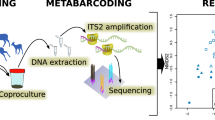
Abstract
Sympatric species are known to host the same parasites species. Nevertheless, surveys examining parasite assemblages in sympatric species are rare. To understand how parasite assemblages in sympatric host species differ in a given locality, we used a noninvasive identification method based on high-throughput sequencing. We collected fecal samples from sympatric species in Ranomafana National Park, Madagascar, from September to December in 2010, 2011, and 2012 and identified their parasites by metabarcoding, sequencing a region of the small ribosomal subunit (18S) gene. Our survey included 11 host species, including endemic primates, rodents, frogs, gastropods, and nonendemic rats and dogs. We collected 872 samples, of which 571 contained nematodes and 249 were successfully sequenced. We identified nine putative species of parasites, although their correspondence to actual parasite species is not clear as the resolution of the marker gene differs between nematode clades. For the host species that we successfully sampled with 10 or more positive occurrences of nematodes, i.e., mouse lemurs (Microcebus rufus), black rats (Rattus rattus), and frogs (Anura), the parasite assemblage compositions differed significantly among host species, sampling sites, and sampling years. Our metabarcoding method shows promise in interrogating parasite assemblages in sympatric host species and our results emphasize the importance of choosing marker regions for parasite identification accuracy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aivelo, T., & Medlar, A. (2017). Opportunities and challenges in metabarcoding approaches for helminth community identification in wild mammals. Parasitology. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182017000610.
Aivelo, T., Medlar, A., Löytynoja, A., Laakkonen, J., & Jernvall, J. (2015). Tracking year-to-year changes in intestinal nematode communities of rufous mouse lemurs (Microcebus rufus). Parasitology, 142(8), 1095–1107.
Andriaholinirina, N., Baden, A., Blanco, M., Chikhi, L., Cooke, A., et al. (2014a). Hapalemur aureus. The IUCN red list of threatened species, 2014, e.T9672A16119513. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2014-1.RLTS.T9672A16119513.en.
Andriaholinirina, N., Baden, A., Blanco, M., Chikhi, L., Cooke, A., et al. (2014b). Prolemur simus. The IUCN red list of threatened species, 2014, e.T9674A16121559. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2014-1.RLTS.T9674A16121559.en.
Avramenko, R. W., Redman, E. M., Lewis, R., Yazwinski, T. A., Wasmuth, J. D., & Gilleard, J. S. (2015). Exploring the gastrointestinal “nemabiome”: deep amplicon sequencing to quantify the species composition of parasitic nematode communities. PLoS One, 10(12), 1–18.
Baermann, G. (1917). Eine einfache methode zur auffindung von Ankylostomum (Nematoden) larven in erdproben. Tijdschrid Ergeneeskd, 57, 131–137.
Bhadury, P., & Austen, M. C. (2010). Barcoding marine nematodes: An improved set of nematode 18S rRNA primers to overcome eukaryotic co-interference. Hydrobiologia, 641, 245–251.
Bik, H. M., Porazinska, D. L., Creer, S., Caporaso, J. G., Knight, R., & Thomas, W. K. (2012). Sequencing our way towards understanding global eukaryotic biodiversity. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 27(4), 233–243.
Blaxter, M., Mann, J., Chapman, T., Thomas, F., Whitton, C., et al (2005). Defining operational taxonomic units using DNA barcode data. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 360(1462), 1935–1943.
Camacho, C., Coulouris, G., Avagyan, V., Ma, N., Papadopoulos, J., et al (2009). BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinformatics, 10, 421.
Chakraborty, D., Hussain, S., Reddy, D. M., Raut, S., Tiwari, S., Kumar, V., & Umapathy, G. (2015). Mammalian gastrointestinal parasites in rainforest remnants of Anamalai Hills, western Ghats, India. Journal of Biosciences, 40(2), 399–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-015-9517-5.
Dallas, T., & Presley, S. J. (2014). Relative importance of host environment, transmission potential and host phylogeny to the structure of parasite metacommunities. Oikos, 123(7), 866–874. https://doi.org/10.1111/oik.00707.
