Abstract
Despite favorable effects from telemedicine (TM) on cardiovascular diseases, outcome and comparative impact of TM on heart failure (HF) adults remain controversial. A meta-analysis was conducted to summarize the evidence from existing randomized controlled trials (RCTs) which compared potential impact of TM on HF with conventional healthcare. TM mainly included structure telephone support (STS), involving interactive vocal response monitoring and telemonitoring. PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library were searched to identify RCTs to fit our analysis (1999 to 2018). Odds ratio (OR) with its 95% confidence interval (CI) was used. Sensitivity analysis, subgroup analysis, and tests for publication bias were conducted. Heterogeneities were also evaluated by I2 tests. A total of 29 RCTs consisting of 10,981 HF adults were selected for meta-level synthesis, with follow-up range of 1–36 months. Telemonitoring is associated with the reduction in total number of all-cause hospitalization (OR 0.82, 95% CI 0.73–0.91, P = 0.0004) and cardiac hospitalization (OR 0.83, 95% CI 0.72–0.95, P = 0.007). Telemonitoring resulted in statistically significant risk reduction of all-cause mortality (OR 0.75, 95% CI 0.62–0.90, P = 0.003). However, the OR of HF-related mortality (OR 0.84, 95% CI 0.61–1.16, P = 0.28) is not significantly distinguishable from that of conventional healthcare. Receiving STS interventions is likely to reduce the hospitalization for all causes (OR 0.86, 95% CI 0.78–0.96, P = 0.006, I2 = 6%) and the hospitalization due to HF (OR 0.74, 95% CI 0.65–0.85, P < 0.0001, I2 = 0%), compared with interventions from conventional healthcare. OR of all-cause STS mortality (OR 0.96, 95% CI 0.83–1.11, P = 0.55) was identified in meta-analyses of eight cases. OR of STS cardiac mortality (OR 0.54, 95% CI 0.34–0.86, P = 0.009) was identified in meta-analyses of three cases. This work represents the comprehensive application of network meta-analysis to examine the comparative effectiveness of telemedicine interventions in improving HF patient outcomes. Compared with conventional healthcare, telemedicine systems with medical support prove to be more effective for HF adults, particularly in reducing all-cause hospitalization, cardiac hospitalization, all-cause mortality, cardiac mortality, and length of stay. While further research is required to confirm these observational findings and identify optimal telemedicine strategies and the duration of follow-up for which it confers benefits.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Heart failure (HF) is one of the most prevalent manifestations of cardiovascular disorders [1], decreasing the health-related quality of life (QoL) of HF patients while increasing the burden of morbidity, mortality, and healthcare. As the result of the rising demand for acute hospital beds for HF, strategies to facilitate early discharge and reduce unplanned readmissions are superior to improving patient outcomes and resource usage. Poor adherence to recommendations provided by healthcare professional is responsible for ~ 50% of HF hospitalization [2]. The overall purpose of education and other intervention modalities, for instance, structured telephone support (STS), home visits, and nurse-led clinics, is to improve self-care and patients’ adherence. In recent years, promising results have been reported for multidisciplinary care strategies for HF patients with and without telemedicine systems. A meta-analysis has shown positive results for home-based interventions, including a reduction of 34% in all-cause mortality and a reduction of 30–56% in HF hospitalizations [3]. However, following prospective randomized multicenter clinical trials of non-invasive approaches cannot confirm these findings for morbidity-related and mortality-related endpoints [4, 5]. Although earlier studies suggest a reduction in mortality, results of the study reported by Chaudhry and colleagues failed to show any beneficial effects of telemonitoring [6].
To determine whether telemedicine systems improve outcomes for adults following an unplanned admission due to HF, we conducted a meta-analysis of existing randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing different forms of telemedicine systems with conventional healthcare after discharge. Interventions included conventional healthcare and the following forms of telemedicine: STS involving regular follow-up calls between the health professional and the patient, telemonitoring systems involving the transmission of information on symptoms and signs (TM), and telemedicine systems involving interactive vocal response monitoring and electrocardiographic transmissions (ECG). The primary endpoints of this study were all-cause hospitalization and all-cause mortality during follow-up. As secondary endpoints, we explored cardiac hospitalization, mortality, and length of stay.
Materials and methods
Search strategy
A search of literature was performed for RCTs of non-invasive telemedicine systems for HF patients compared with conventional healthcare. The PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library databases were searched to extract articles (1999 to 2018) on telemedicine systems in adults. Literature search was informed using keywords heart failure, cardiac failure, remote, telemedicine, telecommunication, telehealth, telecardiology, health information systems, internet, home monitor, and interactive voice response. The meta-analysis of RCTs was performed in accordance with the latest meta-analysis guidelines (PRISMA) [7]. Referenced studies and narrative reviews were searched as well.
