Abstract
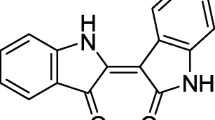
In this study, we investigated anti-inflammatory effects of esculin (ESC) on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury (ALI). ALI was induced in mice by intratracheal instillation of LPS, and ESC (20 and 40 mg/kg) was given orally 1 h prior to LPS administration. After 6 h, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and lung tissue were collected. ESC pretreatment decreased LPS-induced evident lung histopathological changes, lung wet-to-dry weight ratio, and lung myeloperoxidase activity. In addition, pretreatment with ESC inhibited inflammatory cells and proinflammatory cytokines including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β, and interleukin-6 in BALF. Furthermore, we demonstrated that ESC inhibited the Toll-like receptor-2 (TLR2), Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4), myeloid differentiation primary response gene-88 (MyD88), and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) p65 in LPS-induced ALI. The results indicated that the ESC had a protective effect on LPS-induced ALI in mice.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rubenfeld, G.D. 2003. Epidemiology of acute lung injury. Critical Care Medicine 31: S276–S284.
Zhang, X.M., K.J. Song, H.Z. Xiong, H.Y. Li, X. Chu, and X.M. Deng. 2009. Protective effect of florfenicol on acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. International Immunopharmacology 9: 1525–1529.
Matthay, M.A., G.A. Zimmerman, C. Esmon, J. Bhattacharya, B. Coller, C.M. Doerschuk, et al. 2003. Future research directions in acute lung injury summary of a national heart lung and blood institute working group. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 167: 1027–1035.
Chen, Z., X. Zhang, X. Chu, X. Zhang, K. Song, Y. Jiang, L. Yu, and X. Deng. 2010. Preventive effects of Valnemulin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Inflammation 33: 306–314.
Rubenfeld, G.D., E. Caldwell, E. Peabody, J. Weaver, D.P. Martin, M. Neff, et al. 2005. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. The New England Journal of Medicine 353: 1685–1693.
Pahl, H.L. 1999. Activators and target genes of Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene 18: 6853–6866.
Chen, Z., X. Zhang, X. Chu, X. Zhang, K. Song, Y. Jiang, L. Yu, and X. Deng. 2010. Preventive effects of valnemulin on lipopolysaccharideinduced acute lung injury in mice. Inflammation 33: 306–314.
Yang, R., L. Yang, X. Shen, W. Cheng, B. Zhao, K.H. Ali, Z. Qian, and H. Ji. 2012. Suppression of NF-κB pathway by crocetin contributes to attenuation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. European Journal of Pharmacology 674: 391–396.
Di, R., M.T. Huang, and C.T. Ho. 2011. Anti-inflammatory activities of mogrosides from Momordica grosvenoriin murine macrophages and a murine ear edema model. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 59: 7474–7481.
Drexler, S.K., and B.M. Foxwell. 2010. The role of Toll-like receptors in chronic inflammation. International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology 42: 506–518.
Lee, B.C., S.Y. Lee, H.J. Lee, G.S. Sim, J.H. Kim, J.H. Kim, Y.H. Cho, D.H. Lee, H.B. Pyo, T.B. Choe, D.C. Moon, Y.P. Yun, and J.T. Hong. 2007. Anti-oxidative and photo-protective effects of coumarins isolated from Fraxinus chinensis. Archives of Pharmacal Research 30: 1293–1301.
Park, C., C.Y. Jin, G.Y. Kim, I.W. Choi, T.K. Kwon, B.T. Choi, S.J. Lee, W.H. Lee, and Y.H. Choi. 2008. Induction of apoptosis by esculetin in human leukemia U937 cells through activation of JNK and ERK. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 227: 219–228.
Kumazawa, Y., K. Kawaguchi, and H. Takimoto. 2006. Immunomodulating effects of flavonoids on acute and chronic inflammatory responses caused by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Current Pharmaceutical Design 12: 4271–4279.
Rubenfeld, G.D. 2003. Epidemiology of acute lung injury. Critical Care Medicine 31: 276–284.
Knapp, S., S. Florquin, D.T. Golenbock, and T. van der Poll. 2006. Pulmonary lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein inhibits the LPS-induced lung inflammation in vivo. Journal of Immunology 176: 3189–3195.
Chen, H., C. Bai, and X. Wang. 2010. The value of the lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury model in respiratory medicine. Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine 4: 773–783.
Zhang, X.M., K.J. Song, H.Z. Xiong, H.Y. Li, X. Chu, and X.M. Deng. 2009. Protective effect of florfenicol on acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. International Immunopharmacology 9: 1525–1529.
Bhatia, M., and S. Moochhala. 2004. Role of inflammatory mediators in the pathophysiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome. The Journal of Pathology 202: 145–156.
Minamino, T., and I. Komuro. 2006. Regeneration of the endothelium as a novel therapeutic strategy for acute lung injury. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 116: 2316–2319.
Zhang, G., and S. Ghosh. 2001. Toll-like receptor-mediated NF-kappaB activation: a phylogenetically conserved paradigm in innate immunity. Journal of Clinical Investigation 107: 13–19.
Akira, S., K. Takeda, and T. Kaisho. 2001. Toll-like receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nature Immunology 2: 675–680.
Horng, T., G.M. Barton, R.A. Flavell, and R. Medzhitov. 2002. The adaptor molecule TIRAP provides signalling specificity for Toll-like receptors. Nature 420: 329–333.
Moine, P., R. McIntyre, M.D. Schwartz, et al. 2000. NF-kappaB regulatory mechanisms in alveolar macrophages from patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Shock 13: 85–91.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tianzhu, Z., Shumin, W. Esculin Inhibits the Inflammation of LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice Via Regulation of TLR/NF-κB Pathways. Inflammation 38, 1529–1536 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0127-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0127-z