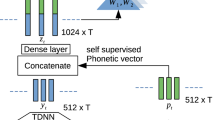
Abstract
Current speaker verification systems achieve impressive results in quiet and controlled environments. However, using these systems in real-life conditions significantly impacts their ability to continue delivering satisfactory performance. In this paper, we present a novel approach that addresses this challenge by optimizing the text-independent speaker verification task in noisy and far-field conditions and when it is subject to spoofing attacks. To perform this optimization, gammatone frequency cepstral coefficients (GFCC) are used as input features of a new factorized time delay neural network (FTDNN) speaker embedding encoder using a time-restricted self-attention mechanism (Att-FTDNN), at the end of the frame level. The Att-FTDNN-based speaker verification system is then integrated into a spoofing-aware configuration to measure the ability of this encoder to prevent false accepts due to spoofing attacks. The in-depth evaluation carried out in noisy and far-field conditions, as well as in the context of spoofing-aware speaker verification, demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed Att-FTDNN encoder. The results showed that compared to the FDNN- and TDNN-based baseline systems, the proposed Att-FTDNN encoder using GFCC achieves 6.85% relative improvement in terms of minDCF for the VOiCES test set. A noticeable decrease of the equal error rate is also observed when the proposed encoder is integrated within a spoofing-aware speaker verification system tested with the ASVSpoof19 dataset.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets and code generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available on reasonable request.
Notes
National Institute of Standards and Technology Speaker Recognition Evaluations.
References
Alenin, A., Torgashov, N., Okhotnikov, A., Makarov, R., & Yakovlev, I. (2022). A subnetwork approach for spoofing aware speaker verification. In Proceedings in Interspeech 2022 (pp. 2888–2892).
Benhafid, Z., Selouani, S. A., & Amrouche, A. (2023). Light-spinenet variational autoencoder for logical access spoof utterances detection in speaker verification systems. In Proceedings in bios-mart (pp. 1–4).
Benhafid, Z., Selouani, S. A., Yakoub, M. S., & Amrouche, A. (2021). LARIHS ASSERT reassessment for logical access ASVspoof 2021 Challenge. In Proceedings of 2021 edition of the automatic speaker verification and spoofing countermeasures challenge (pp. 94–99).
Bogdanov, D., Wack, N., Gómez, E., Gulati, S., Herrera, P., Mayor, O., & Serra, X. (2013). Essentia: An audio analysis library for music information retrieval. In Proceedings of the 14th international society for music information retrieval conference, (ISMIR 2013).
Cai, D., & Li, M. (2021). Embedding aggregation for far-field speaker verification with distributed microphone arrays. In 2021 IEEE spoken language technology workshop (SLT) (pp. 308–315).
Chen, Z., & Lin, Y. (2020). Improving X-vector and PLDA for text-dependent speaker verification. In Proceedings of Interspeech, 2020, 726–730.
Choi, J. -H., Yang, J. -Y., Jeoung, Y. -R., & Chang, J. -H. (2022). HYU submission for the SASV challenge 2022: Reforming speaker embeddings with spoofing-aware conditioning. In Proceedings Interspeech 2022 (pp. 2873-2877).
Chung, J. S., Nagrani, A., & Zisserman, A. (2018). VoxCeleb2: Deep speaker recognition. In Interspeech, 2018, 1086–1090. Retrieved from https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.05622v2
Desplanques, B., Thienpondt, J., & Demuynck, K. (2020). ECAPA-TDNN: Emphasized channel attention, propagation and aggregation in TDNN based speaker verification. In Proceedings Interspeech 2020 (Vol. 2020-Oct, pp. 3830–3834).
Gao, Z., Mak, M. -W., & Lin, W. (2022). UNet-DenseNet for robust far-field speaker verification. In Proceedings Interspeech (pp. 3714–3718).