De Ley, P., De Ley, I. T., Morris, K., Abebe, E., Mundo-Ocampo, M., et al (2005). An integrated approach to fast and informative morphological vouchering of nematodes for applications in molecular barcoding. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 360(1462), 1945–1958.
Dobson, A. P., & May, R. M. (1986). Patterns of invasions by pathogens and parasites. In H. A. Mooney & J. A. Drake (Eds.), Ecology of biological invasions of North America and Hawaii (pp. 58–76). New York, USA: Springer-Verlag.
Dunn, A. M., Torchin, M. E., Hatcher, M. J., Kotanen, P. M., Blumenthal, D. M., Byers, J. E., et al (2012). Indirect effects of parasites in invasions. Functional Ecology, 26(6), 1262–1274. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2435.2012.02041.x.
Edgar, R. C., Haas, B. J., Clemente, J. C., Quince, C., & Knight, R. (2011). UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics, 27(16), 2194–2200.
Freeland, W. J. (1983). Parasites and coexistence of animal host species. The American Naturalist, 121(2), 223–236.
Gillespie, T. R. (2006). Noninvasive assessment of gastrointestinal parasite infections in free-ranging primates. International Journal of Primatology, 27(4), 1129–1143.
Hebert, P. D. N., Ratnasingham, S., & DeWaard, J. R. (2003). Barcoding animal life: cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 270, S96–S99. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2003.0025.
Hogg, K. L. (2002). Effect of habitat disturbance on parasite load and diversity in two species of lemur (Eulemur rubriventer, Propithecus diadema Edwardsi) at Ranomafana National Park. Madagascar: MA Thesis, Stony Brook University, Stony Brook.
Hudson, P., & Greenman, J. (1998). Competition mediated by parasites: biological and theoretical progress. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 13(10), 387–390.
Irwin, M. T., & Raharison, J. L. (2009). A review of the endoparasites of the lemurs of Madagascar. Malagasy Nature, 2, 66–93.
Kelly, D. W., Paterson, R. A., Townsend, C. R., Poulin, R., & Tompkins, D. M. (2009). Parasite spillback: a neglected concept in invasion ecology? Ecology, 90(8), 2047–2056.
Kouassi, R. Y. W., McGraw, S. W., Yao, P. K., Abou-Bacar, A., Brunet, J., Pesson, B., et al (2015). Diversity and prevalence of gastrointestinal parasites in seven non-human primates of the Taï National Park, Côte d’Ivoire. Parasite, 22, 1. https://doi.org/10.1051/parasite/2015001.
Laakkonen, J., Goodman, S. M., Duchemin, J. B., & Duplantier, J. M. (2003). Trypomastigotes and potential flea vectors of the endemic rodents and the introduced Rattus rattus in the rainforests of Madagascar. Biodiversity and Conservation, 12(8), 1775–1783.
Lott, M. J., Hose, G. C., & Power, M. L. (2015). Parasitic nematode communities of the red kangaroo, Macropus rufus: richness and structuring in captive systems. Parasitology Research, 114, 2925–2932.
Loudon, J. E., & Sauther, M. L. (2013). Verreaux’s sifaka (Propithecus Verreauxi) and ring-tailed lemur (Lemur Catta) endoparasitism at the Bezà Mahafaly special reserve. Madagascar Conservation & Development, 8(1), 21–28.
MacLeod, C. J., Paterson, A. M., Tompkins, D. M., & Duncan, R. P. (2010). Parasites lost - do invaders miss the boat or drown on arrival? Ecology Letters, 13(4), 516–527. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2010.01446.x.
Maldonado-López, S., Maldonado-López, Y., Gómez-Tagle Ch, A., Cuevas-Reyes, P., & Stoner, K. E. (2014). Patterns of infection by intestinal parasites in sympatric howler monkey (Alouatta Palliata) and spider monkey (Ateles Geoffroyi) populations in a tropical dry forest in Costa Rica. Primates, 55(3), 383–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10329-014-0413-7.
Medlar, A., Aivelo, T., & Löytynoja, A. (2014). Séance: reference-based phylogenetic analysis for 18S rRNA studies. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 14(235).
Muriuki, S. M. K., Murugu, R. K., Munene, E., Karere, G. M., & Chai, D. C. (1998). Some gastrointestinal parasites of zoonotic ( public health ) importance commonly observed in old world non-human primates in Kenya. Acta Tropica, 71, 73–82.
