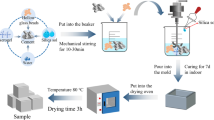
Abstract
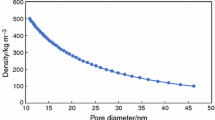
SiO2 aerogel is a sort of nano-particles&pores porous medium possessed of excellent thermal insulation performance which is worth excavating related parameters. Based on simple experiments and simplified heat transfer equations, as many parameters as possible can be deduced under limited conditions. In this paper, the hot surface’s temperature response of SiO2 aerogel composites with different components of fiber and opacifier are measured by experiment, and the thermal conductivity, λ, and thermal effusivity, \(\sqrt {\lambda \rho c_{{\text{p}}} }\), are λ = 0.0270–0.0386 W·m−1·K−1 and \(\sqrt {\lambda \rho c_{{\text{p}}} }\)= 75.933–113.185 J·m−2·K·s−0.5 at Tcold = 298 K & ΔT < 15 K, respectively. Through the inverse analysis of the Levenberg–Marquardt method, the λ, specific heat capacity, cp, and thermal diffusivity, a, can be estimated by analyzing the above hot surface’s temperature response, which is λ = 0.0284–0.0391 W·m−1·K−1, cp = 761.7–2237.3 J·kg−1·K−1, a = 5.575–13.570 × 10–8 m2·s−1, respectively, where the maximum deviation is no more than 6.11 %. Sensitivity coefficients of λ and cp co-influence initial unsteady-state while λ dominates heat transfer after that. Micron SiC and SiO2 hollow spheres inside SiO2 aerogel will inhibit the the thermal radiation and improved the insulation performance at large ΔT.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Thermal diffusivity
- c p :
-
Specific heat, J·kg−1·K−1
- F :
-
Temperature difference, K or °C
- g :
-
Acceleration of gravity, m·s−2
- h c :
-
Convective heat transfer coefficient, W·m−2·K−1
- μ :
-
1st derivative of Thot−Tcold with respect to √t
- L :
-
Characteristic length, m
- q 0 :
-
Heat flux, W·m−2
- P :
-
Heating power, W
- T :
-
Temperature, K or oC
- T mi :
-
Measured temperature
- T ci :
-
Calculated temperature
- T end :
-
Final temperature, K or oC
- T hot :
-
Temperature of the specimen’s hot surface, K or oC
- T cold :
-
Temperature of the specimen’s hot surface, K or oC
- U :
-
Voltage, V
- t:
-
Time, s
- x :
-
Geometrical coordinate along the depth of the object
- x i :
-
Inversed parameter
- X :
-
Collection of inversed parameters
- Δ :
-
Thickness of specimen, m
- Δe :
-
Result bias
- ΔT :
-
Temperature difference, K
- ζ:
-
Sensitivity coefficient matrix
- μ :
-
Damping parameter
- δ k :
-
Second order identity matrix
- σ :
-
Blackbody radiation constant
- ψ :
-
Objective function
- ε :
-
One smaller positive value
- c:
-
Conduction
- cold:
-
Cold surface
- e:
-
Experiment
- hot:
-
Hot surface
- k:
-
Count times
- LM:
-
Levenberg–Marquardt
- p:
-
Number of reversed parameters
- ref:
-
Reference
- T:
-
Transpose
References
A. Du, B. Zhou, Z. Zhang, J. Shen, A special material or a new state of matter: a review and reconsideration of the aerogel. Materials 6, 941–968 (2013)
Y.L. He, T. Xie, Advances of thermal conductivity models of nanoscale silica aerogel insulation material. Appl. Therm. Eng. 81, 28–50 (2015)
W.Z. Fang, H. Zhang, L. Chen, W.Q. Tao, Numerical predictions of thermal conductivities for the silica aerogel and its composites. Appl. Therm. Eng. 115, 1277–1286 (2017)
M. Zhang, Q. Xiao, C. Chen, L. Li, W. Yuan, Developing a heat-insulating composite phase change material with light-to-thermal conversion performance from graphene oxide/silica hybrid aerogel. Appl. Therm. Eng. 174, 115303 (2020)
C.Y. Zhu, Z.Y. Li, H.Q. Pang, N. Pan, Design and optimization of core/shell structures as highly efficient opacifiers for silica aerogels as high-temperature thermal insulation. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 133, 206–215 (2018)
F. He, Z. Qi, W. Zhen, J.Y. Wu, Y.H. Huang, X.W. Xiong, R.Z. Zhang, Thermal conductivity of silica aerogel thermal insulation coatings. Int. J. Thermophys. 40, 1–12 (2019)
J. Feng, D. Le, S.T. Nguyen, V.T.C. Nien, D. Jewell, H.M. Duong, Silica cellulose hybrid aerogels for thermal and acoustic insulation applications. Colloids Surf. A. 506, 298–305 (2016)
G. Wei, Y. Liu, X. Du, X. Zhang, Gaseous conductivity study on silica aerogel and its composite insulation materials. J. Heat Transf. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4004170
H. Zhang, W.Z. Fang, X. Wang, Y.M. Li, W.Q. Tao, Thermal conductivity of fiber and opacifier loaded silica aerogel composite. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 115, 21–31 (2017)
Y.J. Dai, Y.Q. Tang, W.Z. Fang, H. Zhang, W.Q. Tao, A theoretical model for the effective thermal conductivity of silica aerogel composites. Appl. Therm. Eng. 128, 1634–1645 (2018)
C. Meng, H. Yuan, Examination on aerogel based on the heat transfer characteristics of nanotechnology. Ferroelectrics 580, 26–41 (2021)
M.L. Zheng, The model and experiment for heat transfer characteristics of nanoporous silica aerogel. Korean J. Mater. Res. 30, 155–159 (2020)
C.Y. Zhu, Z.Y. Li, Modeling of the apparent solid thermal conductivity of aerogel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 120, 724–730 (2018)
S. Zeng, A. Hunt, R. Greif, Geometric structure and thermal conductivity of porous medium silica aerogel. J. Heat Transf. 117, 1055 (1995)
T. Xie, Y.L. He, Z.J. Hu, Theoretical study on thermal conductivities of silica aerogel composite insulating material. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 58, 540–552 (2013)
