Abstract
Lectins are non-immunological carbohydrate-binding proteins classified on the basis of their structure, origin, and sugar specificity. The binding specificity of such proteins with the surface glycan moiety determines their activity and clinical applications. Thus, lectins hold great potential as diagnostic and drug discovery agents and as novel biopharmaceutical products. In recent years, significant advancements have been made in understanding plant and microbial lectins as therapeutic agents against various viral diseases. Among them, mannose-specific lectins have being proven as promising antiviral agents against a variety of viruses, such as HIV, Influenza, Herpes, Ebola, Hepatitis, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-1 (SARS-CoV-1), Middle Eastern Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) and most recent Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). The binding of mannose-binding lectins (MBLs) from plants and microbes to high-mannose containing N-glycans (which may be simple or complex) of glycoproteins found on the surface of viruses has been found to be highly specific and mainly responsible for their antiviral activity. MBLs target various steps in the viral life cycle, including viral attachment, entry and replication. The present review discusses the brief classification and structure of lectins along with antiviral activity of various mannose-specific lectins from plants and microbial sources and their diagnostic and therapeutic applications against viral diseases.
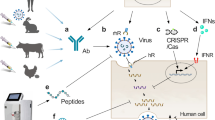
Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith, K.M., Machalaba, C.C., Seifman, R., Feferholtz, Y., Karesh, W.B.: Infectious disease and economics: The case for considering multi-sectoral impacts. One Health. 7, 100080 (2019)
Bloom, D.E., Black, S., Rappuoli, R.: Emerging infectious diseases: A proactive approach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 114(16), 4055–4059 (2017)
Friedrich, M.J.: WHO’s top health threats for 2019. JAMA 321(11), 1041 (2019)
Kausar, S., Said Khan, F., Ishaq Mujeeb Ur Rehman, M., Akram, M., Riaz, M., Rasool, G., Hamid Khan, A., Saleem, I., Shamim, S., Malik, A.: A review: Mechanism of action of antiviral drugs. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 35, 20587384211002621 (2021)
Elfakharany, E., Gerges, M., Behery, E., Mohsen, A., Belald, F.: COVID-19 coronavirus: Pathogenesis, clinical features, diagnostics, epidemiology, prevention and control. Appl. Pharm. 12, 65–66 (2020)
Oroojalian, F., Haghbin, A., Baradaran, B., Hemmat, N., Shahbazi, M.A., Baghi, H.B., Mokhtarzadeh, A., Hamblin, M.R.: Novel insights into the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: an overview of current clinical trials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 165, 18–43 (2020)
Maginnis, M.S.: Virus–receptor interactions: the key to cellular invasion. J. Mol. Biol. 430(17), 2590–2611 (2018)
Nassar, A., Ibrahim, I.M., Amin, F.G., Magdy, M., Elgharib, A.M., Azzam, E.B., Nasser, F., Yousry, K., Shamkh, I.M., Mahdy, S.M., Elfiky, A.A.: A review of human coronaviruses’ receptors: the host-cell targets for the crown bearing viruses. Molecules 26(21), 6455 (2021)
Nabi-Afjadi, M., Heydari, M., Zalpoor, H., Arman, I., Sadoughi, A., Sahami, P., Aghazadeh, S.: Lectins and lectibodies: potential promising antiviral agents. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 27(1), 1–25 (2022)
Mazalovska, M., Kouokam, J.C.: Lectins as promising therapeutics for the prevention and treatment of HIV and other potential coinfections. Biomed Res. Int. (2018)
Kachko, A., Loesgen, S., Shahzad-ul-Hussan, S., Tan, W., Zubkova, I., Takeda, K., Wells, F., Rubin, S., Bewley, C.A., Major, M.E.: Inhibition of hepatitis C virus by the cyanobacterial protein Microcystis viridis lectin: mechanistic differences between the high-mannose specific lectins MVL, CV-N, and GNA. Mol. Pharm. 10(12), 4590–4602 (2013)
Saad, M.H., Sidkey, N.M., Khan, R.H., El-Fakharany, E.M.: Nostoc muscorum is a novel source of microalgal lectins with potent antiviral activity against herpes simplex type-1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 210, 415–429 (2022)
Thompson, A.J., Cao, L., Ma, Y., Wang, X., Diedrich, J.K., Kikuchi, C., Willis, S., Worth, C., McBride, R., Yates, J.R., III., Paulson, J.C.: Human influenza virus hemagglutinins contain conserved oligomannose N-linked glycans allowing potent neutralization by lectins. Cell Host Microbe 27(5), 725–735 (2020)
Kaur, A., Kamboj, S.S., Singh, J., Singh, R., Abrahams, M., Kotwal, G.J., Saxena, A.K.: Purification of 3 monomeric monocot mannose-binding lectins and their evaluation for antipoxviral activity: potential applications in multiple viral diseases caused by enveloped viruses. Biochem. Cell Biol. 85(1), 88–95 (2007)
Favacho, A.R., Cintra, E.A., Coelho, L.C., Linhares, M.I.: In vitro activity evaluation of Parkia pendula seed lectin against human cytomegalovirus and herpes virus 6. Biol. 35(3), 189–194 (2007)
Ooi, L.S., Ho, W.S., Ngai, K.L., Tian, L., Chan, P.K., Sun, S.S., Ooi, V.E.: Narcissus tazetta lectin shows strong inhibitory effects against respiratory syncytial virus, influenza A (H1N1, H3N2, H5N1) and B viruses. J. Biosci. 1, 95–103 (2010)
Covés-Datson, E.M., Dyall, J., DeWald, L.E., King, S.R., Dube, D., Legendre, M., Nelson, E., Drews, K.C., Gross, R., Gerhardt, D.M., Torzewski, L.: Inhibition of Ebola virus by a molecularly engineered banana lectin. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 13(7), e0007595 (2019)
Ahmed, M.N., Jahan, R., Nissapatorn, V., Wilairatana, P., Rahmatullah, M.: Plant lectins as prospective antiviral biomolecules in the search for COVID-19 eradication strategies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 146, 112507 (2022)
Lagarda-Diaz, I., Guzman-Partida, A.M., Vazquez-Moreno, L.: Legume lectins: proteins with diverse applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18(6), 1242 (2017)
Dias, R.D., Machado, L.D., Migliolo, L., Franco, O.L.: Insights into animal and plant lectins with antimicrobial activities. Molecules 20(1), 519–541 (2015)
Santos, A.F., Da Silva, M.D., Napoleão, T.H., Paiva, P.M., Correia, M.D., Coelho, L.C.: Lectins: Function, structure, biological properties andpotential applications. Curr. Top. Pept. Protein Res. (2014)
Jandú, J.J., Moraes Neto, R.N., Zagmignan, A., de Sousa, E.M., Brelaz-de-Castro, M.C., dos Santos Correia, M.T., da Silva, L.C.: Targeting the immune system with plant lectins to combat microbial infections. Front. Pharmacol. 8, 671 (2017)
O’Keefe, B.R., Shenoy, S.R., Xie, D., Zhang, W., Muschik, J.M., Currens, M.J., Chaiken, I., Boyd, M.R.: Analysis of the interaction between the HIV-inactivating protein cyanovirin-N and soluble forms of the envelope glycoproteins gp120 and gp41. Mol. Pharmacol. 58(5), 982–992 (2000)
Bokesch, H.R., O’Keefe, B.R., McKee, T.C., Pannell, L.K., Patterson, G.M., Gardella, R.S., Sowder, R.C., Turpin, J., Watson, K., Buckheit, R.W., Boyd, M.R.: A potent novel anti-HIV protein from the cultured cyanobacterium Scytonema varium. Biochem. 42(9), 2578–2584 (2003)
Botos, I., Wlodawer, A.: Cyanovirin-N: a sugar-binding antiviral protein with a new twist. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 60(2), 277–287 (2003)
Barre, A., Bourne, Y., Van Damme, E.J., Rougé, P.: Overview of the structure–function relationships of mannose-specific lectins from plants, algae and fungi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20(2), 254 (2019)
Barre, A., Van Damme, E.J., Simplicien, M., Le Poder, S., Klonjkowski, B., Benoist, H., Peyrade, D., Rougé, P.: Man-specific lectins from plants, fungi, algae and cyanobacteria, as potential blockers for SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) coronaviruses: Biomedical perspectives. Cells 10(7), 1619 (2021)
Van Damme, E.J., Smeets, K., Peumans, W.J.: The mannose-binding monocot lectins and their genes. Lect. Biomed. pers. 27, 59–80 (1995)
Stewart-Jones, G.B., Soto, C., Lemmin, T., Chuang, G.Y., Druz, A., Kong, R., Thomas, P.V., Wagh, K., Zhou, T., Behrens, A.J., Bylund, T.: Trimeric HIV-1-Env structures define glycan shields from clades A, B, and G. Cell 165(4), 813–826 (2016)
Davenport, Y.W., West, A.P., Jr., Bjorkman, P.J.: Structure of an HIV-2 gp120 in complex with CD4. Virol. J. 90(4), 2112–2118 (2016)
