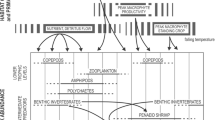
Abstract
To better understand the species composition and nutrition of deepwater sponges in Lake Baikal, we determined the depth, habitat, and stable isotopic signatures for deepwater sponges. All sponge specimens except one were collected at depths below the photic zone and in a variety of benthic habitats including methane seeps and hydrothermal vents. The freshwater sponge species of Lake Baikal generally occurred in aggregations (fields, carpets, and belts), and mainly on hard substrates (different types of bedrock and argillite, and bitumen). New maximum depth records were established for three species. The deepwater sponges clustered into two groups, based on their isotopic values, with members of one group assimilating organic carbon from photosynthetic sources and exhibiting δ13C values (−32 to −26.9‰) similar to those reported previously for littoral sponges. Members of the second group, distinguished by highly depleted δ13C values (−65 to −37.3‰), participate in a chemosynthetic food web. δ15N values of the deepwater sponges ranged widely (2.1–16.7‰) suggesting that they assimilate nitrogen from environmental sources and possibly from their microbial symbionts. Conservation of deepwater sponge diversity is therefore, likely dependent on the diversity of resources found in different habitats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beckman, M. Yu. & R. S. Den’gina, 1969. Benthic populations and food resources of Baikal fishes. In Beckman M. Yu. (ed.), Biological Productivity of Siberian Water Bodies (in Russian). Nauka, Moscow: 42–47.
Bett, B. J., 2001. UK Atlantic Margin Environmental Survey: introduction and overview of bathyal benthic ecology. Continental Shelf Research 21: 917–956.
Brooks, J. M., M. C. Kennicutt II, C. R. Fisher, S. A. Macko, K. Cole, J. J. Chikdress, R. R. Bidigare & R. D. Vetter, 1987. Deep-sea hydrocarbon seep communities: evidence for energy and nutritional carbon sources. Science 238: 1138–1142.
Bukharov, A. A. & V. A. Fialkov, 1996. Geological Structure of the Bottom of Lake Baikal. In Kuzmin M. I. (ed.), Look from “Piscies” (in Russian). Nauka, Novosibirsk.
Bukshuk, N. A. & O. A. Timoshkin, 2013. Some features of Baikalospongia intermedia (Spongia: Lubomirskiidae) morphology and vertical distribution in deepwater zone of Lake Baikal. Bulletin Irkutsk State University, Seria Biology. Ecology 6: 127–130.
Cuylaerts, M., L. Naudts, R. Casier, A. Khabuev, O. Belousov, E. Kononov, O. Khlystov & M. De Batist, 2012. Distribution and morphology of mud volcanoes and other fluid flow-related lake bed structures in Lake Baikal, Russia. Geo-Marine Letters 32: 383–394.
Demopoulos, A. W. J., D. Gualtieri & K. Kovacs, 2010. Food-web structure of seep sediment macrobenthos from the Gulf of Mexico. Deep-Sea Research II 57: 1972–1981.
Efremova, S. M., 2001. Porifera. In Timoshkin, O. A. (ed.), Index of Animal Species Inhabiting Lake Baikal and Its Catchment Area, Book 1, Vol. 1. Nauka, Novosibirsk: 172–192.
Efremova, S. M., 2004. New genus and new species of sponges from family Lubomirskiidae Rezvoj, 1936. In Timoshkin, O. A. (ed.), Index of animal species inhabiting Lake Baikal and its catchment area, Book 2, Vol. 1. Nauka, Novosibirsk: 1261–1278.
Fiore, C. L., D. M. Baker & M. P. Lesser, 2013. Nitrogen biogeochemistry in the Caribbean Sponge, Xestospongia muta: a source or sink of dissolved inorganic nitrogen. PLoS One 8: e72961.
Freeman, C. J. & R. W. Thacker, 2011. Complex interactions between marine sponges and their symbiotic microbial communities. Limnology and Oceanography 56: 1577–1586.
Gebruk, A. V., A. I. Kuznetsov, B. B. Namsaraev & Y. M. Miller, 1993. The role of bacterial organic matter in the nutrition of deepwater benthic fauna in Frolikha Bay (Lake Baikal) under conditions of increased thermal flow. Biology Bulletin, Seria Biologia 6: 903–908.
