Abstract
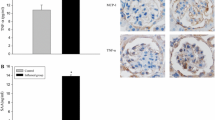
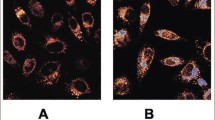
Inflammation and lipids play significant roles in the progression of chronic kidney disease. This study was designed to investigate whether inflammation disrupts cellular cholesterol homeostasis and causes the lipid nephrotoxicity in vitro and in vivo, and explored its underlying mechanisms. Inflammatory stress was induced by cytokines (interleukin-1β (IL-1β); tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α)) to human mesangial cells (HMCs) in vitro and by subcutaneous casein injection in C57BL/6J mice in vivo. The data showed that inflammatory stress exacerbated renal cholesterol ester accumulation in vitro and in vivo. Inflammation increased cellular cholesterol uptake and synthesis via upregulating the expression of low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLr) and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMGCoA-R), while it decreased cholesterol efflux via downregulating the expression of liver X receptor alpha and ATP-binding cassette transporter A1. The increased lipid accumulation by inflammatory stress induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) and increased levels of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress markers (inositol-requiring protein 1 and activating transcription factor 6) in HMCs and kidneys of C57BL/6J mice. This study implied that inflammation promoted renal lipid accumulation and foam cell formation by disrupting cellular cholesterol homeostasis. Increased intracellular lipids under inflammatory stress caused oxidative stress and ER stress in vitro and in vivo which may contribute to renal injury and progression of chronic kidney disease.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carrero, J.J., M.I. Yilmaz, B. Lindholm, and P. Stenvinkel. 2008. Cytokine dysregulation in chronic kidney disease: how can we treat it? Blood Purification 26: 291–299.
Keane, W.F., B.L. Kasiske, and M.P. O’Donnell. 1988. Lipids and progressive glomerulosclerosis. A model analogous to atherosclerosis. American Journal of Nephrology 8: 261–271.
Zienowicz, B., S. Krus, and E. Hagel. 1978. Glomerular foam cells in kidney allograft. International Urology and Nephrology 10: 237–244.
Wu, Y., Y. Chen, D. Chen, C. Zeng, L. Li, and Z. Liu. 2009. Presence of foam cells in kidney interstitium is associated with progression of renal injury in patients with glomerular diseases. Nephron. Clinical Practice 113: c155–c161.
Ruan, X.Z., J.F. Moorhead, J.L. Tao, K.L. Ma, D.C. Wheeler, S.H. Powis, and Z. Varghese. 2006. Mechanisms of dysregulation of low-density lipoprotein receptor expression in vascular smooth muscle cells by inflammatory cytokines. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 26: 1150–1155.
Ruan, X.Z., Z. Varghese, R. Fernando, S.H. Powas, and J.F. Moorhead. 1999. LDL receptor gene expression in human mesangial cells under the influence of calcium channel blockers. Clinical Nephrology 51: 263–271.
Nakanishi, M., J.L. Goldstein, and M.S. Brown. 1988. Multivalent control of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. Mevalonate-derived product inhibits translation of mRNA and accelerates degradation of enzyme. Journal of Biological Chemistry 263: 8929–8937.
Yang, T., P.J. Espenshade, M.E. Wright, D. Yabe, Y. Gong, R. Aebersold, J.L. Goldstein, and M.S. Brown. 2002. Crucial step in cholesterol homeostasis: sterols promote binding of SCAP to INSIG-1, a membrane protein that facilitates retention of SREBPs in ER. Cell 110: 489–500.
Ricote, M., A.F. Valledor, and C.K. Glass. 2004. Decoding transcriptional programs regulated by PPARs and LXRs in the macrophage: effects on lipid homeostasis, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 24: 230–239.
Chen, Y., X.Z. Ruan, Q. Li, A. Huang, J.F. Moorhead, S.H. Powis, and Z. Varghese. 2007. Inflammatory cytokines disrupt LDL-receptor feedback regulation and cause statin resistance: a comparative study in human hepatic cells and mesangial cells. American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology 293: F680–F687.
Moorhead, J.F., M.K. Chan, M. El-Nahas, and Z. Varghese. 1982. Lipid nephrotoxicity in chronic progressive glomerular and tubulo-interstitial disease. Lancet 2: 1309–1311.
Kasiske, B.L., M.P. O’Donnell, P.G. Schmitz, Y. Kim, and W.F. Keane. 1990. Renal injury of diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in rats. Kidney International 37: 880–891.
Remuzzi, A., E. Gagliardini, F. Sangalli, M. Bonomelli, M. Piccinelli, A. Benigni, and G. Remuzzi. 2006. ACE inhibition reduces glomerulosclerosis and regenerates glomerular tissue in a model of progressive renal disease. Kidney International 69: 1124–1130.