Study selection
Studies involved in this meta-analysis were sorted by three independent authors. In the preliminary stage, all publication titles and abstracts were examined by the first two authors to exclude non-pertinent articles clearly not meeting the following inclusion criteria. The two authors reviewed the results of each study with a standardized data extraction tool and also applied standard scales to judge study quality and risk of bias independently. If any doubt of suitability remained after the abstract was examined, the full manuscript was retrieved and assessed. Most of the disagreements were resolved through discussions. When there was any disagreement, the third author mediated the discussion to gain consensus.
Inclusion criteria
-
Studies were included in the meta-analysis if they were RCTs.
-
Patients were objectively confirmed to have symptomatic HF (New York Heart Association [NYHA] Class I–IV) characterized by impaired left ventricular function (left ventricular ejection fraction < 45%).
-
Includes both an experimental group and a control group.
-
Telemedicine treatments include telephone support, telemonitoring involving interactive vocal response monitoring, and monitoring by ECG.
-
Control group only receives conventional healthcare defined as a guideline-based standard care with scheduled clinic visits but without any additional interventions.
-
The primary outcome measurements include all-cause mortality and all-cause hospitalization (defined as an admission to a healthcare facility for less than 24 h for all causes).
-
The secondary outcome measurements include cardiac hospitalization (defined as an admission to a healthcare facility for less than 24 h due to heart failure), cardiac mortality, length of hospital stay, health-related QoL, and hospitalization costs.
Exclusion criteria
Studies were excluded if they met the following criteria:
Not being RCTs and non-English language papers
Not involving patients with acute HF
Not reporting numerical data on the outcomes of interest
Published in the form of letters, congress abstracts, review articles, comments, editorials, case reports, technical reports, or animal studies
Data extraction
A predesigned data abstraction form was used to obtain data on relevant results of the study. Following terms were recorded for each study: authors, years of publication, patient demographic data (gender, age, disease severity, etc.), intervention features, outcomes parameters, as well as the quality of included RCT studies. Detailed information would be requested from the author if some necessary original data could not be acquired. Data were then tabulated and a network meta-analysis (NMA) of the following outcomes was deemed appropriate: all-cause mortality, all-cause hospitalization, cardiac hospitalization, and cardiac mortality. Studies satisfying the inclusion criteria were assigned a quality score based on the revised 7-point Jadad scale [8]. The scale consists of four aspects: generation of allocation sequence (2 points), allocation concealment (2 points), investigator blindness (2 points), and withdrawals and dropouts (1 point). A total score of less than 4 indicates low quality, while the one of more than 5 indicates high quality [9].
Statistical analysis
Separate analyses were performed for each outcome’s odds ratio (OR) or weighted mean difference (WMD) using the Mantel–Haenszel method. Pairwise meta-analyses were conducted by combining studies comparing the same interventions using a random-effects model. Meta-analysis inconsistency was assessed by comparing the deviance and deviance information criteria in fitted consistency and inconsistency models across studies [10]. Specifically, we investigated the heterogeneity through examining both forest plots and Cochran’s Q quantified by I2 tests [11]. An I2 of 0–25% indicates no heterogeneity, an I2 of 25–50% indicates moderate heterogeneity, an I2 of 50–75% indicates large heterogeneity, and an I2 of 75–100% indicates extreme heterogeneity. Results with a P value less than 0.05 and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) exceeding 1 were considered as statistical significance. The analyses were carried out using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis techniques in Review Manager (RevMan, version 5.2, The Cochrane Collaboration, London, England, 2012) [12]. The results from our network meta-analysis were qualitatively compared with direct, frequent, pairwise estimates. Publication bias was tested by funnel plots and the Egger and Begger tests using Stata version 12.0 software (Stata Corporation, College Station, TX, USA) and P < 0.05 was considered significant [13].
Results
Trial flow
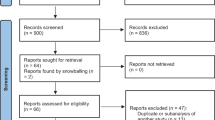
As shown in Fig. 1, 388 citations were identified from our search (up to August 2018). Fifty-two duplication cross-databases were excluded. Three hundred eight were excluded after examining titles and abstracts of full-text articles. Reasons for exclusion were not related to HF, not RCT, unrelated to home-based telemonitoring/telephone support, no outcome of interest, or non-English language papers and so forth. From the remaining articles, we identified 29 non-duplicated RCTs and 10,981 patients eligible for the meta-analysis. Details about the searching strategy and the flow chart for the identification of studies used in the network meta-analysis of telemedicine interventions for HF patients were provided in Fig. 1.
