Abstract
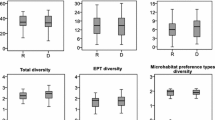
We studied whether and how channelization affects macroinvertebrate communities and biological quality in lowland streams of Estonia (Northern Europe). Two datasets of semi-quantitative samples (collected during 2001–2010) were used: (1) pairwise data (natural sites located upstream of the channelized sites; 22 streams, 24 pairs), and (2) background data (73 natural sites from 62 streams, 73 channelized sites from 62 streams). The mean stream order in both datasets was 3. Channelization had no significant effects on physicochemical parameters or on macroinvertebrates in the pairwise dataset where channelization was done decades earlier. However, it had several negative effects on macroinvertebrates in the background dataset where several areas had probably been maintained more recently. Richness of sensitive data, Shannon diversity, mean sensitivity, organic pollution index, and multimetric quality were significantly lower for the modified sites than for the natural sites. Only total taxon richness and score of hydromorphology were not significantly affected by channelization. Thus, several macroinvertebrate metrics that indicate water pollution, proved to be sensitive to channelization as well. The recovery conditions (such as stream type, channelization season, recovering duration, etc.) have been poorly studied and would deserve further attention.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armitage, P. D., D. Moss, J. F. Wright & M. T. Furse, 1983. The performance of a new biological water quality score system based on a wide range of unpolluted running-water sites. Water Research 17: 333–347.
Balestrini, R., M. Cazzola & A. Buffagni, 2004. Characterising hydromorphological features of selected Italian rivers: a comparative application of environmental indices. Hydrobiologia 516: 365–379.
Barbour, M. T. & C. O. Yoder, 2000. The multimetric approach to bioassessment, as used in the United States of America. In Wright, J. F., D. W. Sutcliffe & M. T. Furse (eds), Assessing the biological quality of fresh waters: RIVPACS and other techniques. Freshwater Biological Association, Ambleside, Cumbria: 281–292.
Bis, B., A. Zdanowicz & M. Zalewski, 2000. Effects of catchment properties on hydrochemistry, habitat complexity and invertebrate community structure in lowland river. Hydrobiologia 422(423): 369–387.
Blann, K. L., J. L. Anderson, G. R. Sands & B. Vondracek, 2009. Effects of agricultural drainage on aquatic ecosystems: a review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology 39: 909–1001.
Brooker, M. P., 1985. The ecological effects of channelization. The Geographical Journal 151: 63–69.
Brookes, A., 1987. Restoring the sinuosity of artificially straightened stream channels. Environmental Geology and Water Sciences 10: 33–41.
Camargo, J. A., A. Alonso & M. De la Puente, 2004. Multimetric assessment of nutrient enrichment in impounded rivers based on benthic macroinvertebrates. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 96: 233–249.
Couceiro, S. R. M., N. Hamada, B. R. Forsberg, T. P. Pimentel & S. L. B. Luz, 2012. A macroinvertebrate multimetric index to evaluate the biological condition of streams in the Central Amazon region of Brazil. Ecological Indicators 18: 118–125.
Dahl, J. & R. K. Johnson, 2004. A multimetric macroinvertebrate index for detecting organic pollution of streams in southern Sweden. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 160: 487–513.
Davy-Bowker, J. & M. T. Furse, 2006. Hydromorphology – major results and conclusions from the STAR project. Hydrobiologia 188: 263–265.
Dewson, Z. S., A. B. W. James & R. G. Death, 2007. A review of the consequences of decreased flow for instream habitat and macroinvertebrates. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 26: 401–415.
Directive 2000/60/EC, 2000. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy.
Dufrêne, M. & P. Legendre, 1997. Species assemblages and indicator species: the need for a flexible asymmetrical approach. Ecological Monographs 67: 345–366.
Duvel, W. A. & R. D. Volkmar, 1976. Environmental impact of stream channelization. Water Resources Bulletin 12: 799–812.
EE, 1990. Eesti Entsüklopeedia 5. Valgus (in Estonian).
European Committee for Standardization, 1994. 1 Water Quality – Methods for Biological Sampling – Guidance on Handnet Sampling of Aquatic Benthic Macro-invertebrates. EN 27828. European Committee for Standardization, Brussels.
Feld, C. K., F. de Bello & S. Doledec, 2014. Biodiversity of traits and species both show weak responses to hydromorphological alteration in lowland river macroinvertebrates. Freshwater Biology 59: 233–248.
Friberg, N., L. Sandin & M. L. Pedersen, 2009. Assessing the effects of hydromorphological degradation on macroinvertebrate indicators in rivers: examples, constraints, and outlook. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management 5: 86–96.
Frueh, D., S. Stoll & P. Haase, 2012. Physicochemical and morphological degradation of stream and river habitats increases invasion risk. Biological Invasions 14: 2243–2253.
