Abstract
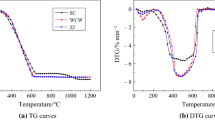
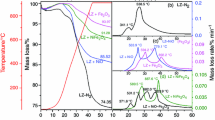
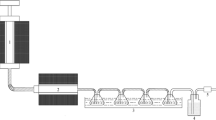
In order to facilitate efficient and clean utilization of coal, a series of Ni–Co ternary molten salt crystals are explored and the catalytic pyrolysis mechanism of Datong coal is investigated. The reaction mechanisms of coal are achieved by thermal gravimetric analyzer (TGA), and a reactive kinetic model is constructed. The microcosmic structure and macerals are observed by scanning electron microscope (SEM). The catalytic effects of ternary molten salt crystals at different stages of pyrolysis are analyzed. The experimental results show that Ni–Co ternary molten salt catalysts have the capability to bring down activation energy required by pyrolytic reactions at its initial phase. Also, the catalysts exert a preferable catalytic action on macromolecular structure decomposition and free radical polycondensation reactions. Furthermore, the high-temperature condensation polymerization is driven to decompose further with a faster reaction rate by the additions of Ni–Co ternary molten salt crystal catalysts. According to pyrolysis kinetic research, the addition of catalysts can effectively decrease the activation energy needed in each phase of pyrolysis reaction.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.S. Yu, Coal Chemistry (Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2008)
I. Mochida, K. Sakanishi, Fuel 79, 221–228 (2000)
E.M. Suuberg, W.A. Peters, J.B. Howard, Fuel 59, 405 (1980)
S. Atul, D.Y. Yaw, G. Anuradha, Fuel 82, 305 (2003)
Y.K. Rao, A. Adjorlolo, Carbon 20, 207 (1982)
D.M. Mckee, Fuel 62, 170 (1983)
J.F. Akyurtlu, Fuel Process. Technol. 43, 71 (1995)
Y.D. Yeboah, Y. Xu, A. Sheth, A. Godavarty, P.K. Agrawal, Carbon 41, 203 (2003)
S. Motoyuki, H. Katsumi, M. Kiyoshi, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 49, 1138 (2010)
F. Li, Z.L. Zhao, H.B. Li, X.Q. Ma, Y. Chen, J. Combust. Sci. Technol. 11, 470 (2005)
E.M. Levin, C.R. Robbins, H.F. McMurdie, Phase Diagrams for Ceramists (The American Ceramic Society, Westerville, 1964)
C.Z. Li, Advances in the Science of Victorian Brown Coal (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2004)
D.J. Allardice, in Advance in the Science of Victorian Brown Coal: Structure, Properties and Consequences for Utilization, ed. by R.A. Durie (Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 1991), p. 103
C.J. Ping, J.H. Zhou, J. Cheng, W.J. Yang, K.F. Cen, China Soc. Elec. Eng. 27, 203 (2007). doi:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2007.17.002
J.B. Yang, Y.W. Zhang, N.S. Cai, J. Eng. Therm. Energy Power 25, 301 (2010)
X.M. He, Coal Chemistry (Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2010)
H.L. Friedman, J. Marromol, SCI. A 1, 57 (1967)
A.W. Coats, J.P. Redfern, Nature 201, 68 (1964)
H. Zhang, X.Y. Li, Q. Hao, Research on Scanning Electron Microscope of China Coal (Geologied Publishing House, Beijing, 2003)
Y. Yu, X.J. Liu, J.J. Xu, Coal Qual. Technol. 41, 9 (2008)
J.D. Yan, H. Cui, J.L. Yang, Z. Liu, J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 32, 311 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2014QNA20). The authors would like to thank Dr. S. Bacha for his language assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, X., Qi, C., Li, L. et al. Effect of Ni–Co Ternary Molten Salt Catalysts on Coal Catalytic Pyrolysis Process. Int J Thermophys 38, 116 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-017-2255-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-017-2255-1