Bonomelli, C., Doores, K.J., Dunlop, D.C., Thaney, V., Dwek, R.A., Burton, D.R., Crispin, M., Scanlan, C.N.: The glycan shield of HIV is predominantly oligomannose independently of production system or viral clade. PLoS ONE 6(8), e23521 (2011)
Shajahan, A., Pepi, L.E., Rouhani, D.S., Heiss, C., Azadi, P.: Glycosylation of SARS-CoV-2: structural and functional insights. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 413(29), 7179–7193 (2021)
Cai, Y., Xu, W., Gu, C., Cai, X., Qu, D., Lu, L., Xie, Y., Jiang, S.: Griffithsin with a broad-spectrum antiviral activity by binding glycans in viral glycoprotein exhibits strong synergistic effect in combination with a pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitor targeting SARS-CoV-2 spike S2 subunit. Virol. Sin. 35(6), 857–860 (2020)
Watanabe, Y., Bowden, T.A., Wilson, I.A., Crispin, M.: Exploitation of glycosylation in enveloped virus pathobiology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Gen. Subj. 1863(10), 1480–1497 (2019)
Seal, S., Dharmarajan, G., Khan, I.: Evolution of pathogen tolerance and emerging infections: A missing experimental paradigm. Elife. 10, e68874 (2021)
Kolchinsky, P., Kiprilov, E., Sodroski, J.: Increased neutralization sensitivity of CD4-independent human immunodeficiency virus variants. Virol. J. 75(5), 2041–2050 (2001)
Peumans, W.J., Van Damme, E.J.: Lectins as plant defense proteins. Plant Physiol. 109(2), 347 (1995)
Wright, C.S.: New folds of plant lectins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 7(5), 631–636 (1997)
Taylor, M., Drickamer, K., Imberty, A., van Kooyk, Y., Schnaar, R., Etzler, M., Varki, A.: Discovery and classification of glycan-binding proteins. Essentials of Glycobiology (2022)
Van Parijs, J., Broekaert, W.F., Goldstein, I.J., Peumans, W.J.: Hevein: an antifungal protein from rubber-tree (Hevea brasiliensis) latex. Planta 183(2), 258–264 (1991)
Van Damme, E.J., Balzarini, J., Smeets, K., van Leuven, F., Peumans, W.J.: The monomeric and dimeric mannose-binding proteins from the Orchidaceae species Listera ovata and Epipactis helleborine: sequence homologies and differences in biological activities. Glycoconj. J. 4, 321–332 (1994)
Sumner, J.B.: The globulins of the jack bean, Canavalia ensiformis: preliminary paper. J. Biol. Chem. 37(1), 137–142 (1919)
Naismith, J.H., Emmerich, C., Habash, J., Harrop, S.J., Helliwell, J.R., Hunter, W.N., Raftery, J., Yariv, J.: Refined structure of concanavalin A complexed with methyl α-D-mannopyranoside at 2.0 Å resolution and comparison with the saccharide-free structure. Acta Crystallogr., Sect. D: Biol. Crystallogr. 50(6), 847–858 (1994)
Ravishankar, R., Thomas, C.J., Suguna, K., Surolia, A., Vijayan, M.: Crystal structures of the peanut lectin–lactose complex at acidic pH: Retention of unusual quaternary structure, empty and carbohydrate bound combining sites, molecular mimicry and crystal packing directed by interactions at the combining site. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinfo. 43(3), 260–270 (2001)
Rutenber, E., Robertus, J.D.: Structure of ricin B‐chain at 2.5 Å resolution. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinfo. 10(3), 260–269 (1991)
Bah, C.S., Fang, E.F., Ng, T.B.: Medicinal applications of plant lectins. Antitumor potential and other emerging medicinal properties of natural compounds. 55–74 (2013)
Mishra, A., Behura, A., Mawatwal, S., Kumar, A., Naik, L., Mohanty, S.S., Manna, D., Dokania, P., Mishra, A., Patra, S.K., Dhiman, R.: Structure-function and application of plant lectins in disease biology and immunity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 134, 110827 (2019)
Van Damme, E.J., Lannoo, N., Peumans, W.J.: Plant lectins. In Advances in botanical research. Acad. Press. 48, 107–209 (2008)
Van Holle, S., Van Damme, E.J.: Messages from the past: New insights in plant lectin evolution. Front. Plant Sci. 10, 36 (2019)
Nakamura-Tsuruta, S., Kominami, J., Kuno, A., Hirabayashi, J.: Evidence that Agaricus bisporus agglutinin (ABA) has dual sugar-binding specificity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 347(1), 215–220 (2006)
Carrizo, M.E., Capaldi, S., Perduca, M., Irazoqui, F.J., Nores, G.A., Monaco, H.L.: The anti neoplastic lectin of the common edible mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) has two binding sites, each specific for a different configuration at a single epimeric hydroxyl. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 10614–10623 (2005)
Rinderle, S.J., Goldstein, I.J., Matta, K.L., Ratcliffe, R.M.: Isolation and characterization of amaranthin, a lectin present in the seeds of Amaranthus caudatus, that recognizes the T-(or cryptic T)-antigen. J. Biol. Chem. 264(27), 16123–16131 (1989)
Transue, T.R., Smith, A.K., Mo, H., Goldstein, I.J., Saper, M.A.: Structure of benzyl T-antigen disaccharide bound to Amaranthus caudatus agglutinin. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 4(10), 779–783 (1997)
Dang, L., Rougé, P., Van Damme, E.J.M.: Amaranthin–like proteins with aerolysin domains in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 8, 1368 (2017)
Van Damme, E.J., Culerrier, R., Barre, A., Alvarez, R., Rougé, P., Peumans, W.J.: A novel family of lectins evolutionarily related to class V chitinases: an example of neofunctionalization in legumes. J. Plant Physiol. 144(2), 662–672 (2007)
Boyd, M.R., Gustafson, K.R., McMahon, J.B., Shoemaker, R.H., O’Keefe, B.R., Mori, T., Gulakowski, R.J., Wu, L., Rivera, M.I., Laurencot, C.M., Currens, M.J.: Discovery of cyanovirin-N, a novel human immunodeficiency virus-inactivating protein that binds viral surface envelope glycoprotein gp120: potential applications to microbicide development. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 41(7), 1521–1530 (1997)
Gustafson, K.R., Sowder, R.C., II., Henderson, L.E., Cardellina, J.H., II., McMahon, J.B., Rajamani, U., Pannell, L.K., Boyd, M.R.: Isolation, primary sequence determination, and disulfide bond structure of cyanovirin-N, an anti-HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) protein from the CyanobacteriumNostoc ellipsosporum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 238(1), 223–228 (1997)
Percudani, R., Montanini, B., Ottonello, S.: The anti‐HIV cyanovirin‐N domain is evolutionarily conserved and occurs as a protein module in eukaryotes. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Genet. 60(4), 670–678 (2005)
Tsaneva, M., Van Damme, E.J.: 130 years of plant lectin research. Glycoconj. J. 37, 533–551 (2020)
Pacak, F., Kocourek, J.: Studies on phytohemagglutinins: xxv. Isolation and characterization of hemagglutinins of the spindle tree seeds (Evonymus europaea L.). Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 400(2), 374–386 (1975)
Petryniak, J., Pereira, M.E., Kabat, E.A.: The lectin of Euonymus europeus: purification, characterization, and an immunochemical study of its combining site. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 178(1), 118–134 (1977)
Van Damme, E.J., Allen, A.K., Peumans, W.J.: Isolation and characterization of a lectin with exclusive specificity towards mannose from snowdrop (Galanthus nivalis) bulbs. FEBS Lett. 215(1), 140–144 (1987)
Barre, A., Van Damme, E.J., Peumans, W.J., Rouge, P.: Structure-function relationship of monocot mannose-binding lectins. Plant Physiol. 112(4), 1531–1540 (1996)
Peumans, W.J., Barre, A., Bras, J., Rougé, P., Proost, P., Van Damme, E.J.: The liverwort contains a lectin that is structurally and evolutionary related to the monocot mannose-binding lectins. Plant physiol. 129(3), 1054–1065 (2002)
Sastry, M.V., Banarjee, P., Patanjali, S.R., Swamy, M.J., Swarnalatha, G.V., Surolia, A.: Analysis of saccharide binding to Artocarpus integrifolia lectin reveals specific recognition of T-antigen (beta-D-Gal (1–3) D-GalNAc). J. Biol. Chem. 261(25), 11726–11733 (1986)
Bourne, Y., Astoul, C.H., Zamboni, V., Peumans, W.J., Menu-Bouaouiche, L., Van Damme, E.J., Barre, A., Rougé, P.: Structural basis for the unusual carbohydrate-binding specificity of jacalin towards galactose and mannose. Biochem. J. 364(1), 173–180 (2002)
Bourne, Y., Zamboni, V., Barre, A., Peumans, W.J., Van Damme, E.J., Rougé, P.: Helianthus tuberosus lectin reveals a widespread scaffold for mannose-binding lectins. Struct. 7(12), 1473–1482 (1999)
Sankaranarayanan, R., Sekar, K., Banerjee, R., Sharma, V., Surolia, A., Vijayan, M.: A novel mode of carbohydrate recognition in jacalin, a Moraceae plant lectin with a β-prism fold. Struct. Mol. Biol. 3(7), 596–603 (1996)