Gomez-Alanis, A., Gonzalez-Lopez, J. A., Dubagunta, S. P., Peinado, A. M., & Magimai.-Doss, M. (2021). On joint optimization of automatic speaker verification and anti-spoofing in the embedding space. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 16, 1579–1593. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2020.3039045
Gusev, A., Volokhov, V., Andzhukaev, T., Novoselov, S., Lavrentyeva, G., Volkova, M., & Matveev, Y. (2020). Deep speaker embeddings for far-field speaker recognition on short utterances. In The speaker and language recognition workshop (Odyssey 2020) (pp. 179–186).
Hao, X., Su, X., Horaud, R., & Li, X. (2021). Fullsubnet: A full-band and sub-band fusion model for real-time single-channel speech enhancement. In ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 6633–6637).
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2015, Dec). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (Vol. 2016-Dec, pp. 770–778). Retrieved from https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385v1
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Van Der Maaten, L., & Weinberger, K. Q. (2017). Densely connected convolutional networks. In 2017 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 2261–2269).
Jeevan, M., Dhingra, A., Hanmandlu, M., & Panigrahi, B. (2017). Robust speaker verification using GFCC based i-vectors. In Proceedings of the international conference on signal, networks, computing, and systems (pp. 85–91).
Jee-weon, J., Tak, H., Jin Shim, H., Heo, H. -S., Lee, B. -J., Chung, S. -W., & Kinnunen, T. (2022). SASV 2022: The first spoofing- aware speaker verification challenge. In Proceedings Interspeech 2022 (pp. 2893–2897).
Jung, J. -w., Heo, H. -S., Tak, H., Shim, H.-j., Chung, J. S., Lee, B. -J., & Evans, N. (2022). Aasist: Audio anti-spoofing using integrated spectro-temporal graph attention networks. In ICASSP 2022 - 2022 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 6367–6371).
Jung, J. -W., Kim, J. -H., Shim, H. -J., Kim, S. -b., & Yu, H. -J. (2020, May). Selective deep speaker embedding enhancement for speaker verification. In Odyssey 2020 the speaker and language recognition workshop (pp. 171–178).
Kanervisto, A., Hautamäki, V., Kinnunen, T., & Yamagishi, J. (2022). Optimizing tandem speaker verification and anti-spoofing systems. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 30, 477–488. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASLP.2021.3138681
Kenny, P. (2010). Bayesian speaker verification with heavy-tailed priors. Odyssey.
Kim, J. -H., Heo, J., Jin Shim, H., & Yu, H. -J. (2022). Extended U-net for speaker verification in noisy environments. In Proceedings Interspeech 2022 (pp. 590–594).
Ko, T., Peddinti, V., Povey, D., Seltzer, M. L., & Khudanpur, S. (2017, Jun). A study on data augmentation of reverberant speech for robust speech recognition. In IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing - proceedings (ICASSP) (pp. 5220–5224).
Krobba, A., Debyeche, M., & Selouani, S. A. (2023). A novel hybrid feature method based on Caelen auditory model and gammatone filterbank for robust speaker recognition under noisy environment and speech coding distortion. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 82(11), 1619516212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-14068-4
Kumar Nandwana, M., Van Hout, J., Richey, C., Mclaren, M., Barrios, M. A., & Lawson, A. (2019). The VOiCES from a distance challenge 2019. In Interspeech 2019 (pp. 2438–2442). Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.21437/Interspeech.2019-1837
Liu, T., Das, R. K., Aik Lee, K., & Li, H. (2022). MFA: TDNN with multi-scale frequency-channel attention for text-independent speaker verification with short utterances. In ICASSP 2022 - 2022 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 7517–7521).
Liu, X., Sahidullah, M., & Kinnunen, T. (2020). A comparative Re-assessment of feature extractors for deep speaker embeddings. In Proceedings Interspeech, 2020, 3221–3225.
Liu, X., Sahidullah, M., & Kinnunen, T. (2021a). Optimized power normalized cepstral coefficients towards robust deep speaker verification. In 2021 IEEE automatic speech recognition and understanding workshop - proceedings (ASRU 2021) (pp. 185–190).