Characteristics of included trials
General characteristics of the population, interventions, and comparison groups included in the 29 RCTs along with the main outcomes of each study were summarized in Table 1. All the RCT studies were classified into two groups based on the type of telemedicine intervention(s): telemonitoring (n = 19) and telephone-supported systems (n = 9). Please note that only one study reported outcomes for both telemonitoring and telephone-supported care. The average duration of the interventions was 10.5 months (range 1 to 36 months). For most of the studies (25 out of 29), the number of males was greater than that of females. Endpoints and adopted telemedicine strategies were similar among the selected studies. In 22 of 29 trials, participants were followed for six or more months. Despite differences in the scope and range of included studies, most RCTs reported on a number of similar outcomes. Most frequently reported outcomes included all-cause hospitalization, cardiac hospitalization, all-cause mortality, and cardiac mortality. Other commonly reported outcomes comprised the impact of telemedicine interventions on quality of life, length of hospital stay, as well as hospitalization costs. Acceptability, patient satisfaction, and emergency room visits were rarely reported in the studies and therefore were excluded from our final analysis. In most of the trials, interventions were typically delivered by nurses. Using the revised 7-point Jadad scale, all the selected RCTs had Jadad scores greater than 3, which suggested a good study design and high study quality. A more detailed description of included trials is provided in Table 1.
Health-related outcomes and meta-analysis
All-cause hospitalization was reported in 23 studies and cardiovascular diseases-related hospitalization was reported in 16 studies. With respect to clinical outcomes, 22 trials contributed to the analysis of the all-cause death and 9 trials analyzed the death due to heart failure. We did the meta-analyses for the outcomes of all-cause of hospitalization, all-cause of mortality, cardiac hospitalization, and cardiac mortality (Fig. 2). Evidence network for interventions included in the analysis of the outcomes of telemedicine versus conventional healthcare was shown in Fig. 3.
a Effect of telemonitoring versus usual care on all-cause hospital admission in patients with chronic heart failure. CI, confidence interval; M-H, Mantel–Haenszel. b Effect of telemonitoring versus usual care on cardiac hospital admission in patients with chronic heart failure. CI, confidence interval; M-H, Mantel–Haenszel. c Effect of telephone support interventions versus usual care on all-cause hospital admission in patients with chronic heart failure. CI, confidence interval; M-H, Mantel–Haenszel. .d Effect of telephone support interventions versus usual care on cardiac hospitalization in patients with chronic heart failure. CI, confidence interval; M-H, Mantel–Haenszel. e Effect of telemonitoring versus usual care on all-cause mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. CI, confidence interval; M-H, Mantel–Haenszel. f Effect of telemonitoring versus usual care on cardiac mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. CI, confidence interval; M-H, Mantel–Haenszel. g Effect of telephone versus usual care on all cause of mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. CI, confidence interval; M-H, Mantel–Haenszel. h Effect of telephone versus usual care on cardiac mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. CI, confidence interval; M-H, Mantel–Haenszel. i Effect of interventions versus usual care on length of hospital stay in patients with chronic heart failure. M-H = Mantel–Haenszel risk ratio. Data are from full peer-reviewed publications only and reflect the most recent meta-analysis of telemedicine in heart failure
All-cause hospitalization and cardiac hospitalization
With respect to all-cause hospitalizations, most studies reported beneficial effects of different telemedicine system interventions. Telemonitoring was associated with a reduction in a total number of all-cause hospitalization (OR 0.82, 95% CI 0.73–0.91, P = 0.0004). The effect was statistically significant for 17 out of 19 studies. Heterogeneity was moderate (I2 = 70%; Fig. 2a), which is supposed to result from individual discrepancies (age, gender distribution, etc.) and interventions (methods, duration, etc.). Two studies reported HF readmission within 30 days [14, 15]. Thirty-day rehospitalization rates were similar in the telemonitoring intervention group and the UC control group. Cardiac hospitalizations were reported in 13 studies. The OR of telemonitoring versus conventional healthcare on cardiac hospitalization was 0.83 (95% CI 0.72–0.95, P = 0.007), suggesting a significant difference between the two groups (Fig. 2b). Compared with conventional healthcare, structured telephone support interventions reduced the hospitalization for all causes (OR 0.86, 95% CI 0.78–0.96, P = 0.006, I2 = 6%) and due to HF (OR 0.74, 95% CI 0.65–0.85, P < 0.0001, I2 = 0%) (Fig. 2c, d).
