Abstract
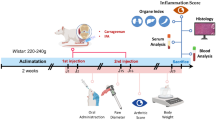
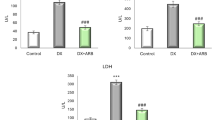
Schisandrin B (SchB) is an active compound extracted from the Chinese herb Schisandra chinensis and shows excellent anti-inflammatory activity. This study was performed to examine the effects of SchB in a rat model of IgA nephropathy (IgAN). IgAN was established in Sprague-Dawley rats by immunization with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), bovine serum albumin, and carbon tetrachloride. Renal function was evaluated by determining the levels of urinary red blood cells, proteinuria, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and creatinine (Cr). Renal tissue and protein samples were collected for further analysis. Pre-treatment and treatment with SchB significantly ameliorated renal function of IgAN rats, which was evidenced by decreased levels of proteinuria, hematuria, BUN, and Cr. IgAN rats exhibited increased serum IgA, renal IgA deposition, mesangial cell proliferation, and inflammatory cell infiltration, which were significantly attenuated by intervention with SchB. Moreover, SchB inhibited infiltration of CD3+ and CD11b+ cells, decreased levels of tumour necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1β, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in the kidney, and decreased the numbers of CD3+CD69+ cells in the spleen. Of note, SchB therapy significantly increased cytoplasmic p65 and IκB expression and decreased nuclear p65 levels both in the damaged renal tissue and LPS-stimulated HK-2 cells, indicating a direct inhibitory effect on the NF-κB pathway in IgAN rats. Taken together, our data provide insight into a new application of SchB for the treatment of IgAN and represent a novel mechanism behind these effects.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lai, K.N., S.C. Tang, F.P. Schena, J. Novak, Y. Tomino, A.B. Fogo, and R.J. Glassock. 2016. IgA nephropathy. Nature Reviews Disease Primers 2: 16001.
Xie, Y., and X. Chen. 2008. Epidemiology, major outcomes, risk factors, prevention and management of chronic kidney disease in China. American Journal of Nephrology 28: 1–7.
Katafuchi, R., K. Ikeda, T. Mizumasa, H. Tanaka, T. Ando, T. Yanase, K. Masutani, M. Kubo, and S. Fujimi. 2003. Controlled, prospective trial of steroid treatment in IgA nephropathy: A limitation of low-dose prednisolone therapy. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 41: 972–983.
Pozzi, C., P.G. Bolasco, G.B. Fogazzi, S. Andrulli, P. Altieri, C. Ponticelli, and F. Locatelli. 1999. Corticosteroids in IgA nephropathy: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 353: 883–887.
Lan, H.Y., D.J. Paterson-Nikolic, W. Mu, and R.C. Atkins. 1997. Local macrophage proliferation in the pathogenesis of glomerular crescent formation in rat anti-glomerular basement membrane (GBM) glomerulonephritis. Clinical and Experimental Immunology 110: 233–240.
Ka, S.M., T.T. Hsieh, S.H. Lin, S.S. Yang, C.C. Wu, H.K. Sytwu, and A. Chen. 2011. Decoy receptor 3 inhibits renal mononuclear leukocyte infiltration and apoptosis and prevents progression of IgA nephropathy in mice. American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology 301: F1218–F1230.
Stangou, M., C. Bantis, M. Skoularopoulou, L. Korelidou, D. Kouloukouriotou, M. Scina, I.T. Labropoulou, N.M. Kouri, A. Papagianni, and G. Efstratiadis. 2016. Th1, Th2 and Treg/T17 cytokines in two types of proliferative glomerulonephritis. Indian Journal of Nephrology 26: 159–166.
Chen, Q., H. Zhang, Y. Cao, Y. Li, S. Sun, J. Zhang, and G. Zhang. 2017. Schisandrin B attenuates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in rats by regulation of Nrf2-ARE and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways. Drug Design Development and Therapy 11: 2179–2191.
Sun, R., R. Zhai, C. Ma, and M. Wei. 2017, 2017. The anti-growth and anti-metastasis effects of Schisandrin B on hepatocarcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.06.022.
