Abstract
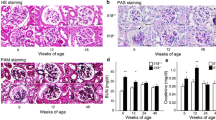
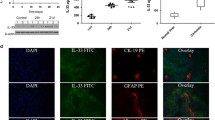
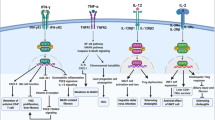
IL-9 is a pleiotropic cytokine, recently recognized as belonging to Th9 cells that are involved in various pathologies. We aimed to evaluate the role of IL-9 in the course of hepatic and renal fibrosis. Female C57BL/6 mice were treated subcutaneously with IL-9 10 ng/mouse and 20 ng/mouse for 40 days, alternating every 5 days each application, the negative control of which was treated with PBS and positive control with CCL4. IL-9 demonstrated fibrogenic activity, leading to increased collagen I and III deposition in both liver and kidney, as well as triggering lobular hepatitis. In addition, IL-9 induced an inflammatory response with recruitment of lymphocytes, neutrophils, and macrophages to both organs. The inflammation was present in the region of the portal and parenchymal zone in the liver and in the cortical and medullary zone in the kidney. IL-9 deregulated liver and kidney antioxidant activities. Our results showed that IL-9 was able to promote hepatorenal dysfunction. Moreover, IL-9 poses as a promising target for therapeutic interventions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaplan, M.H., M.M. Hufford, and M.R. Olson. 2015. The development and in vivo function of T. helper 9 cells. Nature Review 180: 295–307.
Goswami, R., and M.H. Kaplan. 2011. A brief history of IL-9. Journal of Immunology 186: 3283–3288.
Deng, Y., Z. Wang, C. Chang, L. Lu, C.S. Lau, and Q. Lu. 2017. Th9 cells and IL-9 in autoimmune disorders: Pathogenesis and therapeutic potentials. Human Immunology 78: 120–128.
Qin, S.Y., D.H. Lu, X.Y. Guo, et al. 2016. A deleterious role for Th9/IL-9 in hepatic fibrogenesis. Scientific Reports 6: 1–12.
Yu, X., Y. Zheng, Y. Deng, et al. 2016. Serum interleukin (IL)-9 and IL-10, but not T-helper 9 (Th9) cells, are associated with survival of patients with acute-on-chronic hepatitis b liver failure. Medicine 95: 1–8.
Buzio, C., S. Andrulli, R. Santi, L. Pavone, R. Passalacqua, D. Potenzoni, F. Ferrozzi, R. Giacosa, and A. Vaglio. 2001. Long-term immunotherapy with low-dose interleukin-2 and interferon-alpha in the treatment of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 92: 2286–2296.
Knight, V., J. Tchongue, D. Lourensz, et al. 2012. Protease-activated receptor 2 promotes experimental liver fibrosis in mice and activates human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 78: 87–879.
Junqueira, I.C., G. Bignolas, and R.P. Brentani. 1979. Picrosirius staining plus polarization microscopy, a specific method for collagen detection in tissue sections. Histochemistry Journal 45: 55–447.
Reznick, A.Z., and L. Packer. 1994. Oxidative damage to proteins: spectrophotometric method for carbonyl assay. Methods in Enzymology 78: 357–363.
Beutler, E., O. Duron, and B.M. Kelly. 1963. Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine 15: 882–890.
Aebi, H. 1984. Catalase in vitro. Methods in Enzymology 20: 121–126.
Benzie, I.F., and J.J. Strain. 1999. Strain. Ferric reducing antioxidant power assay: direct measure of total antioxidant activity of biological fluids and modified version for simultaneous measurement of total antioxidant power and ascorbic acid concentration. Methods in Enzymology 73: 15–27.
Fernandes, C.G., C.G. Borges, B. Seminotti, et al. 2011. Experimental evidence that methylmalonic acid provokes oxidative damage and compromises antioxidant defenses in nerve terminal and striatum of young rats. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience 5: 1–9.
Bradford, M.M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye-binding. Analytical Biochemistry 23: 248–254.
Steuerwald, N.M., D.M. Foureau, H.J. Norton, et al. 2013. Profiles of serum cytokines in acute drug-induced liver injury and their prognostic significance. PLoS One 8: 1–15.
Stangou, M., A. Papagianni, C. Bantis, H. Liakou, K. Pliakos, P. Giamalis, L. Gionanlis, A. Pantzaki, G. Efstratiadis, and D. Memmos. 2012. Detection of multiple cytokines in the urine of patients with focal necrotising glomerulonephritis may predict short and long term outcome of renal function. Cytokine 57: 120–126.
Salmi, S., D. Adams, and S. Jalkanen. 1998. Cell adhesion and migration. IV. Lymphocyte trafficking in the intestine and liver. American Journal of Physiology 78: 1–6.
Weinbren, K., and G.A. Stirling. 1972. Pathology of viral hepatitis. British Medical Bulletin 28 (2): 125–130.
Ogeturk, M., I. Kus, A. Kavakli, J. Oner, A. Kukner, and M. Sarsilmaz. 2005. Reduction of carbon tetrachloride-induced nephropathy by melatonin administration. Cell Biochemistry and Function 23 (2): 85–92.
Ozturk, A., A.K. Baltaci, R. Mogulkoc, et al. 2003. Effects of zinc deficiency and supplementation on malondialdehyde and glutathione levels in blood and tissues of rats performing swimming exercise. Biological Trace Element Research 15: 157–166.
Roberts, A.B., and M.B. Spurn. 1990. The transform growth factor-is. In Pept. Growth fact and their recep. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Coppo, L., and P. Ghezzi. 2011. Thiol regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and innate immunity: protein S-thiolation as a novel molecular mechanism. Biochemical Society Transactions 2: 1268–1272.
Liu, R.M., and P.K.A. Gaston. 2010. Oxidative stress and glutathione in TGF-beta-mediated fibrogenesis. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 10: 1–15.
Biteau, B., J. Labarre, and M.B. Toledano. 2003. ATP-dependent reduction of cysteine-sulphinic acid by S. cerevisiae sulphiredoxin. Nature 78: 980–984.
Torchinsky, Y. 1981. Sulfur in proteins. Oxford: Pergamon Press, Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NSLS led the project activities, performed experiments, and wrote the manuscript. BCB, AAS, PC, TLT, SCT, MAS, JPSS, ABJ, and DCC contributed to the experiment procedures and manuscript formatting. RGZ, TCT, FSE, and MJBS provided reagents, equipment, and facility access and contributed to the intellectual content of the manuscript. CVS coordinated, supervised, and planned the project and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Lira Silva, N.S., Borges, B.C., da Silva, A.A. et al. The Deleterious Impact of Interleukin 9 to Hepatorenal Physiology. Inflammation 42, 1360–1369 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-00997-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-00997-0