Nowak, R. M. (1999a). Walker’s mammals of the world, Vol. I (6th ed.). Baltimore: The John Hopkins University Press.
Nowak, R. M. (1999b). Walker’s mammals of the world, Vol. II (6th ed.). Baltimore: The John Hopkins University Press.
Petrášová, J., Modrý, D., Huffman, M. A., Mapua, M. I., Bobáková, L., Mazoch, V., et al (2010). Gastrointestinal parasites of indigenous and introduced primate species of Rubondo Island National Park, Tanzania. International Journal of Primatology, 31(5), 920–936. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-010-9439-x.
Porazinska, D. L., Giblin-Davis, R. M., Faller, L., Farmerie, W., Kanzaki, N., Morris, K., et al (2009). Evaluating high-throughput sequencing as a method for metagenomic analysis of nematode diversity. Molecular Ecology Resources, 9(6), 1439–1450. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2009.02611.x.
Porazinska, D. L., Giblin-Davis, R. M., Sung, W., & Thomas, W. K. (2010). Linking operational clustered taxonomic unitus (OCTUs) from parallel ultra sequencing (PUS) to nematode species. Zootaxa, 2427, 55–63.
Pourrut, X., Diffo, J. L. D., Somo, R. M., Bilong Bilong, C. F., Delaporte, E., LeBreton, M., & Gonzalez, J. P. (2011). Prevalence of gastrointestinal parasites in primate bushmeat and pets in Cameroon. Veterinary Parasitology, 175(1–2), 187–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.09.023.
Powers, T., Harris, T., Higgins, R., Mullin, P., Sutton, L., & Powers, K. (2011). MOTUs, morphology, and biodiversity estimation: a case study using nematodes of the suborder Criconematina and a conserved 18S DNA barcode. Journal of Nematology, 43(1), 35–48.
Quast, C., Pruesse, E., Yilmaz, P., Gerken, J., Schweer, T., et al (2013). The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 41(Database issue), D590–D596.
Quince, C., Lanzen, A., Davenport, R. J., & Turnbaugh, P. J. (2011). Removing noise from pyrosequenced amplicons. BMC Bioinformatics, 12(1), 38.
Raharivololona, B., & Ganzhorn, J. (2010). Seasonal variations in gastrointestinal parasites excreted by the gray mouse lemur Microcebus murinus in Madagascar. Endangered Species Research, 11, 113–122.
Raharivololona, B. M., & Ganzhorn, J. U. (2009). Gastrointestinal parasite infection of the gray mouse lemur (Microcebus murinus) in the littoral forest of Mandena, Madagascar: effects of forest fragmentation and degradation. Madagascar Conservation & Development, 4(2), 103–112.
Raharivololona, B. M., Rakotondravao, & Ganzhorn, J. U. (2007). Gastrointestinal parasites of small mammals in the littoral forest of Mandena. In J. U. Ganzhorn, S. M. Goodman, & M. Vincelette (Eds.), Biodiversity, ecology, and conservation of littoral ecosystems in the region of Tolagnaro (Fort Dauphin), southeastern Madagascar (pp. 247–258). Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution.
Schwensow, N., Dausmann, K., Eberle, M., Fietz, J., & Sommer, S. (2010). Functional associations of similar MHC alleles and shared parasite species in two sympatric lemurs. Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 10(5), 662–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2010.03.012.
Stamatakis, A. (2006). RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics, 22(21), 2688–2690.
Taberlet, P., Coissac, E., Pompanon, F., Brochmann, C., & Willerslev, E. (2012). Towards next-generation biodiversity assessment using DNA metabarcoding. Molecular Ecology, 33, 2045–2050.
Tanaka, R., Hino, A., Tsai, I. J., Palomares-Rius, J. E., Yoshida, A., et al (2014). Assessment of helminth biodiversity in wild rats using 18S rDNA based metagenomics. PLoS One, 9(10), e110769.
Tang, C. Q., Leasi, F., Obertegger, U., Kieneke, A., Barraclough, T. G., & Fontaneto, D. (2012). The widely used small subunit 18S rDNA molecule greatly underestimates true diversity in biodiversity surveys of the meiofauna. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 109(40), 16208–16212.