Sarkar, M., Wu, A.M., Kabat, E.A.: Immunochemical studies on the carbohydrate specificity of Maclura pomifera lectin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 209(1), 204–218 (1981)
Van Damme, E.J., Barre, A., Mazard, A.M., Verhaert, P., Horman, A., Debray, H., Rouge, P., Peumans, W.J.: Characterization and molecular cloning of the lectin from Helianthus tuberosus. European J. Biochem. 259(1–2), 135–142 (1999)
Peumans, W.J., Winter, H.C., Bemer, V., Van Leuven, F., Goldstein, I.J., Truffa-Bachi, P., Van Damme, E.J.: Isolation of a novel plant lectin with an unusual specificity from Calystegia sepium. Glycoconj. J. 14(2), 259–265 (1997)
El-Araby, M.M., El-Shatoury, E.H., Soliman, M.M., Shaaban, H.F.: Characterization and antimicrobial activity of lectins purified from three Egyptian leguminous seeds. AMB Exp. 10, 1–4 (2020)
Mitchell, C.A., Ramessar, K., O’Keefe, B.R.: Antiviral lectins: Selective inhibitors of viral entry. Antiviral Res. 142, 37–54 (2017)
Costa, A., Malveira, E.A., Mendonça, L.P., Maia, M.E., Silva, R.R., Roma, R.R., Aguiar, T.K., Grangeiro, Y.A., Souza, P.F.: Plant Lectins: A Review on their Biotechnological Potential Toward Human Pathogens. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 23(12), 851–861 (2022)
Peumans, W.J., Van Damme, J.M., Barre, A., Rougé, P.: Classification of plant lectins in families of structurally and evolutionary related proteins. Mol. Immun. Compl. Carb. 2, 27–54 (2001)
Bateman, A., Bycroft, M.: The structure of a LysM domain from E. coli membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase D (MltD). J. Mol. Biol. 299, 1113–1119 (2000)
Lannoo, N., Vandenborre, G., Miersch, O., Smagghe, G., Wasternack, C., Peumans, W.J., Van Damme, E.J.: The jasmonate-induced expression of the Nicotiana tabacum leaf lectin. Plant Cell Physiol. 48(8), 1207–1218 (2007)
Schouppe, D., Rougé, P., Lasanajak, Y., Barre, A., Smith, D.F., Proost, P., Van Damme, E.J.M.: Mutational analysis of the carbohydrate binding activity of the tobacco lectin. Glycoconj. J. 27, 613–623 (2010)
Stirpe, F., Battelli, M.G.: Ribosome-inactivating proteins: progress and problems. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63, 1850–1866 (2006)
Barbieri, L., Battelli, M.G., Stirpe, F.: Ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Biomembr. Bba-Biomembr. 1154(3–4), 237–282 (1993)
Chan, W.Y., Ng, T.B.: Comparison of the Embryotoxic Effects of Saporin, Agrostin (Type 1 Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins) and Ricin (a Type 2 Ribosome-Inactivating Protein. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 88(6), 300–303 (2001)
Barre, A., Simplicien, M., Benoist, H., Van Damme, E.J., Rougé, P.: Mannose-specific lectins from marine algae: diverse structural scaffolds associated to common virucidal and anti-cancer properties. Mar. Drugs 17(8), 440 (2019)
Notova, S., Bonnardel, F., Lisacek, F., Varrot, A., Imberty, A.: Structure and engineering of tandem repeat lectins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 62, 39–47 (2020)
Hirabayashi, J., Arai, R.: Lectin engineering: the possible and the actual. J. R. Soc. Interface. Foc. 9(2), 20180068 (2019)
Agrawal, B.B., Goldstein, I.J.: Physical and chemical characterization of concanavalin A, the hemagglutinin from jack bean (Canavalia ensiformis). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 133(2), 376–379 (1967)
Pratap, J.V., Jeyaprakash, A.A., Rani, P.G., Sekar, K., Surolia, A., Vijayan, M.: Crystal structures of artocarpin, a Moraceae lectin with mannose specificity, and its complex with methyl-α-D-mannose: implications to the generation of carbohydrate specificity. J. Mol. Biol. 317(2), 237–247 (2002)
Baumann, C.M., Strosberg, A.D., Rüdiger, H.: Purification and Characterization of a Mannose/Glucose-Specific Lectin from Vicia cracca. European J. Biochem. 122(1), 105–110 (1982)
Chowdhury, S., Ahmed, H., Chatterjee, B.P.: Chemical modification studies of Artocarpus lakoocha lectin artocarpin. Biochimie 73(5), 563–571 (1991)
Mann, K., Farias, C.M., Del Sol, F.G., Santos, C.F., Grangeiro, T.B., Nagano, C.S., Cavada, B.S., Calvete, J.J.: The amino-acid sequence of the glucose/mannose-specific lectin isolated from Parkia platycephala seeds reveals three tandemly arranged jacalin-related domains. European J. Biochem. 268(16), 4414–4422 (2001)
Antonyuk, V.O.: Integrated use of the jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus L.) tubers: purification of inulin, fructose and mannosespecific lectin. FARM ZH. (3), 50–60 (2014)
Kaku, H., Van Damme, E.J., Peumans, W.J., Goldstein, I.J.: Carbohydrate-binding specificity of the daffodil (Narcissus pseudonarcissus) and amaryllis (Hippeastrum hybr.) bulb lectins. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 279(2), 298–304 (1990)
Spiwok, V.: CH/π interactions in carbohydrate recognition. Mol. 22(7), 1038 (2017)
Yan, R., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Xia, L., Guo, Y., Zhou, Q.: Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2. Science 367(6485), 1444–1448 (2020)
Watanabe, Y., Bowden, T.A., Wilson, I.A., Crispin, M.: Exploitation of glycosylation in enveloped virus pathobiology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Gen. Subj. BBA-Gen. Subjects. 1863(10), 1480–1497 (2019)
Zhou, D., Tian, X., Qi, R., Peng, C., Zhang, W.: Identification of 22 N-glycosites on spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 and accessible surface glycopeptide motifs: Implications for vaccination and antibody therapeutics. Glycobiol. J. 31(1), 69–80 (2021)
Cipollo, J.F., Parsons, L.M.: Glycomics and glycoproteomics of viruses: Mass spectrometry applications and insights toward structure–function relationships. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 39(4), 371–409 (2020)
Ohyama, Y., Nakajima, K., Renfrow, M.B., Novak, J., Takahashi, K.: Mass spectrometry for the identification and analysis of highly complex glycosylation of therapeutic or pathogenic proteins. Expert Rev. Proteomics 17(4), 275–296 (2020)
Carbaugh, D.L., Lazear, H.M.: Flavivirus envelope protein glycosylation: impacts on viral infection and pathogenesis. J. Virol. 94(11), e00104-e120 (2020)
Vankadari, N., Wilce, J.A.: Emerging COVID-19 coronavirus: glycan shield and structure prediction of spike glycoprotein and its interaction with human CD26. Emerg. Microb. Infect. 9(1), 601–604 (2020)
Bagdonaite, I., Vakhrushev, S.Y., Joshi, H.J., Wandall, H.H.: Viral glycoproteomes: technologies for characterization and outlook for vaccine design. FEBS Lett. 592(23), 3898–3920 (2018)
Reily, C., Stewart, T.J., Renfrow, M.B., Novak, J.: Glycosylation in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 15(6), 346–366 (2019)
Hargett, A.A., Renfrow, M.B.: Glycosylation of viral surface proteins probed by mass spectrometry Curr. Opin. Virol. 36, 56–66 (2019)
Fung, T.S., Liu, D.X.: Post-translational modifications of coronavirus proteins: roles and function. Future Virol. 13(6), 405–430 (2018)
Feng, T., Zhang, J., Chen, Z., Pan, W., Chen, Z., Yan, Y., Dai, J.: Glycosylation of viral proteins: Implication in virus–host interaction and virulence. Virulence. 13(1), 670–683 (2022)
Tortorici, M.A., Walls, A.C., Lang, Y., Wang, C., Li, Z., Koerhuis, D., Boons, G.J., Bosch, B.J., Rey, F.A., de Groot, R.J., Veesler, D.: Structural basis for human coronavirus attachment to sialic acid receptors. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 26(6), 481–489 (2019)
Bagdonaite, I., Wandall, H.H.: Global aspects of viral glycosylation. Glycobiology 28(7), 443–467 (2018)
Wang, D.: Coronaviruses’ sugar shields as vaccine candidates. Trends Immunol. 21, 17 (2020)
Zhao, H., To, K.K., Sze, K.H., Yung, T.T., Bian, M., Lam, H., Yeung, M.L., Li, C., Chu, H., Yuen, K.Y.: A broad-spectrum virus-and host-targeting peptide against respiratory viruses including influenza virus and SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Commun. 11(1), 4252 (2020)
Mathys, L., François, K.O., Quandte, M., Braakman, I., Balzarini, J.: Deletion of the highly conserved N-glycan at Asn260 of HIV-1 gp120 affects folding and lysosomal degradation of gp120, and results in loss of viral infectivity. PLoS ONE 9(6), e101181 (2014)
Quiñones-Kochs, M.I., Buonocore, L., Rose, J.K.: Role of N-linked glycans in a human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein: effects on protein function and the neutralizing antibody response. J. Virol. 76(9), 4199–4211 (2002)