All-cause of mortality and cardiac mortality
A significant reduction in the risk of all-cause mortality (OR 0.75, 95% CI 0.62–0.90, P = 0.003) was identified in meta-analyses of 15 studies of telemonitoring. However, the OR of telemonitoring versus conventional healthcare on cardiac mortality was not significant (OR 0.84, 95% CI 0.61–1.16, P = 0.28) in a meta-analysis of five studies. The heterogeneity of these two analyses was moderate (I2 = 49%; Fig. 2e) and none (I2 = 0%; Fig. 2f), respectively. No significant effect of telephone support intervention on all-cause mortality (OR 0.96, 95% CI 0.83–1.11, P = 0.55) was identified in meta-analyses of eight studies (Fig. 2g). A significant effect of telephone support intervention on cardiac mortality (OR 0.54, 95% CI 0.34–0.86, P = 0.009) was identified in meta-analyses of studies (Fig. 2h).
Length of hospital stay
HF-related length of stay was reported in 13 studies comparing interventions with conventional healthcare [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28], including 3 telephone-supported studies and 10 telemonitoring studies. There was a significant heterogeneity when data from the telemedicine interventions studies were pooled (df = 5, P = 0.002, I2 = 74%, as shown in Fig. 2i). The analysis revealed that there was a significant difference in HF-related length of hospital stay between the overall interventions and control groups (pooled standardized difference in means = − 2.21, 95% CI − 4.35 to − 0.06, Z = 2.02, P = 0.04), the telemonitoring and control groups (pooled standardized difference in means = − 1.71, 95% CI − 4.83 to − 1.42, Z = 1.07, P = 0.28), or the telephone-supported care and control groups (pooled standardized difference in means = − 3.41, 95% CI − 5.01 to − 1.82, Z = 4.2, P = 0.0001). William et al. [16] reported that the length of hospital stay for HF-related hospitalizations was significantly shorter in the treatment group than in the control group (2.2 days [SD 6.8] vs. 3.8 days [SD 11.1], P = 0.02) during 6 months follow-up. However, no significant difference in HF-related length of hospital stay was observed comparing the telemonitoring group with the control group (pooled standardized difference in means = − 1.71, 95% CI − 4.83 to − 1.42, Z = − 1.07, P = 0.28).
Publication bias
Funnel plots and Egger’s testing were performed to assess the publication bias of all of the studies. There was no significant evidence of publication bias for all-cause mortality of telemedicine interventions, which was revealed by the Egger and Begger tests (Egger: P = 0.888; Begger: P = 0.582). The funnel plot did not display asymmetry, while both Egger’s and Begg’s test indicate no publication bias (Fig. 4).
Quality of life
Ten telemedicine studies reported slight improvements in measures of QoL for HF adults receiving telemedicine as compared to those receiving conventional healthcare [18, 22, 25, 26, 28,29,30,31,32,33]. Quality of life was measured by various questionnaires, including the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire (MLHFQ), score for SF-36 and SF-12, and the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ), making it difficult to compare the outcomes. However, patients in the telemedicine group were more likely to report stable or deteriorated symptoms, compared with those in the control group. SF-36 was applied in two studies. One study found [18] that patients randomly allocated to the remote telemedical management (RTM) group showed an improved score for SF-36 physical functioning over the entire study period (P < 0.05) compared with the conventional healthcare group. Ewa et al. [22] observed the improvements in health-related QoL using disease-specific measures of the KCCQ: the telemedicine group had significantly higher score than control group over 3 months follow-up (P < 0.05). Three studies contributed to the analysis of the MLHFQ, while the SF-12 was also applied in three studies. Goldberg reported that among patients completing their 6-month follow-up visit, patients in both groups experienced improvement between baseline and 6 months in their Minnesota Living with Heart Failure, SF-12, and Health Distress scores. Although no difference was statistically significant, the intervention group tended to improve all the quality of life measures [30]. Additionally, GESICA [31] found that the intervention group had a significantly better quality of life than the conventional healthcare group (mean total score on MLHFQ (30.6 vs. 35, P = 0.001).
Hospitalization costs
Five studies [16, 19, 26, 27, 34] examined the effects of telemedicine interventions on hospitalization costs. Although hospitalization costs were reported in the five original studies, different applied methodologies did not allow the pooled results into the meta-analysis. The general outcomes were statistically inconclusive and varied depending on the context and specific telemedicine systems of the studies. Furthermore, many studies showed that there was no significant difference in hospitalization costs between intervention groups and non-intervention groups. Dendale et al. [19] reported that even though the total hospitalization cost for HF was almost doubled in the control group (1458 + 3420 Euro/patient) compared with the telemedicine group (902 + 2277 Euro/patient), the difference was not significant (P = 0.23). Laramee et al. reported that the intervention did not increase costs and no significant differences were found in both outpatient and inpatient resource utilization between the groups [27].
