Abstract
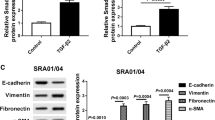
CircRNA circ-PRDM5 (PR/SET domain 5) (circ-PRDM5) is overexpressed in age-related cataracts. Nevertheless, the biological role of circ-PRDM5 in posterior capsule opacities (PCO) (a common complication after cataract surgery) is unclear. Human lens epithelial cells SRA01/04 (LECs) were stimulated with TGF-β2 (transforming growth factor beta-2) to mimic the PCO model in vitro. Cell viability, migration, and invasion were determined by MTT, transwell, or wound-healing assays. Protein levels of EMT (epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition) markers and COL1A2 (collagen type I alpha 2 chain) were analyzed by western blotting (WB). Relative expression of circ-PRDM5, miR-92b-3p, and COL1A2 mRNA was analyzed by qRT-PCR. The targeting relationship was confirmed by dual-luciferase reporter and RIP assays. We observed that circ-PRDM5 and COL1A2 were upregulated in PCO tissues and TGF-β2-treated LECs, while miR-92b-3p was downregulated. Both circ-PRDM5 and COL1A2 knockdown impaired TGF-β2-induced LEC migration, invasion, and EMT. Also, circ-PRDM5 could adsorb miR-92b-3p to regulate COL1A2 expression. Furthermore, miR-92b-3p inhibitor offset circ-PRDM5 knockdown-mediated influence on migration, invasion, and EMT of LECs under TGF-β2 stimulation. Also, COL1A2 overexpression overturned the repressive influence of miR-92b-3p mimic on TGF-β2-induced LEC migration, invasion, and EMT. In summary, TGF-β2-induced circ-PRDM5 facilitated LEC migration, invasion, and EMT by adsorbing miR-92b-3p and increasing COL1A2 expression, offering new insights into the development of PCO.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batur M, Gül A, Seven E, Can E, Yaşar T (2016) Posterior Capsular Opacification in Preschool- and School-Age Patients after Pediatric Cataract Surgery without Posterior Capsulotomy. Turk J Ophthalmol 46:205–208. https://doi.org/10.4274/tjo.24650
Chen X, Ye S, Xiao W, Wang W, Luo L, Liu Y (2014) ERK1/2 pathway mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition by cross-interacting with TGFβ/Smad and Jagged/Notch signaling pathways in lens epithelial cells. Int J Mol Med 33:1664–1670. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2014.1723
Cui G, Wang L, Huang W (2020) Circular RNA HIPK3 regulates human lens epithelial cell dysfunction by targeting the miR-221-3p/PI3K/AKT pathway in age-related cataract. Exp Eye Res 198:108128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2020.108128
Dong N (2019) Long Noncoding RNA MALAT1 Acts as a Competing Endogenous RNA to Regulate TGF-β2 Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Lens Epithelial Cells by a MicroRNA-26a-Dependent Mechanism. BioMed research international 2019: 1569638. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1569638
Dong N (2020) Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 regulates TGF-β2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lens epithelial cells through the miR-34a/Snail1 and miR-204/Zeb1 pathways. BioMed Res Int 2020:8352579. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8352579
Dong N, Xu B, Benya SR, Tang X (2014) MiRNA-26b inhibits the proliferation, migration, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lens epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biochem 396:229–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2158-4
Duan W, Ma J, Ma Q, Xu Q, Lei J, Han L, Li X, Wang Z, Wu Z, Lv S, Ma Z, Liu M, Wang F, Wu E (2014) The activation of β1-integrin by type I collagen coupling with the hedgehog pathway promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 14:446–457. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568009614666140402105101
Exposito J-Y, Valcourt U, Cluzel C, Lethias C (2010) The fibrillar collagen family. Int J Mol Sci 11:407–426. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11020407
Fan C, Liu X, Li W, Wang H, Teng Y, Ren J, Huang Y (2019) Circular RNA circ KMT2E is up-regulated in diabetic cataract lenses and is associated with miR-204-5p sponge function. Gene 710:170–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2019.05.054
Gong L, Ren M, Lv Z, Yang Y, Wang Z (2018) miR-92b-3p promotes colorectal carcinoma cell proliferation, invasion, and migration by inhibiting FBXW7 in vitro and in vivo. DNA Cell Biol 37:501–511. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2017.4080
Han B, Chao J, Yao H (2018) Circular RNA and its mechanisms in disease: from the bench to the clinic. Pharmacol Ther 187:31–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.01.010