Helle, F., Vieyres, G., Elkrief, L., Popescu, C.I., Wychowski, C., Descamps, V., Castelain, S., Roingeard, P., Duverlie, G., Dubuisson, J.: Role of N-linked glycans in the functions of hepatitis C virus envelope proteins incorporated into infectious virions. J. Virol. 84(22), 11905–11915 (2010)
Goffard, A., Callens, N., Bartosch, B., Wychowski, C., Cosset, F.L., Montpellier, C., Dubuisson, J.: Role of N-linked glycans in the functions of hepatitis C virus envelope glycoproteins. J. Virol. 79(13), 8400–8409 (2005)
Dobrica, M.O., Lazar, C., Branza-Nichita, N.: N-glycosylation and N-glycan processing in HBV biology and pathogenesis. Cells 9(6), 1404 (2020)
Lazar, C., Durantel, D., Macovei, A., Zitzmann, N., Zoulim, F., Dwek, R.A., Branza-Nichita, N.: Treatment of hepatitis B virus-infected cells with α-glucosidase inhibitors results in production of virions with altered molecular composition and infectivity. Antivir. Res. 76(1), 30–37 (2007)
Lennemann, N.J., Walkner, M., Berkebile, A.R., Patel, N., Maury, W.: The role of conserved N-linked glycans on Ebola virus glycoprotein 2. J. Infect. Dis. 204, 9 (2015)
Antoine, T.E., Park, P.J., Shukla, D.: Glycoprotein targeted therapeutics: a new era of anti-herpes simplex virus-1 therapeutics. Rev. Med. Virol. 23(3), 194–208 (2013)
Barre, A., Van Damme, E.J., Klonjkowski, B., Simplicien, M., Sudor, J., Benoist, H., Rougé, P.: Legume lectins with different specificities as potential glycan probes for pathogenic enveloped viruses. Cells 11(3), 339 (2022)
Martinez, D., Amaral, D., Markovitz, D., Pinto, L.: The use of lectins as tools to combat SARS-CoV-2. Curr. Pharm. Des. 27(41), 4212–4222 (2021)
Carneiro, D.C., Fernandez, L.G., Monteiro-Cunha, J.P., Benevides, R.G., Cunha Lima, S.T.: A patent review of the antimicrobial applications of lectins: Perspectives on therapy of infectious diseases. J. Appl. Microbiol. 132(2), 841–854 (2022)
Liu, Y., Liu, J., Pang, X., Liu, T., Ning, Z., Cheng, G.: The roles of direct recognition by animal lectins in antiviral immunity and viral pathogenesis. Molecul. 20(2), 2272–2295 (2015)
Fujimoto, Y.K., Green, D.F.: Carbohydrate recognition by the antiviral lectin cyanovirin-N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134(48), 19639–19651 (2012)
McGreal, E.P., Rosas, M., Brown, G.D., Zamze, S., Wong, S.Y., Gordon, S., Martinez-Pomares, L., Taylor, P.R.: The carbohydrate-recognition domain of Dectin-2 is a C-type lectin with specificity for high mannose. Glycobiol. 16(5), 422–430 (2006)
Khan, H., Aziz, A.A., Sulahria, H., Khan, H., Ahmed, A., Choudhry, N., Narayanan, R., Danzig, C., Khanani, A.M.: Emerging treatment options for geographic atrophy (GA) secondary to age-related macular degeneration. Clin. Ophthalmol. 31, 321–327 (2023)
Lu, J., Zhao, Z., Li, Q., Pang, Y.: Review of the unique and dominant lectin pathway of complement activation in agnathans. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 140, 104593 (2023)
Riwes, M.M., Leather, H., Neal, D., Bennett, C., Sugrue, M., Cline, C., Stokes, J., Hiemenz, J., Hsu, J., Wingard, J.R.: Association of mannose-binding lectin levels and invasive fungal disease in hematologic malignancy patients receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy or allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 51(9), 1228–1232 (2016)
Shan, L.H., Lee, P.L., Chen, H.W., Chen, L.K., Kao, C.L., King, C.C.: Analysis of the steps involved in dengue virus entry into host cells. Virol. 257(1), 156–167 (1999)
Upadhyay, A., Upadhyaya, I., Kollanoor-Johny, A., Venkitanarayanan, K.: Combating pathogenic microorganisms using plant-derived antimicrobials: a minireview of the mechanistic basis. Biomed Res. Int. (2014)
Hwang, H.J., Han, J.W., Jeon, H., Cho, K., Kim, J.H., Lee, D.S., Han, J.W.: Characterization of a novel mannose-binding lectin with antiviral activities from red alga. Grateloupia chiangii. Biomolecul. 10(2), 333 (2020)
Sato, Y., Hirayama, M., Morimoto, K., Yamamoto, N., Okuyama, S., Hori, K.: High mannose-binding lectin with preference for the cluster of α1–2-mannose from the green alga Boodlea coacta is a potent entry inhibitor of HIV-1 and influenza viruses. J. Biol. Chem. 286(22), 19446–19458 (2011)
Gupta, A., Gupta, G.S.: Status of mannose-binding lectin (MBL) and complement system in COVID-19 patients and therapeutic applications of antiviral plant MBLs. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 476(8), 2917–2942 (2021)
Barton, C., Kouokam, J.C., Hurst, H., Palmer, K.E.: Pharmacokinetics of the Antiviral Lectin Griffithsin Administered by Different Routes Indicates Multiple Potential Uses. Viruses 8(12), 331 (2016)
Pengcheng, W., Bai, J., Liu, X., Wang, M., Wang, X., Jiang, P.: Tomatidine inhibits porcine epidemic diarrhea virus replication by targeting 3CL protease. Vet. Res. 51, 1–8 (2020)
Pritchard, L.K., Spencer, D.I., Royle, L., Bonomelli, C., Seabright, G.E., Behrens, A.J., Kulp, D.W., Menis, S., Krumm, S.A., Dunlop, D.C., Crispin, D.J.: Glycan clustering stabilizes the mannose patch of HIV-1 and preserves vulnerability to broadly neutralizing antibodies. Nat. Commun. 6(1), 1–1 (2015)
Ward, A.B., Wilson, I.A.: Insights into the trimeric HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein structure. Trends Biochem. Sci. 40(2), 101–107 (2015)
Wang, W., Nie, J., Prochnow, C., Truong, C., Jia, Z., Wang, S., Chen, X.S., Wang, Y.: A systematic study of the N-glycosylation sites of HIV-1 envelope protein on infectivity and antibody-mediated neutralization. Retrovirol. 10(1), 1–4 (2013)
Tilton, J.C., Doms, R.W.: Entry inhibitors in the treatment of HIV-1 infection. Antiviral Res. 85(1), 91–100 (2010)
Akkouh, O., Ng, T.B., Singh, S.S., Yin, C., Dan, X., Chan, Y.S., Pan, W., Cheung, R.C.: Lectins with anti-HIV activity: a review. Molecul. 20(1), 648–668 (2015)
Checkley, M.A., Luttge, B.G., Freed, E.O.: HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein biosynthesis, trafficking, and incorporation. J. Mol. Biol. 410(4), 582–608 (2011)
Murugaiah, V., Yasmin, H., Pandit, H., Ganguly, K., Subedi, R., Al-Mozaini, M., Madan, T., Kishore, U.: Innate Immune Response Against HIV-1. Microb. Pathog. 23–58 (2021)
Xiao, T., Cai, Y., Chen, B.: HIV-1 entry and membrane fusion inhibitors. Viruses 13(5), 735 (2021)
Blumenthal, R., Durell, S., Viard, M.: HIV entry and envelope glycoprotein-mediated fusion. J. Biol. Chem. 287(49), 40841–40849 (2012)
Wilen, C.B., Tilton, J.C., Doms, R.W.: HIV: cell binding and entry. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2(8), a006866 (2012)
Mizuochi, T., Matthews, T.J., Kato, M., Hamako, J., Titani, K., Solomon, J., Feizi, T.: Diversity of oligosaccharide structures on the envelope glycoprotein gp 120 of human immunodeficiency virus 1 from the lymphoblastoid cell line H9. Presence of complex-type oligosaccharides with bisecting N-acetylglucosamine residues. J. Biol. Chem. 265(15), 8519–8524 (1990)
Geyer, H., Holschbach, C., Hunsmann, G., Schneider, J.: Carbohydrates of human immunodeficiency virus. Structures of oligosaccharides linked to the envelope glycoprotein 120. J. Biol. Chem. 263(24), 11760–11767 (1998)
Go, E.P., Hewawasam, G., Liao, H.X., Chen, H., Ping, L.H., Anderson, J.A., Hua, D.C., Haynes, B.F., Desaire, H.: Characterization of glycosylation profiles of HIV-1 transmitted/founder envelopes by mass spectrometry. J. Virol. 85(16), 8270–8284 (2011)
Go, E.P., Herschhorn, A., Gu, C., Castillo-Menendez, L., Zhang, S., Mao, Y., Chen, H., Ding, H., Wakefield, J.K., Hua, D., Liao, H.X.: Comparative analysis of the glycosylation profiles of membrane-anchored HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein trimers and soluble gp140. J. Virol. 89(16), 8245–8257 (2015)
Raska, M., Takahashi, K., Czernekova, L., Zachova, K., Hall, S., Moldoveanu, Z., Elliott, M.C., Wilson, L., Brown, R., Jancova, D., Barnes, S.: Glycosylation patterns of HIV-1 gp120 depend on the type of expressing cells and affect antibody recognition. J. Biol. Chem. 285(27), 20860–20869 (2010)
Zhu, X., Borchers, C., Bienstock, R.J., Tomer, K.B.: Mass spectrometric characterization of the glycosylation pattern of HIV-gp120 expressed in CHO cells. Biochem. 39(37), 11194–11204 (2000)
