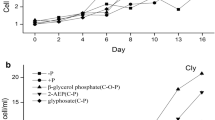
Abstract
Growth and competition between the dinoflagellates Prorocentrum donghaiense and Alexandrium catenella and the diatom Skeletonema costatum sensu lato in response to different forms of phosphorus were investigated in mixed cultures. The results indicated that S. costatum s.l. outcompeted P. donghaiense to become dominant owing to high growth rates, irrespective of the KH2PO4 content or any dissolved organic phosphorus (DOP) substrate. However, P. donghaiense densities in the DOP substrates, particularly lecithin, grew to 2–4 times higher than those in KH2PO4. The growth rates of P. donghaiense and A. catenella were comparable. A. catenella densities decreased when the phosphorus substrate was changed from inorganic to organic, and P. donghaiense outcompeted A. catenella only when lecithin was added. Abundant alkaline phosphatase (AP) was expressed when the external phosphate was lower than 0.1 μmol l−1. The highest bulk AP activities in the lecithin treatments suggested that lecithin might be more difficult to hydrolyze by these algae compared with glucose-6-phosphate and ribonucleic acid. We suggested that the advantage which P. donghaiense was shown to have in utilizing DOP for growth is what allowed it to become abundant or even dominant in natural communities when phosphate was depleted.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, D. M., P. M. Glibert & J. M. Burkholder, 2002. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuaries 25: 704–726.
Antia, N. J., P. J. Harrison & L. Oliveira, 1991. The role of dissolved organic nitrogen in phytoplankton nutrition, cell biology and ecology. Phycologia 30: 1–89.
Benitez-Nelson, C. R., 2000. The biogeochemical cycling of phosphorus in marine systems. Earth-Science Reviews 591: 109–135.
Bruckmeier, B., H. Eisenmann & W. Beisker, 2005. Exogenous alkaline phosphatase activity of algal cells determined by fluorometric and flow cytometric detection of soluble enzyme product (4-methyl-umbelliferone, fluorescein). Journal of Phycology 41: 993–999.
Cembella, A. D., N. J. Antia & P. J. Harrison, 1984a. The utilization of inorganic and organic phosphorous compounds as nutrients by eukaryotic microalgae: a multidisciplinary perspective: part 1. CRC Critical Review in Microbiology 10: 317–391.
Cembella, A. D., N. J. Antia & P. J. Harrison, 1984b. The utilization of inorganic and organic phosphorous compounds as nutrients by eukaryotic microalgae: a multidisciplinary perspective: Part 2. CRC Critical Review in Microbiology 11: 13–81.
Chen, G. F., C. H. Ma, C. Y. Zhang, J. Zhou, Y. Y. Wang, G. C. Wang, B. Y. Zhang, Z. Xu & D. D. Lu, 2013. A rapid and sensitive method for field detection of Prorocentrum donghaiense using reverse transcription-coupled loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Harmful Algae 29: 31–39.
Cottrell, M. T. & C. A. Suttle, 1993. Production of axenic cultures of Micromonas pusilla (Prasinophyceae) using antibiotics. Journal of Phycology 29: 385–387.
Currie, D. J., E. Bentzen & J. Kalff, 1986. Does algal-bacterial phosphorus partitioning vary among lakes? A comparative study of orthophosphate uptake and alkaline phosphatase activity in freshwater. Canadian Journal of Fisheries & Aquatic Sciences 43: 311–318.
Dai, X. F., D. D. Lu, W. B. Guan, P. Xia, H. X. Wang, P. X. He & D. S. Zhang, 2013. The correlation between Prorocentrum donghaiense blooms and the Taiwan warm current in the East China Sea – evidence for the ‘‘pelagic seed bank’’ hypothesis. PloS One 8: e64188. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0064188.
Duan, S. W., F. Xu & L. J. Wang, 2007. Long-term changes in nutrient concentrations of the Changjiang River and principal tributaries. Biogeochemistry 85: 215–234.
Duhamel, S., S. T. Dyhrman & D. M. Karl, 2010. Alkaline phosphatase activity and regulation in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Limnology & Oceanography 55: 1414–1425.
Dyhrman, S., 2005. Ectoenzymes in Prorocentrum minimum. Harmful Algae 4: 619–627.
