retinoic acid. J Interferon Cytokine Res 33:355–368. https://doi.org/10.1089/jir.2012.0063
Rampertab SD, Mullin GE (eds) (2014) Celiac disease. Clinical gastroenterology, 1 edn. Humana Press, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-8560-5
Rashtak S, Murray JA (2012) Review article: coeliac disease, new approaches to therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 35:768–781. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2012.05013.x
Raso GM, Meli R, Di Carlo G, Pacilio M, Di Carlo R (2001) Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 expression by flavonoids in macrophage J774A.1. Life Sci 68:921–931
Reiling N, Ulmer AJ, Duchrow M, Ernst M, Flad HD, Hauschildt S (1994) Nitric oxide synthase: mRNA expression of different isoforms in human monocytes/macrophages. Eur J Immunol 24:1941–1944. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.1830240836
Sabat R, Grutz G, Warszawska K, Kirsch S, Witte E, Wolk K, Geginat J (2010) Biology of interleukin-10. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 21:331–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2010.09.002
Samadi N, Mozaffari-Khosravi H, Rahmanian M, Askarishahi M (2017) Effects of bee propolis supplementation on glycemic control, lipid profile and insulin resistance indices in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial. J Integr Med 15:124–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2095-4964(17)60315-7
Schroder K, Hertzog PJ, Ravasi T, Hume DA (2004) Interferon-gamma: an overview of signals, mechanisms and functions. J Leukoc Biol 75:163–189. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0603252
Sforcin JM (2007) Propolis and the immune system: a review. J Ethnopharmacol 113:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2007.05.012
Song YS, Park EH, Hur GM, Ryu YS, Kim YM, Jin C (2002) Ethanol extract of propolis inhibits nitric oxide synthase gene expression and enzyme activity. J Ethnopharmacol 80:155–161
Tomazevic T, Jazbec J (2013) A double blind randomised placebo controlled study of propolis (bee glue) effectiveness in the treatment of severe oral mucositis in chemotherapy treated children. Complement Ther Med 21:306–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2013.04.002
Toreti VC, Sato HH, Pastore GM, Park YK (2013) Recent progress of propolis for its biological and chemical compositions and its botanical origin. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013:697390. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/697390
Uspenskaya ID, Erzutova MV, Korkotashvili LV, Kolesov SA, Shirokova NY (2014) The significance of increased levels of end nitric oxide metabolites in blood serum of children with celiac disease. Bratislava Med J 115:712–717. https://doi.org/10.4149/bll_2014_138
Wadsworth TL, Koop DR (1999) Effects of the wine polyphenolics quercetin and resveratrol on pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Biochem Pharmacol 57:941–949
Yang H, Dong Y, Du H, Shi H, Peng Y, Li X (2011) Antioxidant compounds from propolis collected in Anhui. China Mol 16:3444–3455. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16043444
Zhang J (2007) Yin and yang interplay of IFN-gamma in inflammation and autoimmune disease. J Clin Investig 117:871–873. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci31860
Ziesche E, Bachmann M, Kleinert H, Pfeilschifter J, Muhl H (2007) The interleukin-22/STAT3 pathway potentiates expression of inducible nitric-oxide synthase in human colon carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 282:16006–16015. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M611040200
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the beekeeper Mohamed Kacioui, Dr. Belanteur (Central laboratory, Nafissa Hamoud University Hospital, Algiers, Algeria), Dr. Nassima Behairi (USTHB, Algiers, Algeria), Sarra Benkhelifa (USTHB, Algiers, Algeria) and Fayçal Medjeber (Spectrol Lab, Algeria) for their technical assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by national thematic research agency in development health science (ATRSS, ex ANDRS), project code N°43-ANDRS-2011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure statement
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Medjeber, O., Touri, K., Rafa, H. et al. Ex vivo immunomodulatory effect of ethanolic extract of propolis during Celiac Disease: involvement of nitric oxide pathway. Inflammopharmacol 26, 1469–1481 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-0460-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-0460-6