Behrens, A.J., Harvey, D.J., Milne, E., Cupo, A., Kumar, A., Zitzmann, N., Struwe, W.B., Moore, J.P., Crispin, M.: Molecular architecture of the cleavage-dependent mannose patch on a soluble HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein trimer. J. Virol. 91(2), e01894-e1916 (2017)
Sok, D., Doores, K.J., Briney, B., Le, K.M., Saye-Francisco, K.L., Ramos, A., Kulp, D.W., Julien, J.P., Menis, S., Wickramasinghe, L., Seaman, M.S.: Promiscuous glycan site recognition by antibodies to the high-mannose patch of gp120 broadens neutralization of HIV. Sci. Transl. Med. 6(236), 236ra63 (2014)
Coss, K.P., Vasiljevic, S., Pritchard, L.K., Krumm, S.A., Glaze, M., Madzorera, S., Moore, P.L., Crispin, M., Doores, K.J.: HIV-1 glycan density drives the persistence of the mannose patch within an infected individual. J. Virol. 90(24), 11132–11144 (2016)
Wang, L.X., Song, H., Liu, S., Lu, H., Jiang, S., Ni, J., Li, H.: Chemoenzymatic synthesis of HIV-1 gp41 glycopeptides: effects of glycosylation on the anti-HIV activity and α-helix bundle-forming ability of peptide C34. ChemBioChem 6(6), 1068–1074 (2005)
Ji, X., Chen, Y., Faro, J., Gewurz, H., Bremer, J., T Spear G.: Interaction of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) glycans with lectins of the human immune system. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 7(4), 317–324 (2006)
Svarovsky, S.A., Joshi, L.: Biocombinatorial selection of carbohydrate binding agents of therapeutic significance. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 5(1), 20–28 (2008)
Jahan, R., Ahmed, M.N., Nissapatorn, V., Wilairatana, P., Rahmatullah, M.: Plant lectins as prospective antiviral biomolecules in the search for COVID-19 eradication strategies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 146, 112507 (2022)
Peng, H., Lv, H., Wang, Y., Liu, Y.H., Li, C.Y., Meng, L., Chen, F., Bao, J.K.: Clematis montana lectin, a novel mannose-binding lectin from traditional Chinese medicine with antiviral and apoptosis-inducing activities. Peptides 30(10), 1805–1815 (2009)
Van Damme, E.J., Rougé, P.: Lectins from plants, algae, fungi, bacteria and animal therapeutic tools for SARS-CoV-2 and other pathogenic enveloped viruses, in a “one-health” perspective. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 13, 49 (2023)
Jaakkonen, A., Volkmann, G., Iwaï, H.: An off-the-shelf approach for the production of fc fusion proteins by protein trans-splicing towards generating a lectibody In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21(11), 4011 (2020)
Boyd, M.R., Gustafson, K.R., McMahon, J.B., Shoemaker, R.H., O’Keefe, B.R., Mori, T., Gulakowski, R.J., Wu, L., Rivera, M.I., Laurencot, C.M., Currens, M.J.: Discovery of cyanovirin-N, a novel human immunodeficiency virus-inactivating protein that binds viral surface envelope glycoprotein gp120: potential applications to microbicide development. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1521, 30 (1997)
Bolmstedt, A.J., O’Keefe, B.R., Shenoy, S.R., McMahon, J.B., Boyd, M.R.: Cyanovirin-N defines a new class of antiviral agent targeting N-linked, high-mannose glycans in an oligosaccharide-specific manner. Mol. Pharmacol. 59(5), 949–954 (2001)
Barrientos, L.G., Gronenborn, A.M.: The highly specific carbohydrate-binding protein cyanovirin-N: structure, anti-HIV/Ebola activity and possibilities for therapy. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 5(1), 21–31 (2005)
Bewley, C.A., Otero-Quintero, S.: The potent anti-HIV protein cyanovirin-N contains two novel carbohydrate binding sites that selectively bind to Man8 D1D3 and Man9 with nanomolar affinity: implications for binding to the HIV envelope protein gp120. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123(17), 3892–3902 (2001)
Liu, Y., Carroll, J.R., Holt, L.A., McMahon, J., Giomarelli, B., Ghirlanda, G.: Multivalent interactions with gp120 are required for the anti-HIV activity of Cyanovirin. Peptide Sci. 92(3), 194–200 (2009)
Nickoloff-Bybel, E.A., Festa, L., Meucci, O., Gaskill, P.J.: Co-receptor signaling in the pathogenesis of neuroHIV. Retrovirology 18(1), 24 (2021)
Keeffe, J.R., Gnanapragasam, P.N., Gillespie, S.K., Yong, J., Bjorkman, P.J., Mayo, S.L.: Designed oligomers of cyanovirin-N show enhanced HIV neutralization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 108(34), 14079–14084 (2011)
Balzarini, J., Van Laethem, K., Peumans, W.J., Van Damme, E.J., Bolmstedt, A., Gago, F., Schols, D.: Mutational pathways, resistance profile, and side effects of cyanovirin relative to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 strains with N-glycan deletions in their gp120 envelopes. J. Virol. 80(17), 8411–8421 (2006)
Tsai, C.C., Emau, P., Jiang, Y., Tian, B., Morton, W.R., Gustafson, K.R., Boyd, M.R.: Cyanovirin-N gel as a topical microbicide prevents rectal transmission of SHIV89. 6P in macaques. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses. 19(7), 535–541 (2003)
Dey, B., Lerner, D.L., Lusso, P., Boyd, M.R., Elder, J.H., Berger, E.A.: Multiple antiviral activities of cyanovirin-N: blocking of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 interaction with CD4 and coreceptor and inhibition of diverse enveloped viruses. J. Virol. 74(10), 4562–4569 (2000)
Barrientos, L.G., O’Keefe, B.R., Bray, M., Sanchez, A., Gronenborn, A.M., Boyd, M.R.: Cyanovirin-N binds to the viral surface glycoprotein, GP1, 2 and inhibits infectivity of Ebola virus. Antiviral Res. 58(1), 47–56 (2003)
Helle, F., Wychowski, C., Vu-Dac, N., Gustafson, K.R., Voisset, C., Dubuisson, J.: Cyanovirin-N inhibits hepatitis C virus entry by binding to envelope protein glycans. J. Biol. Chem. 281(35), 25177–25183 (2006)
O’Keefe, B.R., Smee, D.F., Turpin, J.A., Saucedo, C.J., Gustafson, K.R., Mori, T., Blakeslee, D., Buckheit, R., Boyd, M.R.: Potent anti-influenza activity of cyanovirin-N and interactions with viral hemagglutinin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47(8), 2518–2525 (2003)
Wang, W., Cole, A.M., Hong, T., Waring, A.J., Lehrer, R.I.: Retrocyclin, an antiretroviral θ-defensin, is a lectin. J. Immunol. Res. 170(9), 4708–4716 (2003)
Bewley, C.A., Gustafson, K.R., Boyd, M.R., Covell, D.G., Bax, A., Clore, G.M., Gronenborn, A.M.: Solution structure of cyanovirin-N, a potent HIV-inactivating protein. Nat. Struct. Biol. 5(7), 571–578 (1998)
Zweckstetter, M., Bax, A.: Prediction of sterically induced alignment in a dilute liquid crystalline phase: aid to protein structure determination by NMR. J.Am. Chem. Soc. 122(15), 3791–3792 (2000)
Vamvaka, E., Evans, A., Ramessar, K., Krumpe, L.R., Shattock, R.J., O’Keefe, B.R., Christou, P., Capell, T.: Cyanovirin-N produced in rice endosperm offers effective pre-exposure prophylaxis against HIV-1BaL infection in vitro. Plant Cell Rep. 35(6), 1309–1319 (2016)
Fischetti, L., Barry, S.M., Hope, T.J., Shattock, R.J.: HIV-1 infection of human penile explant tissue and protection by candidate microbicides. AIDS (London, England). 23(3), 319 (2009)
Kehr, J.C., Zilliges, Y., Springer, A., Disney, M.D., Ratner, D.D., Bouchier, C., Seeberger, P.H., De Marsac, N.T., Dittmann, E.: A mannan binding lectin is involved in cell–cell attachment in a toxic strain of Microcystis aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 59(3), 893–906 (2006)
Shahzad-ul-Hussan, S., Gustchina, E., Ghirlando, R., Clore, G.M., Bewley, C.A.: Solution structure of the monovalent lectin microvirin in complex with Manα (1–2) Man provides a basis for anti-HIV activity with low toxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 286(23), 20788–20796 (2000)
Williams, D.C., Lee, J.Y., Cai, M., Bewley, C.A., Clore, G.M.: Crystal structures of the HIV-1 inhibitory cyanobacterial protein MVL free and bound to Man3GlcNAc2: structural basis for specificity and high-affinity binding to the core pentasaccharide from n-linked oligomannoside. J. Biol. Chem. 280(32), 29269–29276 (2005)
Bewley, C.A., Cai, M., Ray, S., Ghirlando, R., Yamaguchi, M., Muramoto, K.: New carbohydrate specificity and HIV-1 fusion blocking activity of the cyanobacterial protein MVL: NMR, ITC and sedimentation equilibrium studies. J. Mol. Biol. 339(4), 901–914 (2004)
Huskens, D., Férir, G., Vermeire, K., Kehr, J.C., Balzarini, J., Dittmann, E., Schols, D.: Microvirin, a novel alpha(1,2)-mannose-specific lectin isolated from Microcystis aeruginosa, has anti-HIV-1 activity comparable with that of cyanovirin-N but a much higher safety profile. J. Biol. Chem. 285(32), 24845–24854 (2010)