Dyhrman, S. T., 2008. Molecular approaches to diagnosing nutritional physiology in harmful algae: implications for studying the effects of eutrophication. Harmful Algae 8: 167–174.
Dyhrman, S. T., J. W. Ammerman & B. A. S. Van Mooy, 2007. Microbes and the marine phosphorus cycle. Oceanography 20: 110–116.
Dyhrman, S. T., P. D. Chappell, S. T. Haley, J. W. Moffett, E. D. Orchard, J. B. Waterbury & E. A. Webb, 2006. Phosphonate utilization by the globally important marine diazotroph Trichodesmium. Nature 439: 25–26.
Dyhrman, S. T. & K. C. Ruttenberg, 2006. Presence and regulation of alkaline phosphatase activity in eukaryotic phytoplankton from the coastal ocean: implications for dissolved organic phosphorus remineralization. Limnology & Oceanography 51: 1381–1390.
Glibert, P. M., J. M. Burkholder & T. Kana, 2012. Recent insights about relationships between nutrient availability, forms, and stoichiometry, and the distribution, ecophysiology, and food web effects of pelagic and benthic Prorocentrum species. Harmful Algae 14: 231–259.
Gong, G. C., Y. L. Lee Chen & K. K. Liu, 1996. Chemical hydrography and chlorophyll a distribution in the East China Sea in summer: implications in nutrient dynamics. Continental Shelf Research 16: 1561–1590.
Granéli, E. & P. J. Hansen, 2006. Allelopathy in harmful algae: a mechanism to compete for resources? In Granéli, E. & J. Turner (eds), Ecology of Harmful Algae. Ecological Studies. Springer, Heidelberg: 189–201.
Guillard, R. R. L., 1975. Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In Smith, W. L. & M. H. Chanley (eds), Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals. Plenum Press, New York: 26–60.
Harrison, P. J., M. H. Hu, Y. P. Yang & X. Lu, 1990. Phosphate limitation in estuarine and coastal waters of China. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology & Ecology 140: 79–87.
Hoppe, H. G., 2003. Phosphatase activity in the sea. Hydrobiologia 493: 187–200.
Huang, X. Q. & J. T. Morris, 2005. Distribution of phosphatase activity in marsh sediments along an estuarine salinity gradient. Marine Ecology Progress Series 292: 75–83.
Huang, B. Q., L. J. Ou, H. S. Hong, H. W. Luo & D. Z. Wang, 2005. Bioavailability of dissolved organic phosphorus compounds to typical harmful dinoflagellate Prorocentrum donghaiense Lu. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51: 838–844.
Huang, B. Q., L. J. Ou, X. L. Wang, W. Y. Huo, R. X. Li, H. S. Hong, M. Y. Zhu & Y. Z. Qi, 2007. Alkaline phosphatase activity of phytoplankton in East China Sea coastal waters with frequent HAB occurrences. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 49: 195–206.
Karl, D. M., 2000. Phosphorus, the staff of life. Nature 406: 31–32.
Kolowith, L. C., E. D. Ingall & R. Benner, 2001. Composition and cycling of marine organic phosphorus. Limnology & Oceanography 46: 309–320.
Jeffries, D. S., F. P. Dieken & D. E. Jones, 1979. Performance of the autoclave digestion method for total phosphorus analysis. Water Research 13: 275–279.
Li, H., M. J. W. Veldhuis & A. F. Post, 1998. Alkaline phosphatase activities among planktonic communities in the northern Red Sea. Marine Ecology Progress Series 173: 107–115.
Li, J., P. M. Glibert, M. J. Zhou, S. H. Lu & D. D. Lu, 2009. Relationships between nitrogen and phosphorus forms and ratios and the development of dinoflagellate blooms in the East China Sea. Marine Ecology Progress Series 383: 11–26.
Li, M. T., K. Q. Xu, M. Watanabe & Z. Y. Chen, 2007. Long-term variations in dissolved silicate, nitrogen, and phosphorus flux from the Yangtze River into the East China Sea and impacts on estuarine ecosystem. Estuarine, Coastal & Shelf Science 71: 3–12.
Li, Y., S. H. Lu, T. J. Jiang, Y. P. Xiao & S. P. You, 2011. Environmental factors and seasonal dynamics of Prorocentrum populations in Nanji Islands National Nature Reserve, East China Sea. Harmful Algae 10: 426–432.
