Abstract
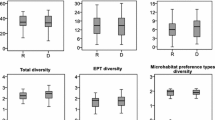
River restoration enhances not only habitat diversity in the stream channel and riparian zone, but also retention of organic matter, which together are expected to enhance aquatic-terrestrial linkages, and the range of autochthonous and allochthonous resources. Consequently, alterations of food-web structure and trophic relationships can be expected. We applied stable isotope analysis (δ13C, δ15N) to characterize changes in the trophic structure of benthic invertebrate communities between paired restored and unrestored river reaches across 16 European catchments. We sampled dominant taxa of invertebrate assemblages belonging to different functional feeding groups and calculated δ13C range to estimate the diversity of basal resources assimilated, δ15N range as an indicator of the trophic length and standard ellipse area corrected for small samples as a measure of isotopic niche width. We analysed (1) if restoration influences the trophic structure of invertebrates, (2) if effects of restoration depend on the extent of restoration effort, and (3) if effects of restoration depend on restoration measures applied. Our European-scale comparison indicates that river habitat restoration effects trophic structure, primarily by increasing the breadth of resources assimilated by consumers; this effect increases with restoration effort and it depends on restoration measure type.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrantes, K., A. Barnett & S. Bouillon, 2014. Stable isotope-based community metrics as a tool to identify patterns in food web structure in east African estuaries. Functional ecology 28: 270–282.
Batschelet, E., 1981. Circular Statistics in Biology. Academic Press, London.
Calizza, E., M. L. Costantini, D. Rossi, P. Carlino & L. Rossi, 2012. Effects of disturbance on an urban river food web. Freshwater Biology 57: 2613–2628.
Cooper, R. N. & B. Wissel, 2012. Loss of trophic complexity in saline prairie lakes as indicated by stable-isotope based community metrics. Aquatic Biosystems 8: 6.
DeNiro, M. J. & S. Epstein, 1978. Influence of diet in the distribution of carbon isotopes in animals. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 42: 495–506.
Fischer, H., F. Kloep, S. Wilzcek & M. T. Pusch, 2005. A river’s liver – microbial processes within the hyporheic zone of a large lowland river. Biogeochemistry 76: 349–371.
Flores, L., A. Larrañaga, J. Díez & A. Elosegi, 2011. Experimental wood addition in streams: effects on organic matter storage and breakdown. Freshwater Biology 56: 2156–2167.
Friberg, N. & D. Jacobsen, 1994. Feeding plasticity of two detritivore-shredders. Freshwater Biology 32: 133–142.
Friberg, N., J. B. Dybkjær, J. S. Olafsson, G. M. Gislason, S. E. Larsen & T. L. Lauridsen, 2009. Relationships between structure and function in streams contrasting in temperature. Freshwater Biology 54: 2051–2068.
Friberg, N., A. Baattrup-Pedersen, E. A. Kristensen, B. Kronvang, S. E. Larsen, M. L. Pedersen, J. Skriver, H. Thodsen & P. Wiberg-Larsen, 2014. The Gelså River Restoration Revisited: community persistence of the invertebrate community over an 11-year period. Ecological Engineering 66: 150–157.
Göthe, E., F. Lepori & B. Malmqvist, 2009. Forestry affects food webs in northern Swedish coastal streams. Fundamental and Applied Limnology/Archiv für Hydrobiologie 175: 281–294.
Göthe, E., A. Timmermann, K. Januschke & A. Baattrup-Pedersen, 2015. Structural and functional responses of floodplain vegetation to stream ecosystem restoration. Hydrobiologia. doi:10.1007/s10750-015-2401-3.
Gücker, B., I. G. Boëchat & A. Giani, 2009. Impacts of agricultural land use on ecosystem structure and whole-stream metabolism of tropical Cerrado streams. Freshwater Biology 54: 2069–2085.
Haase, P., S. Lohse, S. Pauls, K. Schindehütte, A. Sundermann, P. Rolauffs & D. Hering, 2004. Assessing streams in Germany with benthic invertebrates: development of a practical standardized protocol for macroinvertebrate sampling and sorting. Limnologica 34: 349–365.
Haase, P., D. Hering, S. C. Jähnig, A. W. Lorenz & A. Sundermann, 2013. The impact of hydromorphological restoration on river ecological status: a comparison of fish, benthic invertebrates, and macrophytes. Hydrobiologia 704: 475–488.