Siqueira, A.S., Lima, A.R., de Souza, R.C., Santos, A.S., Vianez Júnior, J.L., Gonçalves, E.C.: In silico analysis of the cyanobacterial lectin scytovirin: new insights into binding properties. Mol. Biol. Rep. 44(4), 353–358 (2017)
Xiong, C., O’Keefe, B.R., Botos, I., Wlodawer, A., McMahon, J.B.: Overexpression and purification of scytovirin, a potent, novel anti-HIV protein from the cultured cyanobacterium Scytonema varium. Protein Expr. Purif. 46(2), 233–239 (2006)
Covés-Datson, E.M., King, S.R., Legendre, M., Swanson, M.D., Gupta, A., Claes, S., Meagher, J.L., Boonen, A., Zhang, L., Kalveram, B., Raglow, Z.: Targeted disruption of pi–pi stacking in Malaysian banana lectin reduces mitogenicity while preserving antiviral activity. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 656 (2021)
Hopper, J.T., Ambrose, S., Grant, O.C., Krumm, S.A., Allison, T.M., Degiacomi, M.T., Tully, M.D., Pritchard, L.K., Ozorowski, G., Ward, A.B., Crispin, M.: The tetrameric plant lectin BanLec neutralizes HIV through bidentate binding to specific viral glycans. Structure. 25(5), 773–782 (2017)
Singh, S.S., Devi, S.K., Ng, T.B.: Banana lectin: a brief review. Molecules 19(11), 18817–18827 (2014)
Mordi, R.C., Fadiaro, A.E., Owoeye, T.F., Olanrewaju, I.O., Uzoamaka, G.C., Olorunshola, S.J.: Identification by GC-MS of the components of oils of banana peels extract, phytochemical and antimicrobial analyses. Res. J. Phytochem. 10(1), 39–44 (2016)
Meagher, J.L., Winter, H.C., Ezell, P., Goldstein, I.J., Stuckey, J.A.: Crystal structure of banana lectin reveals a novel second sugar binding site. Glycobiology 15(10), 1033–1042 (2005)
Swanson, M.D., Boudreaux, D.M., Salmon, L., Chugh, J., Winter, H.C., Meagher, J.L., Andre, S., Murphy, P.V., Oscarson, S., Roy, R., King, S.: Engineering a therapeutic lectin by uncoupling mitogenicity from antiviral activity. Cell 163(3), 746–758 (2015)
Lopandić, Z., Dragačević, L., Popović, D., Andjelković, U., Minić, R., Gavrović-Jankulović, M.: BanLec-eGFP chimera as a tool for evaluation of lectin binding to high-mannose glycans on microorganisms. Biomolecules 11(2), 180 (2021)
Subramaniam, G., Batcha, A.T., Wadhwani, A.: In vitro antiviral activity of BanLec against herpes simplex viruses type 1 and 2. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 15(1), 11–18 (2020)
Chan, J.F., Oh, Y.J., Yuan, S., Chu, H., Yeung, M.L., Canena, D., Chan, C.C., Poon, V.K., Chan, C.C., Zhang, A.J., Cai, J.P.: A molecularly engineered, broad-spectrum anti-coronavirus lectin inhibits SARS-CoV-2 and MERS-CoV infection in vivo. Cell Rep. 3(10), 100774 (2022)
Ziółkowska, N.E., Shenoy, S.R., O'Keefe, B.R., McMahon, J.B., Palmer, K.E., Dwek, R.A., Wormald, M.R., Wlodawer, A.: Crystallographic, thermodynamic, and molecular modeling studies of the mode of binding of oligosaccharides to the potent antiviral protein griffithsin. Proteins: Struct. Funct. 67(3), 661–670 (2007)
Derby, N., Lal, M., Aravantinou, M., Kizima, L., Barnable, P., Rodriguez, A., Lai, M., Wesenberg, A., Ugaonkar, S., Levendosky, K., Mizenina, O.: Griffithsin carrageenan fast dissolving inserts prevent SHIV HSV-2 and HPV infections in vivo. Nat. Commun. 9(1), 3881(2018)
Lusvarghi, S., Bewley, C.A.: Griffithsin: an antiviral lectin with outstanding therapeutic potential. Viruses 8(10), 296 (2016)
Alam, A., Jiang, L., Kittleson, G.A., Steadman, K.D., Nandi, S., Fuqua, J.L., Palmer, K.E., Tusé, D., McDonald, K.A.: Technoeconomic modeling of plant-based griffithsin manufacturing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 6, 102 (2018)
Millet, J.K., Séron, K., Labitt, R.N., Danneels, A., Palmer, K.E., Whittaker, G.R., Dubuisson, J., Belouzard, S.: Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection is inhibited by griffithsin. Antiviral Res. 133, 1–8 (2016)
Hoelscher, M., Tiller, N., Teh, A.Y., Wu, G.Z., Ma, J.K., Bock, R.: High-level expression of the HIV entry inhibitor griffithsin from the plastid genome and retention of biological activity in dried tobacco leaves. Plant Mol. Biol. 97, 357–370 (2018)
Li, L., Yu, X., Zhang, H., Cheng, H., Hou, L., Zheng, Q., Hou, J.: In vitro antiviral activity of Griffithsin against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Virus Genes 55, 174–181 (2019)
Mori, T., O’Keefe, B.R., Sowder, R.C., Bringans, S., Gardella, R., Berg, S., Cochran, P., Turpin, J.A., Buckheit, R.W., McMahon, J.B., Boyd, M.R.: Isolation and characterization of griffithsin, a novel HIV-inactivating protein, from the red alga Griffithsia sp. J. Biol. Chem. 280(10), 9345–9353 (2005)
O’Keefe, B.R., Vojdani, F., Buffa, V., Shattock, R.J., Montefiori, D.C., Bakke, J., Mirsalis, J., d’Andrea, A.L., Hume, S.D., Bratcher, B., Saucedo, C.J.: Scaleable manufacture of HIV-1 entry inhibitor griffithsin and validation of its safety and efficacy as a topical microbicide component. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106(15), 6099–6104 (2009)
Barton, C., Kouokam, J.C., Lasnik, A.B., Foreman, O., Cambon, A., Brock, G., Montefiori, D.C., Vojdani, F., McCormick, A.A., O’Keefe, B.R., Palmer, K.E.: Activity of and effect of subcutaneous treatment with the broad-spectrum antiviral lectin griffithsin in two laboratory rodent models. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58(1), 120–127 (2014)
Hoorelbeke, B., Huskens, D., Férir, G., François, K.O., Takahashi, A., Van Laethem, K., Schols, D., Tanaka, H., Balzarini, J.: Actinohivin, a broadly neutralizing prokaryotic lectin, inhibits HIV-1 infection by specifically targeting high-mannose-type glycans on the gp120 envelope. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54(8), 3287–3301 (2010)
Koharudin, L.M., Furey, W., Gronenborn, A.M.: Novel fold and carbohydrate specificity of the potent anti-HIV cyanobacterial lectin from Oscillatoria agardhii. J. Biol. Chem. 286(2), 1588–1597 (2011)
Whitley, M.J., Furey, W., Kollipara, S., Gronenborn, A.M.: B urkholderia oklahomensis agglutinin is a canonical two-domain OAA-family lectin: structures, carbohydrate binding and anti-HIV activity. FEBS J. 280(9), 2056–2067 (2013)
Férir, G., Huskens, D., Noppen, S., Koharudin, L.M., Gronenborn, A.M., Schols, D.: Broad anti-HIV activity of the Oscillatoria agardhii agglutinin homologue lectin family. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 69(10), 2746–2758 (2014)
McFeeters, H., Gilbert, M.J., Wood, A.M., Haggenmaker, C.B., Jones, J., Kutsch, O., McFeeters, R.L.: Scytovirin engineering improves carbohydrate affinity and HIV-1 entry inhibition. Biochem. Physiol. S. 2(2) (2013)
López, S., Armand-Ugon, M., Bastida, J., Viladomat, F., Esté, J.A., Stewart, D., Codina, C.: Anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) activity of lectins from Narcissus species. Planta Med. 69(2), 109–112 (2003)
Swanson, M.D., Winter, H.C., Goldstein, I.J., Markovitz, D.M.: A lectin isolated from bananas is a potent inhibitor of HIV replication. J. Biol. Chem. 285(12), 8646–8655 (2010)
Balzarini, J., Neyts, J., Schols, D., Hosoya, M., Van Damme, E., Peumans, W., De Clercq, E.: The mannose-specific plant lectins from Cymbidium hybrid and Epipactis helleborine and the (N-acetylglucosamine)n-specific plant lectin from Urtica dioica are potent and selective inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus and cytomegalovirus replication in vitro. Antiviral Res. 18(2), 191–207 (1992)
Teixeira, C.S., Assreuy, A.M., da Silva Osterne, V.J., Amorim, R.M., Brizeno, L.A., Debray, H., Nagano, C.S., Delatorre, P., Sampaio, A.H., Rocha, B.A., Cavada, B.S.: Mannose-specific legume lectin from the seeds of Dolichos lablab (FRIL) stimulates inflammatory and hypernociceptive processes in mice. Process Biochem. 49(3), 529–534 (2014)
Jayaprakash, N.G., Singh, A., Vivek, R., Yadav, S., Pathak, S., Trivedi, J., Jayaraman, N., Nandi, D., Mitra, D., Surolia, A.: Correction: The barley lectin, horcolin, binds high-mannose glycans in a multivalent fashion, enabling high-affinity, specific inhibition of cellular HIV infection. J. Biol. Chem. 297(3) (2021)
Gondim, A.C., da Silva, S.R., Mathys, L., Noppen, S., Liekens, S., Sampaio, A.H., Nagano, C.S., Rocha, C.R., Nascimento, K.S., Cavada, B.S., Sadler, P.J.: Potent antiviral activity of carbohydrate-specific algal and leguminous lectins from the Brazilian biodiversity. Med. Chem. Comm. 10(3), 390–398 (2019)
Ghany, M.G., Strader, D.B., Thomas, D.L., Seeff, L.B.: American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C: an update. Hepatology. 49(4), 1335–1374(2009)