Discussion
In this meta-analysis, we performed an up-to-date assessment of the effectiveness of telemedicine systems for the management of HF patients. By summarizing the current best evidence, this network meta-analysis showed that compared to conventional healthcare, telemedicine intervention appears to be beneficial for patients with HF, particularly in reducing all-cause hospitalization, cardiac hospitalization, all-cause mortality, cardiac mortality, and length of stay in HF patients. This work represents the comprehensive application of network meta-analysis to examine the comparative effectiveness of telemedicine interventions in improving HF patient outcomes.
Available studies examining the patient experience and effect of patient education on acceptance and adherence to the intervention of telemonitoring were limited [34, 35]. The adoption of telemedicine is driven by the expectation that it should improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. Few studies, however, have compared telemedicine with conventional health care with respect to healthcare utilization [36]. In a recent network meta-analysis of RCTs by Kotb et al. [37], teletransmission was found to reduce the odds of mortality as well as the HF-related hospitalizations compared with the conventional healthcare. In the present meta-analysis of 29 studies, we have specifically considered planned or unplanned hospital visits that provide additional data to the field with an updated literature search up to 2018. Most of the evidence that is currently available on the impact of telemedicine interventions involves the comparison of an active form of telemedicine to conventional healthcare. Findings from this network meta-analysis are unique in that various comparisons were examined across different forms of telemedicine interventions. Most available literature focused on the primary outcomes of mortality and hospitalizations. We have found that telemedicine is associated with a significant reduction in the total number of hospital visits and mortality. In other words, telemedicine safely reduces healthcare utilization by reducing elective face-to-face hospital visits.
HF is a complex illness, and optimal management requires regular patient monitoring. However, the financial and organizational strain on healthcare systems prevents timely monitoring frequently. This could lead to reliance on patient help-seeking which often occurs when it is too late to prevent hospitalization [38]. Essentially, telemedicine is a diagnostic modality which, without an appropriate therapeutic intervention, could not be expected to alter clinical outcomes. If one assumes that the appropriateness of such interventions is similar with or without telemedicine, the only possible advantage of telemedicine is shortening the time to a treatable, or “actionable,” event. In this respect, we should consider that none of the telemedicine systems should be expected to predict some events, e.g., acute cardiac death or no cardiac death. As was reported by Sarwat et al. [17], non-implantable telemonitoring systems for HF do not seem to improve outcomes compared with conventional healthcare. Being the largest RCT done so far, a comprehensive non-invasive telemonitoring system did not reduce morbidity or mortality in 1653 patients who were randomly assigned to the telemonitoring system versus conventional healthcare. It is still unclear which factor could explain the significant reduction in mortality achieved by telemedicine [6]. The inconsistent outcomes of the telemedicine program may be due to the lack of consensus protocol or guideline for conducting telemedicine care. The purpose of a remote interview may range from improving diet and treatment compliance to regular monitoring of the HF-related symptoms and self-management. However, many home monitoring systems are designed for transmission of body weight, blood pressure, and heart rate via a standard telephone line or network system to a central server. It may be helpful to monitor the real-time clinical condition of the patients for early treatment.
The previous network meta-analysis included 21 studies which included a control group and examined the impact of telemonitoring. Finally, only nine of them were followed participants for more than 6 months [19]. In this meta-analysis, most of the studies had longer than 6 months of follow-up. This may suggest that the potential benefits of telemedicine require longer periods of follow-ups before they are observed. Telemedicine is part of a comprehensive package of care that includes education and empowerment of the patients, early warning of deterioration, access to health professionals’ advice and moral support, and pharmacological intervention. For instance, one of the studies reported [39] that remote monitoring with an automated telemedicine system can successfully facilitate titration of carvedilol in outpatients with class II and III HF defined by NYHA. Telemedicine titrations were as successful as titrations in the clinic. Further, the time to reach the final dose of carvedilol was significantly shorter in the intervention group compared to that of conventional healthcare group (33.6 vs. 63.7 days, P < 0.001). Telemedicine interventions, therefore, reflect complex healthcare strategies and are not limited to simple data-gathering.
Positive results were found on health-related QoL in patients with chronic HF, although data were limited. Indeed, QoL is an important measure of health, particularly for older people and those suffering from HF. Maintaining moderate or a high and improving level of physical activities is associated with a better health-related QoL in patients with chronic HF [40]. Regarding the quality of the studies included in this meta-analysis, different questionnaires were used (SF-36, SF-12, MLHF, KCCQ), making it difficult to compare outcomes. However, the majority demonstrated improvements in the patients who underwent telemedicine intervention, especially in terms of the MLHFQ and SF-36 physical aspects, and these improvements led to both better life quality and favorable prognoses. Further information is required to assess the effect of the telemonitoring use on the patient’s QoL, and perceptions of health status, as this was cited as a barrier against uptake and adherence. This network analysis was limited to RCTs only. This was deemed appropriate, however, given the availability of a substantial amount of evidence and the reduced likelihood of bias and confounding associated with this study design. For the most part, the risk of bias associated with included studies was found to be either low or moderate and further sensitivity analyses did not significantly differ from the main analysis of the study.