Gabriels, W., K. Lock, N. De Pauw & P. L. M. Goethals, 2010. Multimetric Macroinvertebrate Index Flanders (MMIF) for biological assessment of rivers and lakes in Flanders (Belgium). Limnologica 40: 199–207.
Helson, J. E. & D. D. Williams, 2013. Development of a macroinvertebrate multimetric index for the assessment of low-land streams in the neotropics. Ecological Indicators 29: 167–178.
Hong, H. N., G. Everaert, W. Gabriels, H. H. Thu & P. L. M. Goethals, 2014. A multimetric macroinvertebrate index for assessing the water quality of the Cau river basin in Vietnam. Limnologica 45: 16–23.
Horsák, M., J. Bojková, S. Zahrádková, M. Omesová & J. Helešic, 2009. Impact of reservoirs and channelization on lowland river macroinvertebrates: a case study from Central Europe. Limnologica 39: 140–151.
Hortle, K. G. & P. S. Lake, 1982. Macroinvertebrate assemblages in channelized and unchannelized sections of the Bunyip River, Victoria. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 33: 1071–1082.
Johnson, R. K., 1999. Benthic macroinvertebrates. In Wiederholm, T. (ed.), Bedömningsgrunder för miljökvalitet. Sjöar och vattendrag. Bakgrundsrapport 2. Biologiska parametrar. Naturvårdsverket Förlag: 85–166 (in Swedish).
Julien, P. Y., 2010. Erosion and Sedimentation, 2nd ed. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Jun, Y.-C., D.-H. Won, S.-H. Lee, D.-S. Kong & S.-J. Hwang, 2012. A Multimetric Benthic Macroinvertebrate Index for the assessment of stream biotic integrity in Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 9: 3599–3628.
Käiro, K., H. Timm, T. Virro & M. Haldna, 2011. The effect of damming on biological quality according to macroinvertebrates in some Estonian streams, Central – Baltic Europe: a pilot study. River Research and. Applications 27: 895–907.
Käiro, K., H. Timm, M. Haldna & T. Virro, 2012. Biological quality on the basis of macroinvertebrates in dammed habitats of some Estonian streams, Central – Baltic Europe. International Review of Hydrobiology 97: 497–508.
Karr, J. R. & I. J. Schlosser, 1978. Water resources and the landwater interface. Science 201: 229–234.
Lenat, D. R., 1988. Water quality assessment of streams using a qualitative collection method for benthic macroinvertebrates. Journal of North American Benthological Society 7: 222–233.
Lewczuk, K. G. & P. Burandt, 2011. Effect of river straightening on the hydrochemical properties of floodplain lakes: observations from the Łyna and Drwęca Rivers, N Poland. Ecological Engineering 37: 786–795.
Lorenz, A., D. Hering, C. K. Feld & P. Rolauffs, 2004. A new method for assessing the impact of hydromorphological degradation on the macroinvertebrate fauna of five German stream types. Hydrobiologia 516: 107–127.
Maxted, J. R., M. T. Barbour, J. Gerritsen, V. Poretti, N. Primrose, A. Silvia, D. Penrose & R. Renfrow, 2000. Assessment framework for mid-Atlantic coastal plain streams using benthic macroinvertebrates. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 19: 128–144.
Ministry of Environment, 2009. Status classes and class boundaries for surface water bodies and the procedure of classification. Regulation of the Ministry of Environment. https://www.riigiteataja.ee/ert/act.jsp?id=13210253&replstring=33. Accessed 30 June 2011.
Mondy, C. P., B. Villeneuve, V. Archaimbault & P. Usseglio-Polatera, 2012. A new macroinvertebrate-based multimetric index (I2M2) to evaluate ecological quality of French wadeable streams fulfilling the WFD demands: a taxonomical and trait approach. Ecological Indicators 18: 452–467.
Munne, A. & N. Prat, 2009. Use of macroinvertebrate-based multimetric indices for water quality evaluation in Spanish Mediterranean rivers: an intercalibration approach with the IBMWP index. Hydrobiologia 628: 203–225.
Nakamura, F. & H. Yamada, 2005. The effects of pasture development on the ecological functions of riparian forests in Hokkaido in Northern Japan. Ecological Engineering 24: 539–555.
Nakano, D., S. Nagayama, Y. Kawaguchi & F. Nakamura, 2008. River restoration for macroinvertebrate communities in lowland rivers: insights from restorations of the Shibetsu River, north Japan. Landscape and Ecological Engineering 4: 63–68.
Negishi, J. N., M. Inoue & M. Nunokawa, 2002. Effects of channelization on stream habitat in relation to a spate and flow refugia for macroinvertebrates in northern Japan. Freshwater Biology 47: 1515–1529.
Ofenböck, T., O. Moog, J. Gerritsen & M. Barbour, 2004. A stressor specific multimetric approach for monitoring running waters in Austria using benthic macro-invertebrates. Hydrobiologia 516: 251–268.