Moustafa, R.I., Dubuisson, J., Lavie, M.: Function of the HCV E1 envelope glycoprotein in viral entry and assembly. Future Virol. 171–184 (2019)
Lavie, M., Hanoulle, X., Dubuisson, J.: Glycan shielding and modulation of hepatitis C virus neutralizing antibodies. Front. Immunol. 9, 910 (2018)
Helle, F., Duverlie, G., Dubuisson, J.: The hepatitis C virus glycan shield and evasion of the humoral immune response. Viruses 3(10), 1909–1932 (2011)
Shahid, M., Qadir, A., Yang, J., Ahmad, I., Zahid, H., Mirza, S., Windisch, M.P., Shahzad-ul-Hussan, S.: An engineered microvirin variant with identical structural domains potently inhibits human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus cellular entry. Viruses 12(2), 199 (2020)
Meuleman, P., Albecka, A., Belouzard, S., Vercauteren, K., Verhoye, L., Wychowski, C., Leroux-Roels, G., Palmer, K.E., Dubuisson, J.: Griffithsin has antiviral activity against hepatitis C virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 55(11), 5159–5167 (2011)
Loimaranta, V., Hepojoki, J., Laaksoaho, O., Pulliainen, A.T.: Galectin-3-binding protein: A multitask glycoprotein with innate immunity functions in viral and bacterial infections. J. Leukoc. Biol. 104(4), 777–786 (2018)
Ouchida, T., Maeda, H., Akamatsu, Y., Maeda, M., Takamatsu, S., Kondo, J., Misaki, R., Kamada, Y., Ueda, M., Ueda, K., Miyoshi, E.: Pholiota squarrosa lectin (PhoSL), a lectin binding to core-fucose specifically, inhibits HBV infection. Res Sq. (2022)
Bertaux, C., Daelemans, D., Meertens, L., Cormier, E.G., Reinus, J.F., Peumans, W.J., Van Damme, E.J., Igarashi, Y., Oki, T., Schols, D., Dragic, T.: Entry of hepatitis C virus and human immunodeficiency virus is selectively inhibited by carbohydrate-binding agents but not by polyanions. Virology 366(1), 40–50 (2007)
Jensen, S.M., Ruscetti, F.W., Rein, A., Bertolette, D.C., Saucedo, C.J., O’Keefe, B.R., Jones, K.S.: Differential inhibitory effects of cyanovirin-N, griffithsin, and scytovirin on entry mediated by envelopes of gammaretroviruses and deltaretroviruses. J. Virol. 88(4), 2327–2332 (2014)
Ko, S.M., Kwon, J., Vaidya, B., Choi, J.S., Lee, H.M., Oh, M.J., Bae, H.J., Cho, S.Y., Oh, K.S., Kim, D.: Development of lectin-linked immunomagnetic separation for the detection of hepatitis A virus. Viruses 6(3), 1037–1048 (2014)
Taghizadeh, S.F., Azizi, M., Asili, J., Madarshahi, F.S., Rakhshandeh, H., Fujii, Y.: Therapeutic peptides of Mucuna pruriens L.: Anti‐genotoxic molecules against human hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis C virus. Food Sci. Nutr. 9(6), 2908–14 (2021)
Al-Sohaimy, S.A., Hafez, E.E., Abdelwahab, A.E., El-Saadani, M.A.: Anti-HCV lectin from Egyptian Pisum sativum. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 1(3), 213–219 (2007)
Palese, P.: Orthomyxoviridae: the viruses and their replication. Fields virology. 1647–89 (2007)
Ran, Z., Shen, H., Lang, Y., Kolb, E.A., Turan, N., Zhu, L., Ma, J., Bawa, B., Liu, Q., Liu, H., Quast, M.: Domestic pigs are susceptible to infection with influenza B viruses. J. Virol. 89(9), 4818–4826 (2015)
Nickol, M.E., Kindrachuk, J.: A year of terror and a century of reflection: perspectives on the great influenza pandemic of 1918–1919. BMC Infect. Dis. 19(1), 1 (2019)
Morimoto, K., Sato, Y.: Anti-influenza virus activity of high-mannose binding lectins derived from genus Pseudomonas. Virus Res. 223, 64–72 (2016)
Wu, N.C., Young, A.P., Al-Mawsawi, L.Q., Olson, C.A., Feng, J., Qi, H., Chen, S.H., Lu, I., Lin, C.Y., Chin, R.G., Luan, H.H.: High-throughput profiling of influenza A virus hemagglutinin gene at single-nucleotide resolution. Sci. Rep. 4(1), 1–8 (2014)
Wu, C.Y., Lin, C.W., Tsai, T.I., Lee, C.C., Chuang, H.Y., Chen, J.B., Tsai, M.H., Chen, B.R., Lo, P.W., Liu, C.P., Shivatare, V.S.: Influenza A surface glycosylation and vaccine design. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 114(2), 280–5 (2017)
Covés-Datson, E.M., King, S.R., Legendre, M., Gupta, A., Chan, S.M., Gitlin, E., Kulkarni, V.V., Pantaleón García, J., Smee, D.F., Lipka, E., Evans, S.E., Tarbet, E.B., Ono, A., Markovitz, D.M.: A molecularly engineered antiviral banana lectin inhibits fusion and is efficacious against influenza virus infection in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 117(4), 2122–2132 (2020)
Gordts, S.C., Renders, M., Férir, G., Huskens, D., Van Damme, E.J., Peumans, W., Balzarini, J., Schols, D.: NICTABA and UDA, two GlcNAc-binding lectins with unique antiviral activity profiles. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 70(6), 1674–1685 (2015)
Ooi, L.S., Ng, T.B., Geng, Y., Ooi, V.E.: Lectins from bulbs of the Chinese daffodil Narcissus tazetta (family Amaryllidaceae). Biochem. Cell Biol. 78(4), 463–468 (2000)
Ooi, L.S., Sun, S.S., Ng, T.B., Ooi, V.E.: Molecular cloning and the cDNA-derived amino acid sequence of Narcissus tazetta isolectins. J. Protein Chem. 20(4), 305–310 (2001)
Sato, Y., Morimoto, K., Kubo, T., Sakaguchi, T., Nishizono, A., Hirayama, M., Hori, K.: Entry inhibition of influenza viruses with high mannose binding lectin ESA-2 from the red alga Eucheuma serra through the recognition of viral hemagglutinin. Mar. Drugs 13(6), 3454–3465 (2015)
Sato, Y., Morimoto, K., Hirayama, M., Hori, K.: High mannose-specific lectin (KAA-2) from the red alga Kappaphycus alvarezii potently inhibits influenza virus infection in a strain-independent manner. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 405(2), 291–296 (2011)
Vanderlinden, E., Van Winkel, N., Naesens, L., Van Damme, E.J., Persoons, L., Schols, D.: In vitro characterization of the carbohydrate-binding agents HHA, GNA, and UDA as inhibitors of influenza A and B virus replication. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 65(3), e01732-e1820 (2021)
Ooi, L.S., Sun, S.S., Ooi, V.E.: Purification and characterization of a new antiviral protein from the leaves of Pandanus amaryllifolius (Pandanaceae). Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 36(8), 1440–1446 (2004)
Liu, Y.M., Shahed-Al-Mahmud, M., Chen, X., Chen, T.H., Liao, K.S., Lo, J.M., Wu, Y.M., Ho, M.C., Wu, C.Y., Wong, C.H., Jan, J.T.: A carbohydrate-binding protein from the edible lablab beans effectively blocks the infections of influenza viruses and SARS-CoV-2. Cell Rep. 32(6), 108016 (2020)
Kleinschmidt‐DeMasters, B.K., Keohane, C., Gray, F.: Herpes simplex virus infections of the CNS. Infections of the Central Nervous System: Pathology and Genetics. 43–54 (2020)
Lim, T.K.: Edible medicinal and non-medicinal plants. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer. 1, 656–687 (2012)
Luo, Y., Xu, X., Liu, J., Li, J., Sun, Y., Liu, Z., Liu, J., Van Damme, E., Balzarini, J., Bao, J.: A novel mannose-binding tuber lectin from Typhonium divaricatum (L.) Decne (family Araceae) with antiviral activity against HSV-II and anti-proliferative effect on human cancer cell lines. J Biochem Mol Biol. 40(3), 358–67 (2007)
Tiwari, V., Shukla, S.Y., Shukla, D.: A sugar binding protein cyanovirin-N blocks herpes simplex virus type-1 entry and cell fusion. Antiviral Res. 84(1), 67–75 (2009)
Nixon, B., Stefanidou, M., Mesquita, P.M., Fakioglu, E., Segarra, T., Rohan, L., Halford, W., Palmer, K.E., Herold, B.C.: Griffithsin protects mice from genital herpes by preventing cell-to-cell spread. Virol. J. 87(11), 6257–6269 (2013)
Yang, Y., Xu, H.L., Zhang, Z.T., Liu, J.J., Li, W.W., Ming, H., Bao, J.K.: Characterization, molecular cloning, and in silico analysis of a novel mannose-binding lectin from Polygonatum odoratum (Mill.) with anti-HSV-II and apoptosis-inducing activities. Phytomedicine. 18(8–9), 748–55 (2011)
Marchetti, M., Mastromarino, P., Rieti, S., Seganti, L., Orsi, N.: Inhibition of herpes simplex, rabies and rubella viruses by lectins with different specificities. Res. Virol. 146(3), 211–215 (1995)
Gatherer, D.: The 2014 Ebola virus disease outbreak in West Africa. J. Gen. Virol. 95(8), 1619–1624 (2014)
Briand, S., Bertherat, E., Cox, P., Formenty, P., Kieny, M.P.: The international Ebola emergency. N. Engl. J. 371(13), 1180–1183 (2014)
Negredo, A., Palacios, G., Vázquez-Morón, S., González, F., Dopazo, H., Molero, F., Juste, J., Quetglas, J., Savji, N., de la Cruz, M.M., Herrera, J.E.: Discovery of an ebolavirus-like filovirus in europe. PLoS Pathog. 7(10), e1002304 (2001)
Vogel, G.: Infectious disease. Are bats spreading Ebola across sub-Saharan Africa? Science. 344(6180), 140 (2014)