With constrained resources for healthcare expenditures, it is reasonable to expect an evaluation of new technologies not just on safety and efficacy but also on cost-effectiveness. With the substantial societal and economic impacts of HF, telemedicine interventions that can help minimize the likelihood of cost of care associated with HF may provide significant benefits to the healthcare system. Researchers that used an analytical approach for assessing healthcare and patient-related costs showed that most of the telemedicine was cost saving as the telemedicine groups have shorter “stay of length.” There is no consensus on hospitalization costs for HF patients. Some differences across models may be expected. However, many reports showed that there was no significant difference in hospitalization cost use of the intervention and conventional healthcare groups [27].
Admittedly, our meta-analysis has its limitations. Telemedicine interventions were heterogeneous in terms of monitored parameters and HF selection criteria. Our study depended only on the data reported in studies, some endpoint data were unavailable, and considering the limited number of studies, publication and reporting biases were inevitable to some extent. It is difficult to testify differences between intervention duration and intervention designs. These differences in study designs resulted in low to large scores of heterogeneity (0% to 75%). Furthermore, some trials were underpowered to detect the primary outcome and did not report outcome assessor blinding. Telemedicine usually builds on self-monitoring, with evidence that it can help educate patients about which symptoms and signs are most important and what measures can be taken to destabilize the syndrome. The content of telemedicine interventions was often poorly described, making it difficult to understand exactly what was provided. Moreover, due to the differences in the selection criteria of the included studies (e.g., LVEF and New York Heart Association), the generalizability of the treatment effect is unclear.
Conclusions
Telemedicine interventions appear to lead to benefits for patients with CHF, decrease all-cause hospital admissions, and improve QoL, although there are still several important issues to consider. Only limited studies are available on the cost-benefits and appropriate business models for the interventions; impacts of these interventions on patient QoL have only been reported in a few studies, and the optimal duration of these interventions is still not clear. There is also a significant lack of researchers concentrating on HF patients in remote rural areas who might benefit from a telemedicine service. Further research is therefore required to fill in this gap in knowledge. We suggest that other aspects should also be addressed, as telemedicine is not the only one component of managing HF and could not replace face-to-face consultations between healthcare providers and patients. Such studies need to investigate, from the patients’ perspective, the effect of educational methods and technological supports, benefits of tailored monitoring, and cost-effectiveness analysis. The efficacy of telemedicine using an advanced telemonitoring device and newly developed guidelines in the remote follow-up and management of HF patients should also be investigated.
References
Rathi S, Deedwania PC (2012) The epidemiology and pathophysiology of heart failure. Med Clin North Am 96(5):881–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2012.07.011
Desai AS (2012) Home monitoring heart failure care does not improve patient outcomes: looking beyond telephone-based disease management. Circulation 125(6):828–836. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.111.031179
Savard LA, Thompson DR, Clark AM (2011) A meta-review of evidence on heart failure disease management programs: the challenges of describing and synthesizing evidence on complex interventions. Trials 12(194). https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6215-12-194
Pandor A, Gomersall T, Stevens JW, Wang J, Al-Mohammad A, Bakhai A, Cleland JG, Cowie MR, Wong R (2013) Remote monitoring after recent hospital discharge in patients with heart failure: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Heart 99(23):1717–1726. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2013-303811
Koehler F, Winkler S, Schieber M, Sechtem U, Stangl K, Bohm M, de Brouwer S, Perrin E, Baumann G, Gelbrich G, Boll H, Honold M, Koehler K, Kirwan BA, Anker SD (2012) Telemedicine in heart failure: pre-specified and exploratory subgroup analyses from the TIM-HF trial. Int J Cardiol 161(3):143–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2011.09.007
Clarke M, Shah A, Sharma U (2011) Systematic review of studies on telemonitoring of patients with congestive heart failure: a meta-analysis. J Telemed Telecare 17(1):7–14. https://doi.org/10.1258/jtt.2010.100113
