Abstract
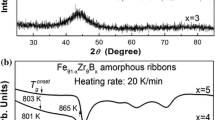
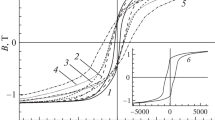
The magnetic and structural properties of amorphous (Fe100-xBx)92Sc8 alloys have been investigated in detail. Amorphous (Fe100-xBx)92Sc8 alloys were chosen because boron atoms lead to unexpected modifications in the physical properties, whose measurements, analysis, interpretation and modeling is the aim of the present study. Generally, the introduction of boron atoms in crystalline transition metal alloys such as iron-boron results in a reduction in the magnetic hyperfine field, Bhf, and the magnetic moment at low temperatures. The substitution of iron by boron atoms in amorphous (Fe100-xBx)92Sc8 alloys, however, induces a significant increase in the average magnetic hyperfine fields, while causing a reduction in the measured macroscopic magnetic moments. The latest observation of the proportionality between magnetic moment and Bhf suggests a need for a better understanding of this effect. It will be shown that the spins of 3d-electrons are the key factor for the proportionality between internal magnetic hyperfine fields, Bhf, and magnetic moment. The measured magnetic moment, however, is the sum of the spins of 3d-electrons and magnetic moment of sp-electrons. For this reason, the measured magnetic moment and the behavior of the magnetic moment of 3d-electrons are different. The magnetic moment of 3d-electrons and the sp- moments are, however, the key factors for understanding the magnetic properties of the amorphous (Fe100-xBx)92Sc8 alloys. Another study compared the influence of boron on the 3d magnetic Fe-moment and the macroscopic measured magnetic moment of the sample. Why the measured magnetic moment and the behavior of the moment of 3d-electrons are different is discussed. This report, in addition, emphasizes the influence of atomistic short-range order on the magnetic phenomena.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levy, R.A., Hasegawa, R., Amorphous Magnetism II, Plenum Press 1977
Day, R.K., Dunlop, J.B., Foley, C.P., Ghafari, M., Pask, H.: Preparation and Mössbauer study of a new Fe-rich amorphous alloy, Fe90Sc10. Sol. State Comm. 56, 843–845 (1985)
Ghafari, M., Day, R.K., Dunlop, J.B., in Conference book „Magnetic Properties of amorphous metals, Editors: A. Hernando, V. Madurga. M.C. Sanchez-Trujillo, M. Vazquez, Elsevier Science Publishers BV, 1987, P.58
R. A, Brand, Mössbauer Fit Programs, Distributed by: WissEl Company GmbH, 2006, Germany
Hesse, J., Rübartsch, A.: Model independent evaluation of overlapped Mossbauer spectra. J. Phys. E: Sci. Instrum. 7, 526–532 (1974)
Kübler, J.: Phys. Lett. A81, 81 (1981)
Shinjo, T., Keune. W.: J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 200, 598 (1999).
Ghafari, M., Louzguine-Luzgin, D.V., Hutchison, W.D., Feng, T., Campbell, S.J., Phys, J.: Condens. Matter. 30(45), 45–5701 (2018)
Ghafari, M., Keune, W., Brand, R.A., Day, R.K., Dunlop, J.B.: Local evidence for re-entrant magnetic behaviour in amorphous Fe90Zr10 alloys. Mat. Sci. Eng. 99, 65–68 (1988)
Ghafari, M., Day, R.K., Dunlop, J.B., McGrath, A.C.: Spin coupling in amorphous Fe90Sc10 alloy. J. of Mag. and Mag. Mater. 104-107, 1668–1670 (1992)
Ghafari, M., Hahn, H., Feng, T., Kruk, R., Yan, M.: On the relationship between magnetic moment and nuclear magnetic hyperfine field of 57Fe. Hyperfine Interact. 242, 2 (2021)
Schwarz, K., Mohn, P., Blaha, P., Kübler, J., J. Phys. F: Met. Phys. 14, 265 (1084)
Stoesser, A., Ghafari, M., Gleiter, H., Kilmametov, A.R., Skaurai, Y., Ito, M., Kohara, S., Hahn, H., Kamali, S.: Influence of interface on structure and magnetic properties of Fe50B50nanoglass. J. App. Phys. 116(13), 134305 (2014)
Ghafari, M., Hahn, H., Gleiter, H., Sakurai, Y., Itou, M., Kamali, S.: Evidence of itinerant magnetism in a metallic nanoglass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 243104 (2012)
Taylor, J.W., Duffy, J.A., Bebb, A.M., Cooper, M.J., Dugdale, S.B., McCarthy, J.E., Timms, D.N., Greig, D., Xu, Y.B.: Magnetic Compton scattering study of the ferromagnetic amorphous alloysFe1−xBx. Phys. Rev. B. 63, 220404 (2001)
Pauling, L.: The Nature of the Interatomic Forces in Metals. Phys. Rev. 54, 899–904 (1938)
Slater, J.C.: Electronic Structure of Alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 8, 385–390 (1937)
Fang, Y.N., Hahn, H., Kobe, S., Witte, R., Singh, S.P., Feng, T., Ghafari, M.: Sci. Rep. 9(412), 1 (2019)
Ghafari, M., Gleiter, H., Feng, T., Ohara, K., Hahn, H.: J. Mat. Sci. Eng. 5, 1000299 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Proceedings of the International Symposium on the Industrial Applications of the Mössbauer Effect (ISIAME), originally planned to be held in 2020 in Olomouc, Czech Republic, but postponed due to the corona-pandemic
Edited by Libor Machala
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghafari, M. Unexpected effect of boron on magnetic properties and structure of amorphous Fe-rich FeSc alloys. Hyperfine Interact 242, 4 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-021-01727-5
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-021-01727-5