Liu, X., Sahidullah, M., & Kinnunen, T. (2021). Optimizing multi-taper features for deep speaker verification. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 28, 2187–2191. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2021.3122796
Min Kye, S., Kwon, Y., & Son Chung, J. (2021). Cross attentive pooling for speaker verification. In 2021 IEEE spoken language technology workshop (SLT) (pp. 294–300).
Mohammadamini, M., Matrouf, D., Bonastre, J. -F., Dowerah, S., Serizel, R., & Jouvet, D. (2022). A comprehensive exploration of noise robustness and noise compensation in resnet and TDNN-based speaker recognition systems. In Eusipco 2022-30th European signal processing conference.
Mošner, L., Plchot, O., Burget, L., & Černockỳ, J. H. (2022). Multisv: Dataset for far-field multichannel speaker verification. In ICASSP 2022 - 2022 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 7977–7981).
Nagrani, A., Chung, J. S., Xie, W., & Zisserman, A. (2020). Voxceleb: Large-scale speaker verification in the wild. Computer Speech & Language, 60, 101027. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CSL.2019.101027
Nagraniy, A., Chungy, J. S., & Zisserman, A. (2017). VoxCeleb: A large-scale speaker identification dataset. In Interspeech 2017 (pp. 2616–2620).
Okabe, K., Koshinaka, T., & Shinoda, K. (2018). Attentive statistics pooling for deep speaker embedding. In Proceedings Interspeech, 2018, 2252–2256.
Povey, D., Cheng, G., Wang, Y., Li, K., Xu, H., Yarmohamadi, M., & Khudanpur, S. (2018). Semi-orthogonal low-rank matrix factorization for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the annual conference of the international speech communication association, Interspeech, 2018, 3743–3747.
Povey, D., Ghoshal, A., Boulianne, G., Burget, L., Glembek, O., Goel, N., & Vesely, K. V. (2011). The Kaldi Speech Recognition Toolkit. In IEEE 2011 workshop on automatic speech recognition and understanding. Hilton Waikoloa Village, Big Island, Hawaii, US.
Povey, D., Hadian, H., Ghahremani, P., Li, K., & Khudanpur, S. (2018, Sep). A time-restricted self-attention layer for ASR. In IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing - proceedings (ICASSP), 2018, 5874–5878).
Povey, D., Zhang, X., & Khudanpur, S. (2015). Parallel training of DNNs with natural gradient and parameter averaging. In 3rd international conference on learning representations, (ICLR 2015) - workshop track proceedings.
Qin, X., Li, M., Bu, H., Narayanan, S., & Li, H. (2022). Far-field speaker verification challenge (FFSVC) 2022: Challenge evaluation plan.
Qin, X., Li, M., Bu, H., Rao, W., Das, R. K., Narayanan, S., & Li, H. (2020). The INTERSPEECH 2020 far-field speaker verification challenge. In Proceedings Interspeech 2020 (pp. 3456–3460).
Richey, C., Barrios, M. A., Armstrong, Z., Bartels, C., Franco, H., Graciarena, M., & Ni, K. (2018). Voices obscured in complex environmental settings (VOICES) corpus. In Proceedings of the annual conference of the international speech communication association, Interspeech, 2018, 1566–1570.
Rybicka, M., Villalba, J., Zelasko, P., Dehak, N., & Kowalczyk, K. (2021). Spine2net: Spinenet with res2net and time-squeeze and - excitation blocks for speaker recognition. In Proceedings Interspeech, 1, 491–495.
Segbroeck, M.V., Zaid, A., Kutsenko, K., Huerta, C., Nguyen, T., Luo, X., & Maas, R. (2020). DiPCo Dinner Party Corpus. In Proceedings Interspeech 2020 (pp. 434–436).
Shao, Y., & Wang, D. L. (2008). Robust speaker identification using auditory features and computational auditory scene analysis. In IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing - proceedings (ICASSP).