Han R, Hao P, Wang L, Li J, Shui S, Wang Y, Ying M, Liu J, Tang X, Li X (2019) )MicroRNA-34a inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lens epithelial cells by targeting Notch1. Exp Eye Res 185:107684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2019.05.024
Haripriya A, Chang DF, Vijayakumar B, Niraj A, Shekhar M, Tanpreet S, Aravind S (2017) Long-term posterior capsule opacification reduction with square-edge polymethylmethacrylate intraocular lens: randomized controlled study. Ophthalmology 124:295–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2016.11.010
Jiang Q, Cao C, Zhou C, Song X, Healey S, Kouttab N, Chu W, Xu A, Bi Z, Wan Y (2008) Quercetin attenuates UV- and H(2)O(2)-induced decrease of collagen type I in cultured human lens epithelial cells. J Ocular Pharmacol Therapeut 24:164–174. https://doi.org/10.1089/jop.2007.0073
Lee JH, Wan XH, Song J, Kang JJ, Chung WS, Lee EH, Kim EK (2002) TGF-beta-induced apoptosis and reduction of Bcl-2 in human lens epithelial cells in vitro. Curr Eye Res 25:147–153. https://doi.org/10.1076/ceyr.25.3.147.13475
Li G, Jiang W, Kang Y, Yu X, Zhang C, Feng Y (2020) High expression of collagen 1A2 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of esophageal cancer cells. Ann Transl Med 8:1672. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-7867
Li J, Yu Z, Song H (2020) The effect of capsulotomy shape on intraocular light-scattering after Nd:YAG laser capsulotomy. J Ophthalmol 2020:4153109. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4153109
Liang S, Dou S, Li W, Huang Y (2020) Profiling of circular RNAs in age-related cataract reveals circZNF292 as an antioxidant by sponging miR-23b-3p. Aging 12:17271–17287. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103683
Liu X, Liu B, Zhou M, Fan F, Yu M, Gao C, Lu Y, Luo Y (2018) Circular RNA HIPK3 regulates human lens epithelial cells proliferation and apoptosis by targeting the miR-193a/CRYAA axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503:2277–2285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.149
Liu X, Wang Q, Zhao J (2020) Acute retinal detachment after Nd:YAG treatment for vitreous floaters and postertior capsule opacification: a case report. BMC Ophthalmol 20:157. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-020-01428-7
Liu Y, Chen T, Zheng G (2021) Exosome-transmitted circ-CARD6 facilitates posterior capsule opacification development by miR-31/FGF7 axis. Exp Eye Res 207:108572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2021.108572
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Long M, Zhan M, Xu S, Yang R, Chen W, Zhang S, Shi Y, He Q, Mohan M, Liu Q, Wang J (2017) miR-92b-3p acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting Gabra3 in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer 16:167. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0723-7
Maruno KA, Lovicu FJ, Chamberlain CG, McAvoy JW (2002) Apoptosis is a feature of TGF beta-induced cataract. Clin Exp Optom 85:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-0938.2002.tb03012.x
Mei L, Yan H, Wang S, Guo C, Zheng X, Yan B, Zhao J, Yang A (2020) Upregulation of miR-630 induced by oxidative damage resists cell migration through targeting ALCAM in human lens epithelium cells. Curr Eye Res 45:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1080/02713683.2019.1656748
Mitra A, Pfeifer K, Park K-S (2018) Circular RNAs and competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) networks. Trans Cancer Res 7:S624–S628. https://doi.org/10.21037/tcr.2018.05.12
Nibourg LM, Gelens E, Kuijer R, Hooymans JMM, van Kooten TG, Koopmans SA (2015) Prevention of posterior capsular opacification. Exp Eye Res 136:100–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2015.03.011
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, Pandolfi PP (2011) A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 146:353–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.014
Shimada A, Miyata Y, Kosano H (2014) Type I collagen accelerates the spreading of lens epithelial cells through the expression and activation of matrix metalloproteinases. Curr Eye Res 39:460–471. https://doi.org/10.3109/02713683.2013.853194
Smith AJO, Eldred JA, Wormstone IM (2019) Resveratrol inhibits wound healing and lens fibrosis: a putative candidate for posterior capsule opacification prevention. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 60:3863–3877. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.18-26248