Southworth, R., M. Kaneda, J. Chen, L. Zhang, H. Zhang, X. Yang, R. Razavi, G. Lanza, and S.A. Wickline. 2009. Renal vascular inflammation induced by Western diet in ApoE-null mice quantified by (19)F NMR of VCAM-1 targeted nanobeacons. Nanomedicine 5: 359–367.
Pesek-Diamond, I., G. Ding, J. Frye, and J.R. Diamond. 1992. Macrophages mediate adverse effects of cholesterol feeding in experimental nephrosis. American Journal of Physiology 263: F776–F783.
Goldsmith, D., and A.C. Covic. 2010. Jupiter or Aurora? Micro-inflammation and dyslipidaemia: twin targets for statin therapy in CKD. International Urology and Nephrology 42: 133–136.
Nobiling, R., and C.P. Buhrle. 1987. The mesangial cell culture: a tool for the study of the electrophysiological and pharmacological properties of the glomerular mesangial cell. Differentiation 36: 47–56.
Ruan, X.Z., Z. Varghese, S.H. Powis, and J.F. Moorhead. 2001. Dysregulation of LDL receptor under the influence of inflammatory cytokines: a new pathway for foam cell formation. Kidney International 60: 1716–1725.
Berfield, A.K., and C.K. Abrass. 2002. IGF-1 induces foam cell formation in rat glomerular mesangial cells. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 50: 395–403.
Xu, Z.E., Y. Chen, A. Huang, Z. Varghese, J.F. Moorhead, F. Yan, S.H. Powis, Q. Li, and X.Z. Ruan. 2011. Inflammatory stress exacerbates lipid-mediated renal injury in ApoE/CD36/SRA triple knockout mice. American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology 4: F713–F722.
Ruan, X.Z., Z. Varghese, S.H. Powis, and J.F. Moorhead. 1999. Human mesangial cells express inducible macrophage scavenger receptor. Kidney International 5: 440–451.
Ruan, X.Z., Z. Varghese, R. Fernando, and J.F. Moorhead. 1998. Cytokine regulation of low-density lipoprotein receptor gene transcription in human mesangial cells. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation: Official Publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association - European Renal Association 6: 1391–1397.
Hattori, M., D.J. Nikolic-Paterson, K. Miyazaki, N.M. Isbel, H.Y. Lan, R.C. Atkins, H. Kawaguchi, and K. Ito. 1999. Mechanisms of glomerular macrophage infiltration in lipid-induced renal injury. Kidney International. Supplement 71: S47–S50.
Lorz, C., P. Justo, A. Sanz, D. Subira, J. Egido, and A. Ortiz. 2004. Paracetamol-induced renal tubular injury: a role for ER stress. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 15: 380–389.
Terawaki, H., K. Yoshimura, T. Hasegawa, Y. Matsuyama, T. Negawa, K. Yamada, M. Matsushima, M. Nakayama, T. Hosoya, and S. Era. 2004. Oxidative stress is enhanced in correlation with renal dysfunction: examination with the redox state of albumin. Kidney International 66: 1988–1993.
Kaysen, G.A., and J.P. Eiserich. 2004. The role of oxidative stress-altered lipoprotein structure and function and microinflammation on cardiovascular risk in patients with minor renal dysfunction. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 15: 538–548.
Vaziri, N.D., M. Dicus, N.D. Ho, L. Boroujerdi-Rad, and R.K. Sindhu. 2003. Oxidative stress and dysregulation of superoxide dismutase and NADPH oxidase in renal insufficiency. Kidney International 63: 179–185.
Jiao, P., J. Ma, B. Feng, H. Zhang, J.A. Diehl, Y.E. Chin, W. Yan, and H. Xu. 2011. FFA-induced adipocyte inflammation and insulin resistance: involvement of ER stress and IKKbeta pathways. Obesity (Silver Spring) 19: 483–491.
Garg, A.D., D.V. Krysko, P. Vandenabeele, and P. Agostinis. 2012. The emergence of phox-ER stress induced immunogenic apoptosis. Oncoimmunology 1: 786–788.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81270493, 81270789, 81200567, 81070631, 81070317, and Key Program, No. 81030008), the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program, Nos. 2012CB517700 and 2012CB517500), and the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (CSTC,2012jjA10016).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare they have no competing interests as defined by Molecular Medicine or other interests that might be perceived to influence the results and discussion reported in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shan Zhong and Lei Zhao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, S., Zhao, L., Li, Q. et al. Inflammatory Stress Exacerbated Mesangial Foam Cell Formation and Renal Injury via Disrupting Cellular Cholesterol Homeostasis. Inflammation 38, 959–971 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-0058-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-0058-0