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ (Clinical research ed) 339:b2700. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2700
Clark HD, Wells GA, Huet C, McAlister FA, Salmi LR, Fergusson D, Laupacis A (1999) Assessing the quality of randomized trials: reliability of the Jadad scale. Control Clin Trials 20(5):448–452
Buzzetti E, Kalafateli M, Thorburn D, Davidson BR, Tsochatzis E, Gurusamy KS (2017) Interventions for hereditary haemochromatosis: an attempted network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 3:Cd011647. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011647.pub2
Stonehouse W, Wycherley T, Luscombe-Marsh N, Taylor P, Brinkworth G, Riley M (2016) Dairy intake enhances body weight and composition changes during energy restriction in 18-50-year-old adults—a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrients 8(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8070394
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ (Clinical research ed) 327(7414):557–560. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Zhang Y, Ma XJ, Shi DZ (2015) Effect of trimetazidine in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 10(9):e0137775. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0137775
Cao J, Li Z, Yang L, Liu C, Luan X (2016) Association between tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 gene methylation and gastric cancer risk: a meta-analysis. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 20(8):427–431. https://doi.org/10.1089/gtmb.2015.0332
Ritchie CS, Houston TK, Richman JS, Sobko HJ, Berner ES, Taylor BB, Salanitro AH, Locher JL (2016) The E-Coach technology-assisted care transition system: a pragmatic randomized trial. Transl Behav Med 6(3):428–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13142-016-0422-8
Gallagher BD, Moise N, Haerizadeh M, Ye S, Medina V, Kronish IM (2017) Telemonitoring Adherence to Medications in Heart Failure Patients (TEAM-HF): a pilot randomized clinical trial. J Card Fail 23(4):345–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cardfail.2016.11.001
Abraham WT, Adamson PB, Bourge RC, Aaron MF, Costanzo MR, Stevenson LW, Strickland W, Neelagaru S, Raval N, Krueger S, Weiner S, Shavelle D, Jeffries B, Yadav JS (2011) Wireless pulmonary artery haemodynamic monitoring in chronic heart failure: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet (London, England) 377(9766):658–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(11)60101-3
Chaudhry SI, Mattera JA, Curtis JP, Spertus JA, Herrin J, Lin Z, Phillips CO, Hodshon BV, Cooper LS, Krumholz HM (2010) Telemonitoring in patients with heart failure. N Engl J Med 363(24):2301–2309. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1010029
Koehler F, Winkler S, Schieber M, Sechtem U, Stangl K, Bohm M, Boll H, Baumann G, Honold M, Koehler K, Gelbrich G, Kirwan BA, Anker SD (2011) Impact of remote telemedical management on mortality and hospitalizations in ambulatory patients with chronic heart failure: the telemedical interventional monitoring in heart failure study. Circulation 123(17):1873–1880. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.111.018473
Dendale P, De Keulenaer G, Troisfontaines P, Weytjens C, Mullens W, Elegeert I, Ector B, Houbrechts M, Willekens K, Hansen D (2012) Effect of a telemonitoring-facilitated collaboration between general practitioner and heart failure clinic on mortality and rehospitalization rates in severe heart failure: the TEMA-HF 1 (TElemonitoring in the MAnagement of Heart Failure) study. Eur J Heart Fail 14(3):333–340. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurjhf/hfr144
Kashem A, Droogan MT, Santamore WP, Wald JW, Bove AA (2008) Managing heart failure care using an internet-based telemedicine system. J Card Fail 14(2):121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cardfail.2007.10.014
Kashem A, Cross RC, Santamore WP, Bove AA (2006) Management of heart failure patients using telemedicine communication systems. Curr Cardiol Rep 8(3):171–179
Hagglund E, Lynga P, Frie F, Ullman B, Persson H, Melin M, Hagerman I (2015) Patient-centred home-based management of heart failure. Findings from a randomised clinical trial evaluating a tablet computer for self-care, quality of life and effects on knowledge. Scand Cardiovasc J 49(4):193–199. https://doi.org/10.3109/14017431.2015.1035319
Boyne JJ, Vrijhoef HJ, Crijns HJ, De Weerd G, Kragten J, Gorgels AP (2012) Tailored telemonitoring in patients with heart failure: results of a multicentre randomized controlled trial. Eur J Heart Fail 14(7):791–801. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurjhf/hfs058
Blue L, Lang E, McMurray JJ, Davie AP, McDonagh TA, Murdoch DR, Petrie MC, Connolly E, Norrie J, Round CE, Ford I, Morrison CE (2001) Randomised controlled trial of specialist nurse intervention in heart failure. BMJ (Clinical research ed) 323(7315):715–718
Wade MJ, Desai AS, Spettell CM, Snyder AD, McGowan-Stackewicz V, Kummer PJ, Maccoy MC, Krakauer RS (2011) Telemonitoring with case management for seniors with heart failure. Am J Manag Care 17(3):e71–e79