Golubev, V. A., 2007. Conductive and Convective Heat Output in the Baikal Rift Zone. Academic Publishing House “Geo”, Novosibirsk.
Granin, N. G. & L. Z. Granina, 2002. Gas hydrates and gas venting in Lake Baikal. Russian Geology and Geophysics 43: 629–637.
Granin, N. G., M. M. Makarov, K. M. Kucher & R. Y. Gnatovsky, 2010. Gas seeps in Lake Baikal – detection, distribution, and implications for water column mixing. Geo-Marine Letters 30: 399–409.
Hentschel, U., J. Piel, S. M. Degnan & M. W. Taylor, 2012. Genomic insights into the marine sponge microbiome. Nature Reviews Microbiology 10: 641–654.
Hoffmann, F., R. Radax, D. Woebken, M. Holtappels, G. Lavik, H. T. Rapp, M. L. Schläppy, C. Schleper & M. M. Kuypers, 2009. Complex nitrogen cycling in the sponge Geodia barretti. Environmental Microbiology 11: 2228–2243.
Hogg, M. M., O. S. Tendal, K. W. Conway, S. A. Pomponi, R. W. M. van Soest, J. Gutt, M. Krautter & J. M. Roberts, 2010. Deep-sea sponge grounds: reservoirs of biodiversity. UNEP-WCMC Biodiversity Series, 32. UNEP-WCMC, Cambridge.
Itskovich, V. B., O. V. Kaluzhnaya, E. Veynberg, D. Erpenbeck, 2015. Endemic Lake Baikal sponges from deep water. 1: potential cryptic speciation and discovery of living species known only from fossils. Zootaxa 3990: 123–137.
Jones, R. I. & J. Grey, 2011. Biogenic methane in freshwater food webs. Freshwater Biology 56: 213–229.
Kaluzhnaya, O. V. & V. B. Itskovich, 2014. Phylogenetic diversity of microorganisms associated with the deepwater sponge Baikalospongia intermedia. Russian Journal of Genetic 50: 667–676.
Khlystov, O. M., T. I. Zemskaya, T. Y. Sitnikova, I. V. Mekhamikova, I. A. Kaigorodova, A. G. Gorshkov, O. V. Shubenkova, S. M. Chernitsyna, A. V. Lomakina, A. V. Likhoshvai, A. M. Sagalevich, V. I. Moskvin, V. I. Peresypkin, N. A. Belyaev & M. V. Slipenchuk, 2009. Bottom bituminous constructions and biota inhabiting them according to investigation of Lake Baikal with the Mir submersible. Doklady Earth Sciences 429: 1333–1336.
Khlystov, O., M. De Batist, H. Shoji, A. Hachikubo, S. Nishio, L. Naudts, J. Poort, A. Khabuev, O. Belousov, A. Manakov & G. Kalmychkov, 2013. Gas hydrate of Lake Baikal: discovery and varieties. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 62: 162–166.
Kiyashko, S. I., P. Richard, T. Chandler, T. A. Kozlova & D. Willams, 1998. Stable carbon isotope ratios differentiate autotrophs supporting animal diversity in Lake Baikal. Comptes Rendus de L’Academy des Science, Ser III, Sciences de la Vie 321: 509–516.
Kiyashko, S. I., T. Narita & E. Wada, 2001. Contribution of methanotrophs to freshwater macroinvertebrates: evidence from stable isotope ratios. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 24: 203–207.
Klitgaard, A. B. & O. S. Tendal, 2004. Distribution and species composition of mass occurrences of large-sized sponges in the northeast Atlantic. Progress in Oceanography 61: 57–98.
Kuznetsov, A. P., V. P. Strizhev, V. S. Kuzin, V. A. Fialkov & V. S. Yastrebov, 1991. New in Lake Baikal nature. Community based on bacterial chemosynthesis. Biology Bulletin 5: 766–772.
Levin, L. A., 2005. Ecology of cold seep sediments: interactions of fauna with flow, chemistry and microbes. Oceanography and Marine Biology 43: 1–46.