Tay Y, Rinn J, Pandolfi PP (2014) The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 505:344–352. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12986
Wernecke L, Keckeis S, Reichhart N, Strauß O, Salchow DJ (2018) Epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation in pediatric lens epithelial cells. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 59:5785–5794. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.18-23789
Wormstone IM, Eldred JA (2016) Experimental models for posterior capsule opacification research. Exp Eye Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2015.04.021
Yang MC, Wang CJ, Liao PC, Yen CJ, Shan YS (2014) Hepatic stellate cells secretes type I collagen to trigger epithelial mesenchymal transition of hepatoma cells. Am J Cancer Res 4:751–763
Yang Y, Ye Y, Lin X, Wu K, Yu M (2013) Inhibition of pirfenidone on TGF-beta2 induced proliferation, migration and epithlial-mesenchymal transition of human lens epithelial cells line SRA01/04. PLoS ONE 8:e56837. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0056837
Yao L, Yang L, Song H, Liu T, Yan H (2020) )MicroRNA miR-29c-3p modulates FOS expression to repress EMT and cell proliferation while induces apoptosis in TGF-β2-treated lens epithelial cells regulated by lncRNA KCNQ1OT1. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy =. Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie 129:110290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110290
Yin W, Zhu H, Tan J, Xin Z, Zhou Q, Cao Y, Wu Z, Wang L, Zhao M, Jiang X, Ren C, Tang G (2021) Identification of collagen genes related to immune infiltration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in glioma. Cancer Cell Int 21:276. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-021-01982-0
Yu X-J, Huang Y-Q, Shan Z-X, Zhu J-N, Hu Z-Q, Huang L, Feng Y-Q, Geng Q-S (2019) MicroRNA-92b-3p suppresses angiotensin II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy via targeting HAND2. Life Sci 232:116635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116635
Zhang C, Hu J, Yu Y (2020) CircRNA Is a Rising Star in Researches of Ocular Diseases. Frontiers in cell and developmental biology 8:850. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.00850
Zhang R-P, Xie Z-G (2020) Research progress of drug prophylaxis for lens capsule opacification after cataract surgery. J Ophthalmol 2020:2181685. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2181685
Zhang Y, Liu M-W, He Y, Deng N, Chen Y, Huang J, Xie W (2020) Protective effect of resveratrol on estrogen deficiency-induced osteoporosis though attenuating NADPH oxidase 4/nuclear factor kappa B pathway by increasing miR-92b-3p expression. Int J ImmunoPathol Pharmacol 34:2058738420941762. https://doi.org/10.1177/2058738420941762
Zhang Z, Yang T, Xiao J (2018) Circular RNAs: promising biomarkers for human diseases. EBioMedicine 34:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.07.036
Zhang Z, Zhu H, Liu Y, Quan F, Zhang X, Yu L (2018) )LncRNA HOTAIR mediates TGF-β2-induced cell growth and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human lens epithelial cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 50:1028–1037. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmy101
Zhong Y, Du Y, Yang X, Mo Y, Fan C, Xiong F, Ren D, Ye X, Li C, Wang Y, Wei F, Guo C, Wu X, Li X, Li Y, Li G, Zeng Z, Xiong W (2018) Circular RNAs function as ceRNAs to regulate and control human cancer progression. Mol Cancer 17:79. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0827-8
Acknowledgement
None.
Funding
Wuhan Medical Research Project No. WX20B27
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10735_2021_10053_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Sup. Fig. 1 Western blotting exhibiting the effects of COL1A2 knockdown on E-cadherin and N-cadherin protein levels in TGF-β2-stimulated LECs. **P <0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 (TIFF 132 kb)
10735_2021_10053_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Sup. Fig. 2 The transfection efficiencies of si-circ-PRDM5, circ-PRDM5, si-circ-COL1A2, and COL1A2. (A) QRT-PCR showing the efficiencies of si-circ-PRDM5 and circ-PRDM5. (B) WB exhibiting the efficiencies of si-circ-COL1A2 and COL1A2. ****P < 0.0001 (TIFF 52 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, P., Hu, Y. & Duan, Y. TGF-β2-induced circ-PRDM5 regulates migration, invasion, and EMT through the miR-92b-3p/COL1A2 pathway in human lens epithelial cells. J Mol Histol 53, 309–320 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10053-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10053-7