Hering, D., J. Aroviita, A. Baattrup-Pedersen, K. Brabec, T. Buijse, F. Ecke, N. Friberg, M. Gielczewski, K. Januschke, J. Köhler, B. Kupilas, A. Lorenz, S. Muhar, A. Paillex, M. Poppe, T. Schmidt, S. Schmutz, P. J. Vermaat, P. F. M. Verdonschot & R. Verdonschot, 2015. Contrasting the roles of section length and instream habitat enhancement for river restoration success: a field study on 20 European restoration projects. Journal of Applied Ecology 50: 97–106. doi:10.1111/1365-2664.12531.
Hieber, M. & M. O. Gessner, 2002. Contribution of stream detrivores, fungi, and bacteria to leaf breakdown based on biomass estimates. Ecology 83: 1026–1038.
Jähnig, S. C., K. Brabec, A. Buffagni, S. Erba, A. W. Lorenz, T. Ofenböck, P. F. M. Verdonschot & D. Hering, 2010. A comparative analysis of restoration measures and their effects on hydromorphology and benthic invertebrates in 26 central and southern European rivers. Journal of Applied Ecology 47: 671–680.
Jackson, A. L., R. Inger, A. C. Parnell & S. Bearhop, 2011. Comparing isotopic niche widths among and within communities: SIBER – Stable Isotope Bayesian Ellipses in R. Journal of Animal Ecology 80: 595–602.
Jackson, M. C., I. Donohue, A. L. Jackson, J. R. Britton, D. M. Harper & J. Grey, 2012. Population-level metrics of trophic structure based on stable isotopes and their application to invasion ecology. Plos One 7(2): e31757.
Januschke, K., S. C. Jähnig, A. W. Lorenz & D. Hering, 2014. Mountain river restoration measures and their success(ion): effects on river morphology, local species pool, and functional composition of three organism groups. Ecological Indicators 38: 243–255.
Layer, K., A. G. Hildrew & G. Woodward, 2013. Grazing and detritivory in 20 stream food webs across a broad pH gradient. Oecologia 171: 459–471.
Layman, C. A., J. P. Quattrochi, C. M. Peyer & J. E. Allgeier, 2007a. Niche width collapse in a resilient top predator following ecosystem fragmentation. Ecology Letters 10: 937–944.
Layman, C. A., D. A. Arrington, C. G. Montana & D. M. Post, 2007b. Can stable isotope ratios provide for community-wide measures of trophic structure? Ecology 88: 42–48.
Lepori, F., D. Palm, E. Brännäs & B. Malmqvist, 2005a. Does restoration of structural heterogeneity in streams enhance fish and invertebrate diversity? Ecological Applications 15: 2060–2071.
Lepori, F., D. Palm & B. Malmqvist, 2005b. Effects of stream restoration on ecosystem functioning: detritus retentiveness and decomposition. Journal of Applied Ecology 42: 228–238.
Lepori, F., D. Gaul, D. Palm & B. Malmqvist, 2006. Food-web responses to restoration of channel heterogeneity in boreal streams. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 63: 2478–2486.
Lorenz, A. W., T. Korte, A. Sundermann, K. Januschke & P. Haase, 2012. Macrophytes respond to reach-scale river restorations. Journal of Applied Ecology 49: 202–212.
McCarthy, M. A., 2007. Bayesian Methods for Ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
McCutchan Jr, J. H., W. M. Jr, C. Kendall Lewis & C. C. McGrath, 2003. Variation in trophic shift for stable isotope ratios of carbon, nitrogen and sulfur. Oikos 102: 378–390.
McKie, B. & B. Malmqvist, 2009. Assessing ecosystem functioning in streams affected by forest management: increased leaf decomposition occurs without changes to the composition of benthic assemblages. Freshwater Biology 54: 2086–2100.
Mihuc, T. B., 1997. The functional trophic role of lotic primary consumers: generalist versus specialist strategies. Freshwater Biolology 37: 455–462.
Minagawa, M. & E. Wada, 1984. Stepwise enrichment of 15 N along food chains: further evidence and the relation between δ15 N and animal age. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 48: 1135–1140.
Muhar, S., K. Januschke, J. Kail, M. Poppe, D. Hering & A. D. Buijse, 2015. Evaluating good-practice cases for river restoration across Europe: context, methodological framework, selected results and recommendations. Hydrobiologia (this issue)
Osenberg, C. W., O. Sarnelle & S. D. Cooper, 1997. Effect size in ecological experiments: the application of biological models in meta-analysis. The American Naturalist 150: 798–812.