Oliveira, R. B. S., D. F. Baptista, R. Mugnai, C. M. Castro & R. M. Hughes, 2011. Towards rapid bioassessment of wadeable streams in Brazil: development of the Guapiacu-Macau Multimetric Index (GMMI) based on benthic macroinvertebrates. Ecological Indicators 11: 1584–1593.
Pedersen, M. L. & N. Friberg, 2009. Influence of disturbance on habitats and biological communities in lowland streams. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 174: 27–41.
Pinto, P., J. Rosado, M. Morais & I. Antunes, 2004. Assessment methodology for southern siliceous basins in Portugal. Hydrobiologia 516: 191–214.
Pliūraite, V. & V. Kesminas, 2011. Response of benthic macroinvertebrates to agricultural pollution and channelization in the Mūša River, Lithuania. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin 19: 2929–2934.
Quinn, J. M., R. B. Williamson, R. K. Smith & M. L. Vickers, 1992. Effects of riparian grazing and channelization on streams in Southland, New Zealand. 2. Benthic invertebrates. New Zealand. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 26: 259–273.
R Core Team, 2014. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. http://www.R-project.org/.
Rabeni, C. F., 2000. Evaluating physical habitat integrity in relation to the biological potential of streams. Hydrobiologia 422(423): 245–256.
Raukas, A. & A. M. Rõuk, 1995. Relief and its formation. In Raukas, A. (ed.), Estonian Nature. Valgus and Eesti Entsüklopeediakirjastus: 120–175 (in Estonian).
Rohasliney, H. & D. C. Jackson, 2008. Lignite mining and stream channelization influences on aquatic macroinvertebrate assemblages along the Natchez Trace Parkway, Mississippi, USA. Hydrobiologia 598: 149–162.
Rosenberg, D. M., P. McCully & C. M. Pringle, 2000. Global-scale environmental effects of hydrological alternations: introduction. BioScience 50: 746–752.
Skriver, J., N. Friberg & J. Kirkegaard, 2000. Biological assessment of watercourse quality in Denmark: introduction of the Danish Stream Fauna Index (DSFI) as the official biomonitoring method. Verhandlungen des Internationalen Verein Limnologie 27: 1822–1830.
Smiley, P. C. & E. D. Dibble, 2008. Influence of spatial resolution on assessing channelization impacts on fish and macroinvertebrate communities in a warm water stream in southeastern United Stated. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 138: 17–29.
Timm, H., M. Ivask & T. Möls, 2001. Response of macroinvertebrates and water quality to long-term decrease in organic pollution in some Estonian streams during 1990–1998. Hydrobiologia 464: 153–164.
Timm, H., K. Käiro, T. Möls & T. Virro, 2011. An index to assess hydromorphological quality of Estonian surface waters based on macroinvertebrate taxonomic composition. Limnologica 41: 398–410.
Townsend, C. R., R. M. Thompson, A. R. McIntosh, C. Kilroy, E. Edwards & M. R. Scarsbrook, 1998. Disturbance, resource supply, and food-web architecture in streams. Ecology Letters 1: 200–209.
Tuulmets, H. & L. Aasalo, 1980. Jõed ja järved. In Põllumajandusmaastik Eestis. Tallinn: 45–50 (in Estonian).
van de Bund, W. (ed.), 2009. Water Framework Directive Intercalibration Technical Report. Part 1: Rivers. JRC Scientific and Technical Reports.
Vlek, H. E., P. F. M. Verdonschot & R. C. Nijboer, 2004. Towards a multimetric index for the assessment of Dutch streams using benthic macroinvertebrates. Hydrobiologia 516: 173–189.
Wooster, D. E., S. W. Miller & S. J. Debano, 2013. An examination of the impact of multiple disturbances on a river system: taxonomic metrics versus biological traits. River Research and Applications 28: 1630–1643.
Yoshimura, M., 2012. Effects of forest disturbances on aquatic insect assemblages. Entomological Science 15: 145–154.
Acknowledgements
The study was carried out at the Estonian University of Life Sciences, Centre for Limnology. It was supported by the IUT 21-2 of the Estonian Ministry of Education and Research and by the European Social Fund’s Doctoral Studies and Internationalisation Programme DoRa, which is carried out by Foundation Archimedes. We would also like to thank Ester Jaigma and two anonymous reviewers who helped to improve the contents of text.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Checo Colón-Gaud
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10750_2017_3091_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Supplementary material 1 List of species. * Represents presence or encounter of taxon in site/dataset during sampling (DOC 422 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Käiro, K., Haldna, M., Timm, H. et al. The effect of channelization on the biological quality of lowland streams using macroinvertebrates as proxies. Hydrobiologia 794, 167–177 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3091-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3091-9