A. Bernasconi, T. Sleator, D. Posselt, H.R. Ott, Dynamic technique for measurement of the thermal conductivity and the specific heat: application to silica aerogels. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 61, 2420–2426 (1990)
V. Bock, O. Nilsson, J. Blumm, J. Fricke, Thermal properties of carbon aerogels. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 185, 233–239 (1995)
H.Q. Pang, Z.Y. Li, Experimental investigations on the thermal insulation performance of SiC opacifier doped silica aerogel at large temperature difference. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 160, 106681 (2021)
S. Chen, X. Jiang, G. Lu, Interior temperature measurement using curved mercury capillary sensor based on X-ray radiography. Int. J. Thermophys. 38, 97 (2017)
M. Cui, X. Gao, J. Zhang, A new approach for the estimation of temperature-dependent thermal properties by solving transient inverse heat conduction problems. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 58, 113–119 (2012)
J.I. Frankel, Residual-minimization least-squares method for inverse heat conduction. Comput. Math. Appl. 32, 117–130 (1996)
M. Cui, Y. Zhao, B. Xu, X.W. Gao, A new approach for determining damping factors in Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm for solving an inverse heat conduction problem. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 107, 747–754 (2017)
P. Duda, A general method for solving transient multidimensional inverse heat transfer problems. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 93, 665–673 (2016)
R. Sajedi, J. Faraji, F. Kowsary, A new damping strategy of Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm with a fuzzy method for inverse heat transfer problem parameter estimation. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 126, 105433 (2021)
M. Cui, Y. Zhao, B. Xu, S. Wang, X.W. Gao, Inverse analysis for simultaneously estimating multi-parameters of temperature-dependent thermal conductivities of an Inconel in a reusable metallic thermal protection system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 125, 480–488 (2017)
T. Xie, Y.L. He, Z.X. Tong, W.X. Yan, X.Q. Xie, An inverse analysis to estimate the endothermic reaction parameters and physical properties of aerogel insulating material. Appl. Therm. Eng. 87, 214–224 (2015)
K. Yang, G.H. Jiang, H.F. Peng, X.W. Gao, A new modified Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm for identifying the temperature-dependent conductivity of solids based on the radial integration boundary element method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 144, 118615 (2019)
S.Y. Zhao, B.M. Zhang, S.Y. Du, An inverse analysis to determine conductive and radiative properties of a fibrous medium. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 110, 1111–1123 (2009)
H.P. Gavin, The Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm for nonlinear least squares curve-fitting problems. Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Duke University (2019), pp. 1–19
H.P. Ebert, S. Braxmeier, G. Reichenauer, F. Hemberger, F. Lied, D. Weinrich, M. Fricke, Intercomparison of thermal conductivity measurements on a nanoporous organic aerogel. Int. J. Thermophys. 42, 1–18 (2021)
V.R. Voller, Fast implicit finite-difference method for the analysis of phase change problems. Numer. Heat Transf. 17, 155–169 (1990)
D.W. Marquardt, An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 11, 431–441 (1963)
H. Zhang, W.Z. Fang, Y.M. Li, W.Q. Tao, Experimental study of the thermal conductivity of polyurethane foams. Appl. Therm. Eng. 115, 528–538 (2017)
L.W. Hrubesh, Aerogel applications. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 225, 335–342 (1998)
J.J. Zhao, Y.Y. Duan, X.D. Wang, X.R. Zhang, Y.H. Han, Y.B. Gao, Z.H. Lv, H.T. Yu, B.X. Wang, Optical and radiative properties of infrared opacifier particles loaded in silica aerogels for high temperature thermal insulation. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 70, 54–64 (2013)
C. Buratti, E. Moretti, E. Belloni, F. Merli, V. Piermatti, T. Ihara, Field experimental study on energy performance of Aerogel Glazings with hollow silica: preliminary results in mid-season conditions, in Sustainability in Energy and Buildings. ed. by A. Hakansson, M. Höjer (Springer, Berlin, 2020), pp. 185–197
P. Yonathan, J.H. Lee, D.H. Yoon, W.J. Kim, J.Y. Park, Improvement of SiCf/SiC density by slurry infiltration and tape stacking. Mater. Res. Bull. 44, 2116–2122 (2009)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported financially by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M681711), the Natural Science Fund for Colleges and Universities in Jiangsu Province under Grant 19KJB470030, and the Key Laboratory of Advanced Carbon Materials and Wearable Energy Technologies of Jiangsu Province MZ26100119.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, TH., Pang, HQ., Zhong, WR. et al. Experiment and Inverse Analysis to Estimate SiO2 Aerogel Composite’s Thermophysical Properties by the Surface’s Temperature Response. Int J Thermophys 43, 79 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-022-03000-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-022-03000-5