Li, Y. B., X. L. Wang, X. R. Han, K. Q. Li, X. X. Zhao & X. Y. Shi, 2008. An ecosystem model of the phytoplankton competition in the East China Sea, as based on filed experiments. Hydrobiologia 600: 283–296.
Liu, L. S., J. Zhuo, B. H. Zheng, W. Q. Cai, K. X. Lin & J. L. Tang, 2013. Temporal and spatial distribution of red tide outbreaks in the Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent waters, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin 72: 213–221.
Liu, S. M., J. Zhang, H. T. Chen, Y. Wu, H. Xiong & Z. F. Zhang, 2003. Nutrients in the Changjiang and its tributaries. Biogeochemistry 62: 1–18.
Lorenzo, J. I., M. Nieto-Cid, X. A. Álvarez-Salgado, P. Pérez & R. Beiras, 2007. Contrasting complexing capacity of dissolved organic matter produced during the onset, development and decay of a simulated bloom of the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum. Marine Chemistry 103: 61–75.
Lu, D. D., J. Goebel, Y. Z. Qi, J. Z. Zou, X. T. Han, Y. H. Gao & Y. G. Li, 2005. Morphological and genetic study of Prorocentrum donghaiense Lu from the East China Sea, and comparison with some related Prorocentrum species. Harmful Algae 4: 493–505.
Murphy, J. & J. P. Riley, 1962. A modified single solution method for determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta 27: 31–36.
Nausch, M., 1998. Alkaline phosphatase activities and the relationship to inorganic phosphate in the Pomeranian Bight (southern Baltic Sea). Aquatic Microbial Ecology 16: 87–94.
Ou, L. J., B. Q. Huang, H. S. Hong, Y. Z. Qi & S. H. Lu, 2010. Comparative alkaline phosphatase characteristics of the typical harmful algal bloom species Prorocentrum donghaiense, Alexandrium catenella and Skeletonema costatum. Journal of Phycology 46: 260–265.
Ou, L. J., V. Lundgren, S. H. Lu & E. Granéli, 2014. The effect of riverine dissolved organic matter and other nitrogen forms on the growth and physiology of the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum (Pavillard) Schiller. Journal of Sea Research 85: 499–507.
Ou, L. J., D. Wang, B. Q. Huang, H. S. Hong, Y. Z. Qi & S. H. Lu, 2008. Comparative study on phosphorus strategies of three typical harmful algae in Chinese coastal waters. Journal of Plankton Research 30: 1007–1017.
Ruttenberg, K. C. & S. T. Dyhrman, 2012. Dissolved organic phosphorus production during simulated phytoplankton blooms in a coastal upwelling system. Frontiers in Microbiology 3: 1–12.
Sarno, D., W. H. C. F. Kooistra, L. K. Medlin, I. Percopo & A. Zingone, 2005. Diversity in the genus Skeletonema (Bacillariophyceae). II. An assessment of the taxonomy of S. costatum s.l.-like species with the description of four new species. Journal of Phycology 41: 151–176.
Sarthou, G., K. R. Timmermans, S. Blain & P. Tréguer, 2005. Growth physiology and fate of diatoms in the ocean: a review. Journal of Sea Research 53: 25–42.
Sebastián, M., J. Arítegui, M. F. Montero & F. X. Niell, 2004. Kinetics of alkaline phosphatase activity, and effect of phosphate enrichment: a case study in the NW African upwelling region. Marine Ecology Progress Series 270: 1–13.
Smayda, T. J., 1997. Harmful algal blooms: their ecophysiology and general relevance to phytoplankton blooms in the sea. Limnology & Oceanography 42: 1137–1153.
Smayda, T. J. & C. S. Reynolds, 2001. Community assembly in marine phytoplankton: application or recent models to harmful dinoflagellate bloom. Journal of Plankton Research 23: 447–461.
Suksomjit, M., S. Nagao, K. Ichimi, T. Yamada & K. Tada, 2009. Variation of dissolved organic matter and fluorescence characteristics before, during and after phytoplankton bloom. Journal of Oceanography 65: 835–846.
Sunda, W. G. & D. R. Hardison, 2007. Ammonium uptake and growth limitation in marine phytoplankton. Limnology & Oceanography 52: 2496–2506.