Lin, Q., X. Qin, M. Shi, Z. Qin, Y. Meng, Z. Qin, and S. Guo. 2017. Schisandrin B inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory response in human umbilical vein endothelial cells by activating Nrf2. International Immunopharmacology 49: 142–147.
Zhang, W., Z. Sun, and F. Meng. 2017. Schisandrin B ameliorates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through attenuation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. Inflammation 40: 1903–1911.
Xu, Y., Z. Liu, J. Sun, Q. Pan, F. Sun, Z. Yan, and X. Hu. 2011. Schisandrin B prevents doxorubicin- induced chronic cardiotoxicity and enhances its anticancer activity in vivo. PLoS One 6: e28335.
Ko, K.M., and B.Y. Lam. 2002. Schisandrin B protects against tert-butylhydroperoxide induced cerebral toxicity by enhancing glutathione antioxidant status in mouse brain. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 238: 181–186.
Chen, Z., M. Guo, G. Song, J. Gao, Y. Zhang, Z. Jing, T. Liu, and C. Dong. 2016. Schisandrin B inhibits Th1/Th17 differentiation and promotes regulatory T cell expansion in mouse lymphocytes. International Immunopharmacology 35: 257–264.
Leong, P.K., and K.M. Ko. 2015. Schisandrin B induces an Nrf2-mediated thioredoxin expression and suppresses the activation of inflammasome in vitro and in vivo. Biofactors 41: 314–323.
Checker, R., R.S. Patwardhan, D. Sharma, J. Menon, M. Thoh, H.N. Bhilwade, T. Konishi, and S.K. Sandur. 2012. Schisandrin B exhibits anti-inflammatory activity through modulation of the redox-sensitive transcription factors Nrf2 and NF-κB. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 53: 1421–1430.
Park, E.J., J.N. Chun, S.H. Kim, C.Y. Kim, H.J. Lee, H.K. Kim, J.K. Park, S.W. Lee, I. So, and J.H. Jeon. 2012. Schisandrin B suppresses TGFβ1 signaling by inhibiting Smad2/3 and MAPK pathways. Biochemical Pharmacology 83: 378–384.
Chiu, P.Y., H.Y. Leung, and K.M. Ko. 2008. Schisandrin B enhances renal mitochondrial antioxidant status, functional and structural integrity, and protects against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 31: 602–605.
Zhu, S., Y. Wang, M. Chen, J. Jin, Y. Qiu, M. Huang, and Z. Huang. 2012. Protective effect of schisandrin B against cyclosporine A-induced nephrotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. American Journal of Chinese Medicine 40: 551–566.
Stacchiotti, A., Volti.G. Li, A. Lavazza, I. Schena, M.F. Aleo, L.F. Rodella, and R. Rezzani. 2011. Different role of Schisandrin B on mercury-induced renal damage in vivo and in vitro. Toxicology 286: 48–57.
Wei, L., Y. Du, L. Jia, X. Ma, Z. Chen, J. Lu, L. Tian, Z. Duan, F. Dong, Z. Lv, G. Yao, R. Fu, and L. Wang. 2017. Therapeutic effects of FK506 on IgA nephropathy rat. Kidney & Blood Pressure Research 42: 983–998.
Lai, K.N., L.Y. Chan, H. Guo, S.C. Tang, and J.C. Leung. 2011. Additive effect of PPAR-γ agonist and ARB in treatment of experimental IgA nephropathy. Pediatric Nephrology 26: 257–266.
Hu, Y., Z. Hu, S. Wang, X. Dong, C. Xiao, M. Jiang, A. Lv, W. Zhang, and R. Liu. 2013. Protective effects of Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Tang and its component group on collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 150: 1137–1144.
Cox, S.N., G. Serino, F. Sallustio, A. Blasi, M. Rossini, F. Pesce, and F.P. Schena. 2015. Altered monocyte expression and expansion of non-classical monocyte subset in IgA nephropathy patients. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 30: 1122–1232.
Sakatsume, M., Y. Xie, M. Ueno, H. Obayashi, S. Goto, I. Narita, N. Homma, K. Tasaki, Y. Suzuki, and F. Gejyo. 2001. Human glomerulonephritis accompanied by active cellular infiltrates shows effector T cells in urine. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 12: 2636–2644.
