Abstract
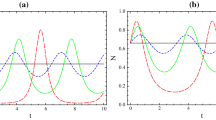
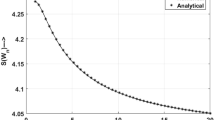
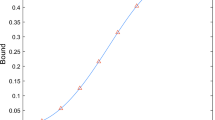
For carrying out many quantum information protocols entanglement must be established in advance between two distant parties. Practically, inevitable interaction of entangled subsystems with their environments during distribution and storage will result in degradation of entanglement. Here we show that some partially entangled states are more robust than maximally entangled states in terms of the residual quantum correlation measured by concurrence, fully entangled fraction, and quantum discord, respectively. This phenomenon leads to the fact that nonmaximally entangled states can outperform maximally entangled states for quantum correlation distribution and storage under the amplitude damping. These results can also educe a noticeable consequence that the ordering of states under quantum correlation monotones can be reversed even by local trace-preserving and completely positive maps.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pan, J.W., Chen, Z.B., Lu, C.Y., Weinfurter, H., Zeilinger, A., Żukowski, M.: Rev. Mod. Phys. 84, 777–838 (2012)
Kraus, B., Cirac, J. I.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 013602 (2004)
Paternostro, M., Son, W., Kim, M.S.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 197901 (2004)
Guo, Y.: Int. J. Theor. Phys. 51, 2954–2959 (2012)
Slodička, L., Hétet, G., Röck, N., Schindler, P., Hennrich, M., Blatt, R.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 083603 (2013)
Cirac, J.I., Zoller, P., Kimble, H.J., Mabuchi, H.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 3221–3224 (1997)
Qiu, T.H., Yang, G.J.: Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52, 2530–2536 (2013)
Sangouard, N., Simon, C, de Riedmatten, H., Gisin, N. Rev. Mod. Phys. 83, 33–80 (2011)
Duan, L.M., Monroe, C.: Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 1209–1224 (2010)
Bellomo, B., Lo Franco, R., Compagno, G.: Phys. Rev. A 77, 032342 (2008)
Maziero, J., Céleri, L.C., Serra, R.M., Vedral, V.: Phys. Rev. A 80, 044102 (2009)
Fanchini, F.F., Werlang, T., Brasil, C.A., Arruda, L.G.E., Caldeira, A.O.: Phys. Rev. A 81, 052107 (2010)
Wang, B., Xu, Z.Y., Chen, Z.Q., Feng, M.: Phys. Rev. A 81, 014101 (2010)
Li, J.G., Zou, J., Shao, B.: Phys. Rev. A 82, 042318 (2010)
Huang, P., Zhu, J., Qi, X.X., He, G.Q., Zeng, G.H.: Quantum Inf. Process 11, 1845–1865 (2012)
Zhang, J.: Quantum Inf. Process 12, 1627–1636 (2013)
Shang, C.J., Chen, T., Liu, J.B., et al. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 49, 717–727 (2010)
Ji, Y.H., Wang, Z.S., Hu, J.J.: Int. J. Theor. Phys. 50, 644–653 (2011)
Konrad, T., De Melo, F., Tiersch, M., et al.: Nature Phys. 4, 99–102 (2008)
Xu, J.S., Li, C.F., Xu, X.Y., et al.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 240502 (2009)
Tiersch, M., de Melo, F., Konrad, T., Buchleitner, A.: Quantum Inf. Process. 8, 523–534 (2009)
Nielsen, M., Chuang, I.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Wootters, W.K.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 2245 (1998)
Horodecki, M., Horodecki, P., Horodecki, R.: Phys. Rev. A 60, 1888–1898 (1999)
Ollivier, H., Zurek, W.H.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 017901 (2001)
Henderson, L., Vedral, V.: J. Phys. A 34, 6899–6905 (2001)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Popescu, S., et al. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 722 (1996)
Bandyopadhyay, S., Ghosh, A.: Phys. Rev. A 86 (R), 020304 (2012)
Lo Franco, R., Bellomo, B., Maniscalco, S., Compagno, G.: Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 27, 1345053 (2013)
Modi, K., Brodutch, A., Cable, H., Paterek, T., Vedral, V.: Rev. Mod. Phys. 84, 1655–1707 (2012)
Dakić, B., Lipp, Y.O., Ma, X., et al.: Nature Phys. 8, 666–670 (2012)
Brodutch, A.: Phys. Rev. A 88, 022307 (2013)
Brodutch, A., Terno, D.R. Phys. Rev. A 83 (R), 010301 (2011)
Yin, J., Ren, J.G., Lu, H., et al.: Nature 488, 185 (2012)
Yu, T., Eberly, J.H.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 140404 (2004)
Bellomo, B., Lo Franco, R., Compagno, G.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 160502 (2007)
Almeida, M.P, de Melo, F., Hor-Meyll, M., et al.: Science 316, 579–582 (2007)
Lo Franco, R., DArrigo, A., Falci, G., Compagno, G., Paladino, E.: Phys. Scr. T147, 014019 (2012)
Badziag, P., Horodecki, M., Horodecki, P., Horodecki, R.: Phys. Rev. A 62, 012311 (2000)
Bandyopadhyay, S.: Phys. Rev. A 65, 022302 (2002)
Verstraete, F., Verschelde, H.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 097901 (2003)
Verstraete, F., Verschelde, H.: Phys. Rev. A 66, 022307 (2002)
Vidal, G., Werner, R.F.: Phys. Rev. A 65, 032314 (2002)
Luo, S.: Phys. Rev. A 77, 042303 (2008)
Ali, M., Rau, A.R.P., Alber, G.: Phys. Rev. A 81, 042105 (2010)
Chen, Q., Zhang, C., Yu, S., Yi, X.X., Oh, C.H.: Phys. Rev. A 84, 042313 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the NSFC (No. 11004050 and No. 11375060), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (No. 2013T60769), and the Hunan Provincial Applied Basic Research Base of Optoelectronic Information Technology (No. GDXX007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, XW., Tang, SQ., Yuan, JB. et al. Nonmaximally Entangled States can be Better for Quantum Correlation Distribution and Storage. Int J Theor Phys 54, 1461–1469 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-014-2343-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-014-2343-y