Kasper EK, Gerstenblith G, Hefter G, Van Anden E, Brinker JA, Thiemann DR, Terrin M, Forman S, Gottlieb SH (2002) A randomized trial of the efficacy of multidisciplinary care in heart failure outpatients at high risk of hospital readmission. J Am Coll Cardiol 39(3):471–480
Laramee AS, Levinsky SK, Sargent J, Ross R, Callas P (2003) Case management in a heterogeneous congestive heart failure population: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Intern Med 163(7):809–817. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.163.7.809
Lynga P, Persson H, Hagg-Martinell A, Hagglund E, Hagerman I, Langius-Eklof A, Rosenqvist M (2012) Weight monitoring in patients with severe heart failure (WISH). A randomized controlled trial. Eur J Heart Fail 14(4):438–444. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurjhf/hfs023
Soreca S, Aprile S, Cardone A, Carella G, Fimiani B, Guarnaccia F, Santoro G, Apuzzi V, Bosso G, Valvano A, Zito G, Oliviero U (2012) Management of chronic heart failure: role of home echocardiography in monitoring care programs. World J Cardiol 4(3):72–76. https://doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v4.i3.72
Goldberg LR, Piette JD, Walsh MN, Frank TA, Jaski BE, Smith AL, Rodriguez R, Mancini DM, Hopton LA, Orav EJ, Loh E (2003) Randomized trial of a daily electronic home monitoring system in patients with advanced heart failure: the Weight Monitoring in Heart Failure (WHARF) trial. Am Heart J 146(4):705–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-8703(03)00393-4
(2005) Randomised trial of telephone intervention in chronic heart failure: DIAL trial. BMJ (Clinical research ed) 331(7514):425. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.38516.398067.E0
DeBusk RF, Miller NH, Parker KM, Bandura A, Kraemer HC, Cher DJ, West JA, Fowler MB, Greenwald G (2004) Care management for low-risk patients with heart failure: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 141(8):606–613
Ferrante D, Varini S, Macchia A, Soifer S, Badra R, Nul D, Grancelli H, Doval H (2010) Long-term results after a telephone intervention in chronic heart failure: DIAL (Randomized Trial of Phone Intervention in Chronic Heart Failure) follow-up. J Am Coll Cardiol 56(5):372–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2010.03.049
Antonicelli R, Testarmata P, Spazzafumo L, Gagliardi C, Bilo G, Valentini M, Olivieri F, Parati G (2008) Impact of telemonitoring at home on the management of elderly patients with congestive heart failure. J Telemed Telecare 14(6):300–305. https://doi.org/10.1258/jtt.2008.071213
Anker SD, Koehler F, Abraham WT (2011) Telemedicine and remote management of patients with heart failure. Lancet (London, England) 378(9792):731–739. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(11)61229-4
Omboni S, Gazzola T, Carabelli G, Parati G (2013) Clinical usefulness and cost effectiveness of home blood pressure telemonitoring: meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. J Hypertens 31(3):455–467; discussion 467-458. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0b013e32835ca8dd
Kotb A, Cameron C, Hsieh S, Wells G (2015) Comparative effectiveness of different forms of telemedicine for individuals with heart failure (HF): a systematic review and network meta-analysis. PLoS One 10(2):e0118681. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0118681
O'Connor M, Asdornwised U, Dempsey ML, Huffenberger A, Jost S, Flynn D, Norris A (2016) Using telehealth to reduce all-cause 30-day hospital readmissions among heart failure patients receiving skilled home health services. Appl Clin Inform 7(2):238–247. https://doi.org/10.4338/aci-2015-11-soa-0157
Spaeder J, Najjar SS, Gerstenblith G, Hefter G, Kern L, Palmer JG, Gottlieb SH, Kasper EK (2006) Rapid titration of carvedilol in patients with congestive heart failure: a randomized trial of automated telemedicine versus frequent outpatient clinic visits. Am Heart J 151(4):844.e841–844.e810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2005.06.044
van Tol BA, Huijsmans RJ, Kroon DW, Schothorst M, Kwakkel G (2006) Effects of exercise training on cardiac performance, exercise capacity and quality of life in patients with heart failure: a meta-analysis. Eur J Heart Fail 8(8):841–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejheart.2006.02.013
Acknowledgements
We thank Northern Jiangsu People’s Hospital for helpful statistical advice.
Funding
This work was supported by funds from the Science and Technology Department of Jiangsu Province, China (No. BL2013022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Gu, X. & Xu, C. Effectiveness of telemedicine systems for adults with heart failure: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Heart Fail Rev 25, 231–243 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-019-09801-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-019-09801-5