Palmer, M. A., K. L. Hondula & B. J. Koch, 2014. Ecological restoration of streams and rivers: shifting strategies and shifting goals. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 45: 247–269.
Poppe, M., J. Kail, J. Aroviita, M. Stelmaszczyk, M. Giełczewski & S. Muhar, 2015. Assessing restoration effects on hydromorphology in European mid-sized rivers by key hydromorphological parameters. Hydrobiologia. doi:10.1007/s10750-015-2468-x.
Parnell, A. C., R. Inger, S. Bearhop & A. L. Jackson, 2008. SIAR: Stable isotope analysis in R. http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/siar.
Parnell, A. C., R. Inger, S. Bearhop & A. L. Jackson, 2010. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: coping with too much variation. Plos One 5(3): e9672.
Post, D. M., 2002. Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: models, methods and assumptions. Ecology 83: 703–718.
R Development Core Team, 2007. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org.
Rooney, N., K. McCann, G. Gellner & J. C. Moore, 2006. Structural asymmetry and the stability of diverse food webs. Nature 442: 265–269.
Schmidt-Kloiber, A. & D. Hering, 2015. www.freshwaterecology.info – an online tool that unifies, standardises and codifies more than 20,000 European freshwater organisms and their ecological preferences. Ecological Indicators 53: 271–282.
Stoll, S., J. Kail, A. W. Lorenz, A. Sundermann & P. Haase, 2014. The importance of the regional species pool, ecological species traits and local habitat conditions for the colonization of restored river reaches by fish. Plos One 9(1): e84741.
Schmutz, S., H. Kremser, A. Melcher, M. Jungwirth, S. Muhar, H. Waidbacher & G. Zauner, 2014. Ecological effects of rehabilitation measures at the Austrian Danube: a meta-analysis of fish assemblages. Hydrobiologia 729: 49–60.
Sundermann, A., C. Antons, N. Cron, A. W. Lorenz, D. Hering & P. Haase, 2011. Hydro-morphological restoration of running waters: effects on benthic invertebrate assemblages. Freshwater Biology 56: 1689–1702.
Vander Zanden, M. J. & J. B. Rasmussen, 1999. Primary consumer delta C-13 and delta N-15 and the trophic position of aquatic consumers. Ecology 80: 1395–1404.
Vander Zanden, M. J. & J. B. Rasmussen, 2001. Variation in δ15N and δ13C trophic fractionation: implications for aquatic food web studies. Limnology and Oceanography 46: 2061–2066.
Webster, J. R. & J. L. Meyer, 1997. Stream organic matter budgets. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 16: 3–4.
Wissinger, S., J. Steinmetz, J. S. Alexander & W. Brown, 2004. Larval cannibalism, time constraints, and adult fitness in caddisflies that inhabit temporary wetlands. Oecologia 138: 39–47.
Woodward, G., 2009. Biodiversity, ecosystem functioning and food webs in fresh waters: assembling the jigsaw puzzle. Freshwater Biology 54: 2171–2187.
Woodward, G. & A. G. Hildrew, 2002. Food web structure in riverine landscapes. Freshwater Biology 47: 777–798.
Woodward, G., B. Ebenman, M. Emmerson, J. M. Montoya, J. M. Olesen, A. Valido & P. H. Warren, 2005. Body size in ecological networks. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 20: 402–409.
Woodward, G., J. B. Christensen, J. S. Olafsson, G. M. Gislason, E. R. Hannesdottir & N. Friberg, 2010. Sentinel systems on the razor’s edge: effects of warming on Arctic geothermal stream ecosystems. Global Change Biology 16: 1979–1991.
Acknowledgments
This study results from the EU-funded project REFORM (Restoring rivers FOR effective catchment Management), European Union’s Seventh Programme for research, technological development and demonstration under Grant Agreement No. 282656. We further acknowledge a PhD fellowship of the German Environment Foundation (Deutsche Bundesstiftung Umwelt, DBU) to B.K. We are grateful to many colleagues who spent their time sampling in the field and preparing samples and to the crew of the stable isotope facility for analysing the samples. Two anonymous reviewers provided detailed and constructive comments which have improved this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: Jochem Kail, Brendan G. McKie, Piet F. M. Verdonschot & Daniel Hering / Effects of hydromorphological river restoration
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kupilas, B., Friberg, N., McKie, B.G. et al. River restoration and the trophic structure of benthic invertebrate communities across 16 European restoration projects. Hydrobiologia 769, 105–120 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2569-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2569-6