Levin, L. A. & R. H. Michener, 2002. Isotopic evidence for chemosynthesis-based nutrition of macrobenthos: the lightness of being at Pacific methane seeps. Limnology and Oceanography 47: 1336–1345.
Lomakina, A. V., T. V. Pogodaeva, I. V. Morozov & T. I. Zemskaya, 2014. Microbial communities of the discharge zone of oil and gas-bearing fluids in low-mineral Lake Baikal. Microbiology 83: 278–287.
Masuda, Y., 2009. Studies on the taxonomy and distribution of the freshwater sponges in Lake Baikal. Progress in Molecular and Subcellular Biology 47: 81–110.
Mats, V. D. & T. I. Perepelova, 2011. A new perspective on evolution of the Baikal Rift. Geoscience Frontiers, China University of Geosciences (Bejing) 2: 349–365.
Minami, H., A. Hachikubo, H. Sakagami, S. Yamashita, Yu. Soramoto, T. Kotake, N. Takahashi, H. Shoji, T. Pogodaeva, O. Khlystov, A. Khabuev, L. Naudts & M. De Batist, 2014. Sequentially sampled gas hydrate water, coupled with pore water and bottom water isotopic and ionic signatures at the Kukuy mud volcano, Lake Baikal: ambiguous deep-rooted source of hydrate-forming water. Geo-Marine Letters 34: 241–251.
Mintenbeck, K., U. Jacob, R. Knust, W. E. Arntz & T. Brey, 2007. Depth-dependence in stable isotope ratio δ15N of benthic POM consumers: the role of particle dynamics and organism trophic guild. Deep-Sea Research I 54: 1015–1023.
Murillo, F. J., P. D. Muñoz, J. Cristobo, P. Pios, C. González, E. Kenchington & A. Serrano, 2012. Deep-sea sponge ground of the Flemish Cap, Flemish Pass and the Grand Banks of Newfoundland (Northwest Atlantic Ocean): distribution and species composition. Marine Biological Research 8: 842–854.
Pile, A. J., M. R. Patterson, M. Savarese, V. I. Chernykh & V. A. Fialkov, 1997. Trophic effects of sponge feeding within Lake Baikal’s littoral zone. 2. Sponge abundance, diet, feeding efficiency, and carbon flux. Limnology and Oceanography 42: 178–184.
Rezvoj, P. D., 1936. Freshwater Sponges. Fauna of the USSR. AN SSSR Publishers, Moscow.
Schmid, M., N. M. Budnev, N. G. Granin, M. Sturm, M. Schurter & A. Wuest, 2008. Lake Baikal deepwater renewal mystery solved. Geophysical Research Letters 35: L09605.
Sitnikova, T. Y. & A. A. Shirokaya, 2013. New data on deepwater Baikal limpets in hydrothermal vents and oil-seeps. Archive für Molluskenkunde 142: 257–278.
Skelton, J. & M. Strand, 2013. Trophic ecology of a freshwater sponge (Spongilla lacustris) revealed by stable isotope analysis. Hydrobiologia 709: 227–235.
Southwell, M. W., B. N. Popp & C. S. Martens, 2008. Nitrification controls on fluxes and isotopic composition of nitrate from Florida Keys sponges. Marine Chemistry 108: 96–108.
Steger, D., P. Ettinger-Epstein, S. Whalan, U. Hentschel, R. de Nys, M. Wagner & M. W. Taylor, 2008. Diversity and mode of transmission of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea in marine sponges. Environmental Microbiology 10: 1087–1094.
Stone, R. P., H. Lehnert & H. Reiswig, 2011. A guide to the deepwater sponges of the Aleutian Island Archipelago. NOAA Professional papers NMFS, National Marine Fisheries Service, Seattle [available on internet at http://spo.nmfs.noaa.gov/pp12.pdf].
Thacker, R. W. & C. J. Freeman, 2013. Sponge-microbe symbioses: recent advances and new directions. In Becerro M. A. & M. J. Utiz (eds), Advances in sponge science: physiology, chemical and microbial diversity, biotechnology. Advances in Marine Biology 62: 57–112.
Thurber, A. R., K. Kroger, C. Neira, H. Wiklund & L. A. Levin, 2010. Stable isotope signatures and methane use by New Zealand cold seep benthos. Marine Geology 272: 260–269.