Shim, H.-j., Jung, J.-w., Kim, J.-h., Kim, S.-b, & Yu, H.-j. (2020). Integrated replay spoofingaware text-independent speaker verification. Applied Sciences, 10(18), 6292. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10186292
Shtrosberg, A., Villalba, J., Dehak, N., Cohen, A., & Ben-Yair, B. (2021). Invariant representation learning for robust far-field speaker recognition. In International conference on statistical language and speech processing (pp. 97–110).
Snyder, D., Chen, G., & Povey, D. (2015). MUSAN: A music, speech, and noise corpus. arXiv preprint,Retrieved from arXiv:1510.08484v1http://www.itl.nist.gov/iad/mig/tests/sre/
Snyder, D., Garcia-Romero, D., Povey, D., & Khudanpur, S. (2017). Deep neural network embeddings for text-independent speaker verification. In Proceedings Interspeech 2017 (pp. 999–1003).
Snyder, D., Garcia-Romero, D., Sell, G., Povey, D., & Khudanpur, S. (2018). XVectors: Robust DNN embeddings for speaker recognition. In IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing - proceedings (ICASSP), 2018, 5329–5333.
Taherian, H., Wang, Z. Q., Chang, J., & Wang, D. (2020). Robust speaker recognition based on single-channel and multi-channel speech enhancement. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio Speech and Language Processing, 28, 1293–1302. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASLP.2020.2986896
Thienpondt, J., Desplanques, B., & Demuynck, K. (2021). Integrating frequency translational invariance in TDNNs and frequency positional information in 2D ResNets to enhance speaker verification. In Proceedings Interspeech, 3, 2018–2022.
Valero, X., & Alias, F. (2012). Gammatone cepstral coefficients: Biologically inspired features for non-speech audio classification. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 14(6), 1684–1689. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2012.2199972
Variani, E., Lei, X., Mcdermott, E., Lopez Moreno, I., & Gonzalez-Dominguez, J. (2014). Deep neural networks for small footprint text-dependent speaker verification. In 2014 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 4052–4056).
Villalba, J., Chen, N., Snyder, D., Garcia-Romero, D., McCree, A., Sell, G., & Dehak, N. (2020). State-of-the-art speaker recognition with neural network embeddings in NIST SRE18 and speakers in the wild evaluations. Computer Speech & Language, 60, 101026. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CSL.2019.101026
Wang, M., Feng, D., Su, T., & Chen, M. (2022). Attention-based temporal-frequency aggregation for speaker verification. Sensors, 22(6), 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22062147
Wang, X., Qin, X., Wang, Y., Xu, Y., & Li, M. (2022). The DKU-OPPO system for the 2022 spoofing-aware speaker verification challenge. In Proceedings Interspeech, (pp. 4396–4400).
Wang, X., Yamagishi, J., Todisco, M., Delgado, H., Nautsch, A., Evans, N., & Ling, Z.-H. (2020). Asvspoof 2019: A large-scale public database of synthesized, converted and replayed speech. Computer Speech & Language, 64, 101114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csl.2020.101114
Yu, Y. Q., & Li, W. J. (2020). Densely connected time delay neural network for speaker verification. In Proceedings Interspeech, 2020, 921–925.
Zhang, R., Wei, J., Lu, W., Wang, L., Liu, M., Zhang, L., & Xu, J. (2020). ARET: Aggregated residual extended time-delay neural networks for speaker verification. In Proceedings Interspeech, 2020, 946–950.
Zhu, Y., Ko, T., Snyder, D., Mak, B., & Povey, D. (2018). Self-attentive speaker embeddings for text-independent speaker verification. In Proceedings Interspeech, 2018, 3573–3577.
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank the Digital Research Alliance of Canada for supplying the computational resources used to achieve the experiments.
Funding
This work has received funding from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada under the reference number RGPIN-2018-05221.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Benhafid, Z., Selouani, S.A., Amrouche, A. et al. Attention-based factorized TDNN for a noise-robust and spoof-aware speaker verification system. Int J Speech Technol 26, 881–894 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-023-10059-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-023-10059-4