Abstract
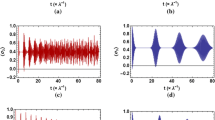
Using dressed state method, we cleverly solve the dynamics of atom-field interaction in the process of two-photon absorption and emission between atomic levels. Here we suppose that the atom is initially in the ground state and the optical field is initially in Fock state, coherent state or thermal state, respectively. The properties of the atom, including the population in excited state and ground state, the atom inversion, and the properties for optical field, including the photon number distribution, the mean photon number, the second-order correlation function and the Wigner function, are discussed in detail. We derive their analytical expressions and then make numerical analysis for them. In contrast with Jaynes-Cummings model, some similar results, such as quantum Rabi oscillation, revival and collapse, are also exhibit in our considered model. Besides, some novel nonclassical states are generated.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scully, M.O., Zubairy, M.S.: Quantum Optics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1997)
Walls, D.F., Milburn, G.J.: Quantum optics. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Orszag, M.: Quantum optics. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Gerry, C.C., Knight, P.: Introductory Quantum Optics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2005)
Barnett, S.M., Radmore, P.M.: Methods in Theoretical Quantum Optics. Claredon Press, Oxford (1997)
Haroche, S., Raimond, J.M.: Exploring the quantum: Atoms, Cavities and Photons. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2006)
Meystre, P., Sargent, M. III: Element of quantum optics. Springer, Berlin (2007)
Cohen-Tannoudji, C., Dupont-Roc, J., Grynberg, G.: Atom-Photon Interactions. Wiley, New York (1992)
Weissbluth, M.: Photon-Atom Interactions. Academic Press, New York (1989)
Allen, L., Eberly, J.H.: Optical Resonance and Two-Level Atoms. Wiley, New York (1975)
Eberly, J.H., Narozhny, N.B., Sanchez-Mondragon, J.J.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 44, 1323–1326 (1980)
Narozhny, N.B., Sanchez-Mondragon, J.J., Eberly, J.H.: Phys. Rev. A 23, 236–247 (1981)
Jaynes, E.T., Cummings, F.W.: Proc. Inst. Elect. Eng. 51, 89–109 (1963)
Cummings, F.W.: Phys. Rev. 149, A1051–A1056 (1965)
Knight, P.L., Radmore, P.M.: Phys. Rev. A 26, 676–679 (1982)
Rabi, I.I.: Phys. Rev. 51, 652–654 (1937)
Dell’Anno, F., De Siena, S., Illuminati, F.: Phys. Rep. 428, 53–168 (2006)
Yoo, H.J., Eberly, J.H.: Phys. Rep. 118, 239–337 (1985)
Shore, B.W., Knight, P.L.: J. Mod. Opt. 40, 1195–1238 (1993)
Messina, A., Maniscalco, S., Napoli, A.: J. Mod. Opt. 50, 1–49 (2003)
Schleich, W.P.: Quantum Optics in Phase Space. Wiley-Vch Verlag, Berlin (2001)
Knight, P.L., Milonni, P.W.: Phys. Rep. 66, 21–107 (1980)
Allen, L., Knight, P.L.: Concepts of Quantum Optics. Pergamon, Oxford (1983)
Wigner, E.P.: Phys. Rev. 40, 749–759 (1932)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11665013).
Appendix: Wigner function for the operator |n〉〈m|
Appendix: Wigner function for the operator |n〉〈m|
Substituting
into (17), we have
Inserting the completeness of the coherent states, i.e. \(\int \frac {d^{2}z_{1} }{\pi }\left \vert z_{1}\right \rangle \left \langle z_{1}\right \vert = 1\) and \(\int \frac {d^{2}z_{2}}{\pi }\left \vert z_{2}\right \rangle \left \langle z_{2}\right \vert = 1\), we have
After employing the integration, we obtain the Wigner function for the operator |n〉〈m|,
Using this expression, the Wigner function for any quantum state can be expressed based on its expansion in Fock state space.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Jm., Xu, Xx. Dynamical Evolution of Properties for Atom and Field in the Process of Two-Photon Absorption and Emission Between Atomic Levels. Int J Theor Phys 57, 2167–2191 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3741-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3741-3