Timoshkin, O.A., 2001. Lake Baikal: diversity of fauna, problems of its immiscibility and origin, ecology and ‘exotic’ communities. In Timoshkin OA (ed) Index of animal species inhabiting lake Baikal and its catchment area, book 1, Vol. 1. Nauka, Novosibirsk: 74–116.
Tsimitri, C., B. Rockel, A. Wuest, N. M. Budnev, M. Sturm & M. Schmid, 2015. Drivers of deep-water renewal events observed over 13 years in the South Basin of Lake Baikal. Journal of Geophysical Research-Oceans 120: 1508–1526.
Vacelet, J. & E. Duport, 2004. Prey capture and digestion in the carnivorous sponge Asbestopluma hypogea (Porifera: Demospongiae). Zoomorphology 123: 179–190.
Wada, E., H. Mizutani & M. Minagawa, 1991. The use of stable isotopes for food web analysis. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 30: 361–371.
Webster, N. S. & M. W. Taylor, 2012. Marine sponges and their microbial symbionts: love and other relationships. Environmental Microbiology 14: 335–346.
Whiticar, M. J. & E. Faber, 1986. Methane oxidation in sediment and water column environments—isotope evidence. Organic Geochemistry 10: 759–768.
Yoshii, K., 1999. Stable isotope analyses of benthic organisms in Lake Baikal. Hydrobiologia 411: 145–159.
Yoshii, K., N. G. Melnik, O. A. Timoshkin, N. A. Bondarenko, P. N. Anoshko, T. Yoshioka & E. Wada, 1999. Stable isotope analyses of the pelagic food web in Lake Baikal. Limnology and Oceanography 44: 502–511.
Zapata-Hernández, G., J. Sellanes, C. Mayr & P. Muñoz, 2014a. Benthic food structure in the Comau fjord, Chile (~42°S): preliminary assessment including a site with chemosynthetic activity. Progress in Oceanography 129: 149–158.
Zapata-Hernández, G., J. Sellanes, A. Thurber & L. Levin, 2014b. Trophic structure of the bathyal benthos at an area with evidence of methane seep activity off southern Chile (~45°S). Journal Marine Biological Association UK 94: 659–669.
Zemskaya, T. I., S. M. Chernitsyna, N. M. Dul’tseva, V. N. Sergeeva, T. V. Pogodaeva & B. B. Namsaraev, 2009. Colorless sulfur bacteria Thioploca from different sites in Lake Baikal. Microbiologia 78: 134–143.
Zemskaya, T. I., T. Y. Sitnikova, S. I. Kiyashko, G. V. Kalmychkov, T. V. Pogodaeva, I. V. Mekhanikova, T. V. Naumova, O. V. Shubenkova, S. M. Chernitsina, O. V. Kotsar, E. S. Chernyaev & O. M. Khlystov, 2012. Faunal communities at sites of gas- and oil-bearing fluids in Lake Baikal. Geo-Marine Letters 32: 437–451.
Zemskaya, T. I., A. V. Lomakina, E. V. Mamaeva, A. S. Zakharenko, T. V. Pogodaeva, D. P. Petrova & Y. P. Galachyants, 2015. Bacterial communities in sediments of Lake Baikal from areas with oil and gas discharge. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 76: 95–109.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Lake Baikal Protection Fund and the METROPOL Group of Companies (field research); the praesidium of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, program No. 23.8, State Project No, VIII.76.1.7 (0345–2014–0009) (Limnological Institute SB RAS); and the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project Nos. 09-04-00781 and 14-44-04126. The authors are grateful to the crews of the remote vehicles “G.Yu. Vereshchagin” (Captain: A.G. Palvich) and “V.A. Koptyug” (Captain: A.N. Bityutskii), the pilots of the Mir-1 and Mir-2 submersibles, different investigators who helped with sponge collection, and Drs. M. Sakirko and S. Chernitsyna who processed material on the ship. Language support of the first version was provided by Oxford Science Editing Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Vasilis Valavanis
This article was updated on April 20, 2016.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sitnikova, T., Kiyashko, S., Bukshuk, N. et al. Stable isotope signatures and distribution of deepwater sponges in Lake Baikal. Hydrobiologia 773, 11–22 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2674-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2674-1