Abstract
Background
Resveratrol exerts an anti-inflammatory effect on collagen-induced arthritis and osteoarthritis in rats via activation of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1). Autophagy can be induced by resveratrol and leads to amelioration of interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) release in vitro. We aimed to determine the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of resveratrol in patients with gout.
Methods
Blood samples were obtained from patients with acute gout, intercritical gout (IG) and healthy controls (HC). The mRNA and protein levels of SIRT1 and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kB) p65 were determined in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) lysate from these patients. In the in vitro experiment, SIRT1, autophagy-related genes (beclin-1 and microtubule-associated protein 1 light-chain 3) and key genes involved in the gouty inflammatory pathway, including NF-κB p65, NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3), caspase-1 and IL-1β, were determined in PBMCs lysate or plasma from IG patients exposed to monosodium urate (MSU) crystals with or without resveratrol.
Results
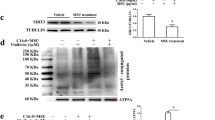
The mRNA and protein levels of SIRT1 were downregulated in PBMCs from gout patients in comparison with HC. In the in vitro experiment, the protein levels of SIRT1 were downregulated in PBMCs from IG patients exposed to MSU crystals and were restored by resveratrol in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, high doses of resveratrol ameliorated the release of the inflammatory cytokine IL-1β. In addition, the mRNA levels of NLRP3 and NF-κB p65 were regulated by resveratrol, but caspase-1 and IL-1β were not. Furthermore, resveratrol promoted MSU-induced autophagy in PBMCs from patients with gout.
Conclusion
These findings suggest that resveratrol ameliorates gouty inflammation via upregulation of SIRT1 to promote autophagy in patients with gout.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baur JA (2010) Resveratrol sirtuins and the promise of a DR mimetic. Mech Ageing Dev 131:261–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2010.02.007
Baur JA, Sinclair DA (2006) Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: the in vivo evidence. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:493–506. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2060
Carneiro LA, Travassos LH (2013) The interplay between NLRS and autophagy in immunity and inflammation. Front Immunol 4:361. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2013.00361
Chen CJ et al (2006) MyD88-dependent IL-1 receptor signaling is essential for gouty inflammation stimulated by monosodium urate crystals. J Clin Investig 116:2262–2271. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci28075
Choi AM, Ryter SW, Levine B (2013) Autophagy in human health and disease. New Engl J Med 368:651–662. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1205406
Du Jin-feng LF, Jing Tian, Xi Xie, Jin-wei Chen, Jie-Sheng Gao (2009) The anti-inflammatory effect of Resveratrol on collagen-induced arthritis rats. Chin J Rheumatol 13:123–126
Elmali N, Esenkaya I, Harma A, Ertem K, Turkoz Y, Mizrak B (2005) Effect of resveratrol in experimental osteoarthritis in rabbits. Inflamm Res Off J Eur Histamine Res Soc 54:158–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-004-1341-6
Getting SJ, Christian HC, Flower RJ, Perretti M (2002) Activation of melanocortin type 3 receptor as a molecular mechanism for adrenocorticotropic hormone efficacy in gouty arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 46:2765–2775. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.10526
Haigis MC, Sinclair DA (2010) Mammalian sirtuins: biological insights and disease relevance. Ann Rev Pathol 5:253–295. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pathol.4.110807.092250
Howitz KT et al (2003) Small molecule activators of sirtuins extend Saccharomyces cerevisiae lifespan. Nature 425:191–196. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01960
Jones SA, Mills KH, Harris J (2013) Autophagy and inflammatory diseases. Immunol Cell Biol 91:250–258. https://doi.org/10.1038/icb.2012.82
Levine B, Mizushima N, Virgin HW (2011) Autophagy in immunity and inflammation. Nature 469:323–335. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09782
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Martinon F, Petrilli V, Mayor A, Tardivel A, Tschopp J (2006) Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NALP3 inflammasome. Nature 440:237–241. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04516
Qing YF, Zhang QB, Yang QB, Xie WG, Zhou JG (2014a) Altered expression of NLRP3 inflammasome in peripheral blood from gout patients might be associated with gouty arthritis. Gout Hyperuricemia 1:25–32. https://doi.org/10.3966/231191872014030001005
Qing YF, Zhang QB, Zhou JG, Jiang L (2014b) Changes in toll-like receptor (TLR)4-NFkappaB-IL1beta signaling in male gout patients might be involved in the pathogenesis of primary gouty arthritis. Rheumatol Int 34:213–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2856-3
Shi CS et al (2012) Activation of autophagy by inflammatory signals limits IL-1beta production by targeting ubiquitinated inflammasomes for destruction. Nat Immunol 13:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2215
Shintani T, Klionsky DJ (2004) Autophagy in health and disease: a double-edged sword. Science 306:990–995. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1099993
Stark K et al (2008) Association of common polymorphisms in GLUT9 gene with gout but not with coronary artery disease in a large case-control study. PLoS ONE 3:e1948. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001948
Wallace SL, Robinson H, Masi AT, Decker JL, McCarty DJ, Yu TF (1977) Preliminary criteria for the classification of the acute arthritis of primary gout. Arthritis Rheum 20:895–900
Wang B et al (2014) Resveratrol-enhanced autophagic flux ameliorates myocardial oxidative stress injury in diabetic mice. J Cell Mol Med 18:1599–1611. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12312
Weavers H, Evans IR, Martin P, Wood W (2016) Corpse engulfment generates a molecular memory that primes the macrophage inflammatory response. Cell 165:1658–1671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.04.049
Wu Y et al (2011) Resveratrol-activated AMPK/SIRT1/autophagy in cellular models of Parkinson’s disease. Neuro-Signals 19:163–174. https://doi.org/10.1159/000328516
Wu J, Li X, Zhu G, Zhang Y, He M, Zhang J (2016) The role of Resveratrol-induced mitophagy/autophagy in peritoneal mesothelial cells inflammatory injury via NLRP3 inflammasome activation triggered by mitochondrial ROS. Exp Cell Res 341:42–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.01.014
Xuzhu G, Komai-Koma M, Leung BP, Howe HS, McSharry C, McInnes IB, Xu D (2012) Resveratrol modulates murine collagen-induced arthritis by inhibiting Th17 and B-cell function. Ann Rheum Dis 71:129–135. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2011.149831
Yeung F, Hoberg JE, Ramsey CS, Keller MD, Jones DR, Frye RA, Mayo MW (2004) Modulation of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription and cell survival by the SIRT1 deacetylase. EMBO J 23:2369–2380. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600244
Acknowledgements
This research was supported partly by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81670801, 81800776), Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2017JY0037, 2018JY0498), Education Agency of Sichuan Province (15ZB0202), Sichuan Medical Association (S16027), Sichuan Health and Family Planning Commission (17PJ059) and Science and Technology Strategic Cooperation Program between Nanchong City and University (NSMC170429).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Qi-Bin Yang and Yong-Long He are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, QB., He, YL., Zhong, XW. et al. Resveratrol ameliorates gouty inflammation via upregulation of sirtuin 1 to promote autophagy in gout patients. Inflammopharmacol 27, 47–56 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-00555-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-00555-4