Sunda, W. G., N. M. Price & F. M. M. Morel, 2005. Trace metal ion buffers and their use in culture studies. In Andersen, R. A. (ed.), Algal Culturing Techniques. Academic Press, Burlington: 35–64.
Suzumura, M., K. Ishikawa & H. Ogawa, 1998. Characterization of dissolved organic phosphorus in coastal seawater using ultrafiltration and phosphohydrolytic enzymes. Limnology & Oceanography 43: 1553–1564.
Tang, D. L., B. P. Di, G. F. Wei, I. H. Ni, I. S. Oh & S. F. Wang, 2006. Spatial, seasonal and species variations of harmful algal blooms in the South Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Hydrobiologia 568: 245–253.
Thingstad, T. F., M. D. Krom, R. F. Mantoura, G. A. F. Flaten, S. Groom, B. Herut, N. Kress, C. S. Law, A. Pasternak, P. Pitta, S. Psarra, F. Rassoulzadegan, T. Tanaka, A. Tselepides, P. Wassmann, E. M. S. Woodward, C. Wexels Riser, G. Zodiatis & T. Zohary, 2005. Nature of phosphorus limitation in the ultraoligotrophic eastern Mediterranean. Science 309: 1068–1071.
Thingstad, T. F., E. F. Skjoldal & R. A. Bohne, 1993. Phosphorus cycling and algal-bacterial competition in Sandsfjord, western Norway. Marine Ecology Progress Series 99: 239–259.
Vidal, M., C. M. Duarte, S. Agusti, J. M. Gasol & D. Vaqué, 2003. Alkaline phosphatase activities in the central Atlantic Ocean indicate large areas with phosphorus deficiency. Marine Ecology Progress Series 262: 43–53.
Wang, J. T., Y. W. Zhang, H. Li & J. Cao, 2013. Competitive interaction between diatom Skeletonema costatum and dinoflagellate Prorocentrum donghaiense in laboratory culture. Journal of Plankton Research 35: 367–378.
Wang, Y., Z. M. Yu, X. X. Song & S. D. Zhang, 2006. Interactions between the bloom-forming dinoflagellates Prorocentrum donghaiense and Alexandrium tamarense in laboratory cultures. Journal of Sea Research 56: 17–26.
Wong, G. T. F., G. C. Gong, K. K. Liu & S. C. Pai, 1998. ‘Excess Nitrate’ in the East China Sea. Estuarine, Coastal & Shelf Science 46: 411–418.
Wu, J. F., W. Sunda, E. A. Boyle & D. M. Karl, 2000. Phosphate depletion in the western north Atlantic Ocean. Science 289: 759–762.
Xu, N., S. S. Duan, A. F. Li, C. W. Zhang, Z. P. Cai & Z. X. Hu, 2010. Effect of temperature, salinity and irradiance on the growth of the harmful dinoflagellate Prorocentrum donghaiense Lu. Harmful Algae 9: 13–17.
Zhang, J., S. M. Liu, J. L. Ren, Y. Wu & G. L. Zhang, 2007. Nutrient gradients from the eutrophic Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary to the oligotrophic Kuroshio waters and re-evaluation of budgets for the East China Sea Shelf. Progress in Oceanography 74: 449–478.
Zhu, M. Y., Z. J. Xu, R. X. Li, Z. L. Wang & X. Y. Shi, 2009. Interspecies competition for nutrients between Prorocentrum donghaiense Lu and Skeletonema costatum (Grev.) Cleve in mesocosm experiments. Acta Oceanologica Sinica 28: 72–82.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the three anonymous reviewers for constructive suggestions and comments on the MS. This work was supported by grants of the National Basic Research Program (No. 2011CB403603 and 2010CB428702), and the China NSF (No. 41176087 and 41276153). This study was also partly supported by “the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities” (No. 21611205). Professor John Hodgkiss of the University of Hong Kong is thanked for his assistance with the English in this MS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: Song Sun, Xiaoxia Sun & Ian Jenkinson / Giant Jellyfish Blooms and Ecosystem Change
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ou, L., Huang, X., Huang, B. et al. Growth and competition for different forms of organic phosphorus by the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum donghaiense with the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella and the diatom Skeletonema costatum s.l.. Hydrobiologia 754, 29–41 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-1994-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-1994-2