Wu, T.H., S.C. Wu, T.P. Huang, C.L. Yu, and C.Y. Tsai. 1996. Increased excretion of tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 beta in urine from patients with IgA nephropathy and Schönlein-Henoch purpura. Nephron 74: 79–88.
Lim, C.S., S. Zheng, Y.S. Kim, C. Ahn, J.S. Han, S. Kim, J.S. Lee, D.W. Chae, J.R. Koo, R.W. Chun, and J.W. Noh. 2001. Th1/Th2 predominance and proinflammatory cytokines determine the clinicopathological severity of IgA nephropathy. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 16: 269–275.
Syrjänen, J., M. Hurme, T. Lehtimäki, J. Mustonen, and A. Pasternack. 2002. Polymorphism of the cytokine genes and IgA nephropathy. Kidney International 61: 1079–1085.
Lee, S.H., E.J. Lee, S.W. Chung, R. Song, J.Y. Moon, S.H. Lee, S.J. Lim, Y.A. Lee, S.J. Hong, and H.I. Yang. 2013. Renal involvement in ankylosing spondylitis: Prevalence, pathology, response to TNF-a blocker. Rheumatology International 33: 1689–1692.
Lai, K.N., J.C. Leung, L.Y. Chan, M.A. Saleem, P.W. Mathieson, F.M. Lai, and S.C. Tang. 2008. Activation of podocytes by mesangial-derived TNF-alpha: Glomerulo-podocytic communication in IgA nephropathy. American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology 294: F945–F955.
Guo, Y., Z. Song, M. Zhou, Y. Yang, Y. Zhao, B. Liu, and X. Zhang. 2017. Infiltrating macrophages in diabetic nephropathy promote podocytes apoptosis via TNF-α-ROS-p38MAPK pathway. Oncotarget 8: 53276–53287.
Nee, L., N. Tuite, M.P. Ryan, and T. McMorrow. 2007. TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta-mediated regulation of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in human glomerular mesangial cells. Nephron Experimental Nephrology 107: e73–e86.
Tesch, G.H., H.Y. Lan, R.C. Atkins, and D.J. Nikolic-Paterson. 1997. Role of interleukin-1 in mesangial cell proliferation and matrix deposition in experimental mesangioproliferative nephritis. American Journal of Pathology 151: 141–150.
Zeng, K.W., T. Zhang, H. Fu, G.X. Liu, and X.M. Wang. 2012. Schisandrin B exerts anti-neuroinflammatory activity by inhibiting the Toll-like receptor 4-dependent MyD88/IKK/NF-κB signaling pathway in lipopolysaccharide-induced microglia. European Journal of Pharmacology 692: 29–37.
Cai, Z., J. Liu, H. Bian, J. Cai, and G. Zhu. 2016. Suppression of P2X7/NF-κB pathways by Schisandrin B contributes to attenuation of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in acute lung injury. Archives of Pharmacal Research 39: 499–507.
Kopitar-Jerala, N. 2015. Innate immune response in brain, NF-kappa B signaling and cystatins. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience 8: 73.
Park, M.H., and J.T. Hong. 2016. Roles of NF-κB in cancer and inflammatory diseases and their therapeutic approaches. Cells 5(2). pii: E15.
Giridharan, V.V., R.A. Thandavarayan, H.N. Bhilwade, K.M. Ko, K. Watanabe, and T. Konishi. 2012. Schisandrin B, attenuates cisplatin-induced oxidative stress, genotoxicity and neurotoxicity through modulating NF-κB pathway in mice. Free Radical Research 46: 50–60.
Liu, W., Y. Liu, Z. Wang, T. Yu, Q. Lu, and H. Chen. 2015. Suppression of MAPK and NF-κ B pathways by schisandrin B contributes to attenuation of DSS-induced mice model of inflammatory bowel disease. Pharmazie 70: 598–603.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Medical Research Project of the Sichuan Medical Association (No. 201363).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
All contributing authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
The present study was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Southwest Medical University (Luzhou, China), and all procedures performed in the studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, JH., Lin, JR., Ding, WF. et al. Schisandrin B Improves the Renal Function of IgA Nephropathy Rats Through Inhibition of the NF-κB Signalling Pathway. Inflammation 42, 884–894 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0943-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0943-z