Taraschewski, H. (2006). Hosts and parasites as aliens. Journal of Helminthology, 80(2), 99–128. https://doi.org/10.1079/JOH2006364.
Teichroeb, J. A., Kutz, S. J., Parkar, U., Thompson, R. C. A., & Sicotte, P. (2009). Ecology of the gastrointestinal parasites of Colobus Vellerosus at Boabeng-Fiema, Ghana: possible anthropozoonotic transmission. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 140(3), 498–507. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajpa.21098.
Torchin, M. E., Lafferty, K. D., Dobson, A. P., McKenzie, V. J., & Kuris, A. M. (2003). Introduced species and their missing parasites. Nature, 421, 628–630. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01346.1.
Trejo-Macías, G., & Estrada, A. (2012). Risk factors connected to gastrointestinal parasites in mantled Alouatta Palliata Mexicana and black howler monkeys Alouatta Pigra living in continuous and in fragmented rainforests in Mexico. Current Zoology, 58(3), 375–383.
Trejo-Macías, G., Estrada, A., & Mosqueda-Cabrera, M.A. (2007). Survey of helminth parasites in populations of Alouatta palliata mexicana and A. pigra in continuous and fragmented habitat in southern Mexico. International Journal of Primatology 28, 931–945. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-007-9137-5.
R Core Team (2013). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. http://www.r-project.org/.
Wang, Y., Naumann, U., Wright, S., Eddelbuettel, D., & Warton, D. I. (2016). mvabund: Statistical method for analysing multivariate abundance data. http://cran.r-project.org/package=mvabund.
Wimmer, B., Craig, B. H., Pilkington, J. G., & Pemberton, J. M. (2004). Non-invasive assessment of parasitic nematode species diversity in wild Soay sheep using molecular markers. International Journal for Parasitology, 34, 625–631.
Wright, P. C., & Andriamihaja, B. (2002). Making a rain forest national park work in Madagascar: Ranomfana National Park and its long-term research commitment. In J. Terborgh, C. van Schaik, L. Davenport, & M. Rao (Eds.), Making parks work: Strategies for preserving tropical nature (pp. 112–136). Washington, DC: Island Press.
Wright, P. C., Andriamihaja, B., King, S. J., Guerriero, J., & Hubbard, J. (2014). Lemurs and tourism in Ranomafana National Park, Madagascar: Economic boom and other consequences. In A. Russon & J. Wallis (Eds.), Primate tourism: A tool for conservation? (pp. 123–146). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Acknowledgments
We thank the handling editor and two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments. We also thank Eric Hoberg, Holly Bik and three anonymous reviewers for their comments on the previous drafts of this article. We thank Madagascar National Parks, Madagascar Institute pour la Conservation des Ecosystèmes Tropicaux, and the Institute for the Conservation of Tropical Environments and research station Centre Valbio for logistical help and facilitation of research. Victor Rasendry, Herman Rafalinirina, Hannah Price, Kendall Harris, and Kelsey DeZalia helped with sample collection in the field and Anu Näreaho, Jukka T. Lehtonen, and Carina Holmberg gave us additional nematode specimens. Ritva Rice, Raija Savolainen, and Agnes Viherä assisted with the laboratory work. We also thank Voitto Haukisalmi for helpful comments. Funding was provided by Suoma Loimaranta-Airila Fund, Science Foundation of University of Helsinki, Otto A. Malm Fund, and Oskar Öflunds Foundation to T. Aivelo and Academy of Finland to J. Jernvall.
T. Aivelo, J. Jernvall, and J. Laakkonen designed the overall study and data collection. Samples were collected and amplified by T. Aivelo. A. Medlar, and A. Löytynoja developed the sequence analysis method. All authors participated in analysis of the results. T. Aivelo wrote the first draft with major contributions from A. Medlar. All authors commented on the draft and approved the final article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Joanna M. Setchell
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aivelo, T., Medlar, A., Löytynoja, A. et al. Metabarcoding Gastrointestinal Nematodes in Sympatric Endemic and Nonendemic Species in Ranomafana National Park, Madagascar. Int J Primatol 39, 49–64 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-017-0010-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-017-0010-x