Paessler, S., Walker, D.H.: Pathogenesis of the viral hemorrhagic fevers. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 8(1), 411 (2013)
Maier, I., Schiestl, R.H., Kontaxis, G.: Cyanovirin-N binds viral envelope proteins at the low-affinity carbohydrate binding site without direct virus neutralization ability. Molecules. 26(12), 3621(2021)
Brudner, M., Karpel, M., Lear, C., Chen, L., Yantosca, L.M., Scully, C., Sarraju, A., Sokolovska, A., Zariffard, M.R., Eisen, D.P., Mungall, B.A.: Lectin-dependent enhancement of Ebola virus infection via soluble and transmembrane C-type lectin receptors. PLoS ONE 8(4), e60838 (2013)
Guo, Y.R., Cao, Q.D., Hong, Z.S., Tan, Y.Y., Chen, S.D., Jin, H.J., Tan, K.S., Wang, D.Y., Yan, Y.: The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak–an update on the status. Mil. Med. Res. 1, 1 (2020)
Baud, D., Qi, X., Nielsen-saines, K., Musso, D., Pomar, L., Favre, G.: Real estimates of mortality following COVID-19 infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. (2020)
El Zowalaty, M.E., Järhult, J.D.: From SARS to COVID-19: A previously unknown SARS-related coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) of pandemic potential infecting humans–Call for a One Health approach. One Health. 9, 100124 (2020)
Shereen, M.A., Khan, S., Kazmi, A., Bashir, N., Siddique, R.: COVID-19 infection: Emergence, transmission, and characteristics of human coronaviruses. J. Adv. Res. 24, 91–98 (2020)
Banerjee, A., Kulcsar, K., Misra, V., Frieman, M., Mossman, K.: Bats and coronaviruses. Viruses. 11(1), 41 (2019)
Lu, R., Zhao, X., Li, J., Niu, P., Yang, B., Wu, H., Wang, W., Song, H., Huang, B., Zhu, N., Bi, Y.: Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding. The lancet. 395(10224), 565–574 (2020)
Kumaki, Y., Wandersee, M.K., Smith, A.J., Zhou, Y., Simmons, G., Nelson, N.M., Bailey, K.W., Vest, Z.G., Li, J.K., Chan, P.K., Smee, D.F.: Inhibition of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus replication in a lethal SARS-CoV BALB/c mouse model by stinging nettle lectin. Urtica dioica agglutinin. Antiviral Res. 90(1), 22–32 (2011)
Koch, B., Schult-Dietrich, P., Büttner, S., Dilmaghani, B., Lohmann, D., Baer, P.C., Dietrich, U., Geiger, H.: Lectin affinity plasmapheresis for middle east respiratory syndrome-coronavirus and Marburg virus glycoprotein elimination. Blood Purif. 46(2), 126–133 (2018)
Tripathi, N., Goel, B., Bhardwaj, N., Vishwakarma, R.A., Jain, S.K.: Exploring the potential of chemical inhibitors for targeting post-translational glycosylation of coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). ACS Omega 7(31), 27038–27051 (2022)
Sharifkashani, S., Bafrani, M.A., Khaboushan, A.S., Pirzadeh, M., Kheirandish, A., Yavarpour Bali, H., Hessami, A., Saghazadeh, A., Rezaei, N.: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor and SARS-CoV-2: potential therapeutic targeting. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 884, 173455 (2020)
Wu, F., Zhao, S., Yu, B., Chen, Y.M., Wang, W., Song, Z.G., Hu, Y., Tao, Z.W., Tian, J.H., Pei, Y.Y., Yuan, M.L.: A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 579(7798), 265–269 (2020)
Ritchie, G., Harvey, D.J., Feldmann, F., Stroeher, U., Feldmann, H., Royle, L., Dwek, R.A., Rudd, P.M.: Identification of N-linked carbohydrates from severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) spike glycoprotein. Virology 399(2), 257–269 (2010)
Barre, A., Damme, E.J., Simplicien, M., Benoist, H., Rougé, P.: Man-specific, GalNAc/T/Tn-specific and Neu5Ac-specific seaweed lectins as glycan probes for the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) coronavirus. Marine drugs. 18(11), 543(2020)
Fouad, A.K.: Lectin therapy: A way to explore in order to inhibit the binding of COVID-19 to these host cells. Int J Innov Sci Res Technol. 5, 1280–1286 (2020)
Harvey, W.T., Carabelli, A.M., Jackson, B., Gupta, R.K., Thomson, E.C., Harrison, E.M., Ludden, C., Reeve, R., Rambaut, A., Peacock, S.J., Robertson, D.L.: SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 19(7), 409–424 (2021)
Abdool Karim, S.S., de Oliveira, T.: New SARS-CoV-2 variants—clinical, public health, and vaccine implications. N. Engl. J. Med. 384(19), 1866–1868 (2021)
Chi, X., Yan, R., Zhang, J., Zhang, G., Zhang, Y., Hao, M., Zhang, Z., Fan, P., Dong, Y., Yang, Y., Chen, Z.: A neutralizing human antibody binds to the N-terminal domain of the Spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. Science 369(6504), 650–655 (2020)
Watanabe, Y., Berndsen, Z.T., Raghwani, J., Seabright, G.E., Allen, J.D., Pybus, O.G., McLellan, J.S., Wilson, I.A., Bowden, T.A., Ward, A.B., Crispin, M.: Vulnerabilities in coronavirus glycan shields despite extensive glycosylation. Nat. Commun. 11(1), 2688 (2020)
Shajahan, A., Supekar, N.T., Gleinich, A.S., Azadi, P.: Deducing the N-and O-glycosylation profile of the spike protein of novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Glycobiology 30(12), 981–988 (2020)
Ahan, R.E., Hanifehnezhad, A., Kehribar, E.S., Oguzoglu, T.C., Foldes, K., Özçelik, C.E., Filazi, N., Öztop, S., Palaz, F., Önder, S., Bozkurt, E.U.: A Highly Potent SARS-CoV-2 Blocking Lectin Protein. ACS Infect. Dis. 8(7), 1253–1264 (2021)
Wang, W., Li, Q., Wu, J., Hu, Y., Wu, G., Yu, C., Xu, K., Liu, X., Wang, Q., Huang, W., Wang, L., Wang, Y.: Lentil lectin derived from Lens culinaris exhibit broad antiviral activities against SARS-CoV-2 variants. Emerg Microbes Infect. 10(1), 1519–1529 (2021)
Lokhande, K.B., Apte, G.R., Shrivastava, A., Singh, A., Pal, J.K., Swamy, K.V., Gupta, R.K.: Sensing the interactions between carbohydrate-binding agents and N-linked glycans of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein using molecular docking and simulation studies. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 40(9), 3880–3898 (2022)
Saggam, A., Limgaokar, K., Borse, S., Chavan-Gautam, P., Dixit, S., Tillu, G., Patwardhan, B.: Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal: opportunity for clinical repurposing in COVID-19 management. Front. pharmacol. 835 (2021)
Chikhale, R.V., Gurav, S.S., Patil, R.B., Sinha, S.K., Prasad, S.K., Shakya, A., Shrivastava, S.K., Gurav, N.S., Prasad, R.S.: Sars-cov-2 host entry and replication inhibitors from Indian ginseng: an in-silico approach. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 39(12), 4510–4521 (2021)
Kumar, N., Shala, A.Y., Khurana, S.M.: Antiviral and immuno-boosting potential of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera L.). Medicinal Plants-International Med. Plants - Int. J. Phytomed. 13(2), 237–44(2021)
George, B.S., Silambarasan, S., Senthil, K., Jacob, J.P., Ghosh, D.M.: Characterization of an Insecticidal Protein from Withania somnifera Against Lepidopteran and Hemipteran Pest. Mol. Biotechnol. 60(4), 290–301 (2018)
Naidoo, D., Kar, P., Roy, A., Mutanda, T., Bwapwa, J., Sen, A., Anandraj, A.: Structural insight into the binding of cyanovirin-n with the spike glycoprotein, mpro and PLpro of SARS-CoV-2: Protein–protein interactions, dynamics simulations and free energy calculations. Molecules 26(17), 5114 (2021)
O’Keefe, B.R., Giomarelli, B., Barnard, D.L., Shenoy, S.R., Chan, P.K., McMahon, J.B., Palmer, K.E., Barnett, B.W., Meyerholz, D.K., Wohlford-Lenane, C.L., McCray, P.B., Jr.: Broad-spectrum in vitro activity and in vivo efficacy of the antiviral protein griffithsin against emerging viruses of the family Coronaviridae. J. Virol. 84(5), 2511–2521 (2010)
Keyaerts, E., Vijgen, L., Pannecouque, C., Van Damme, E., Peumans, W., Egberink, H., Balzarini, J., Van Ranst, M.: Plant lectins are potent inhibitors of coronaviruses by interfering with two targets in the viral replication cycle. Antivir. Res. 75(3), 179–187 (2007)
Jang, H., Lee, D.H., Kang, H.G., Lee, S.J.: Concanavalin A targeting N-linked glycans in spike proteins influence viral interactions. Dalton Trans. 49(39), 13538–13543 (2020)
Wang, D., Lu, J.: Glycan arrays lead to the discovery of autoimmunogenic activity of SARS-CoV.Physiol. Genom. 18(2), 245–248 (2004)
Alsaidi, S., Cornejal, N., Mahoney, O., Melo, C., Verma. N., Bonnaire, T., Chang, T., O'Keefe, B.R., Sailer, J., Zydowsky, T.M., Teleshova, N., Romero, J.A.F.: Griffithsin and Carrageenan Combination Results in Antiviral Synergy against SARS-CoV-1 and 2 in a Pseudoviral Model. Mar. Drugs. 19(8), 418 (2021)
Gooldy, M., Roux, C.M., LaRosa, S.P., Spaulding, N., Fisher, C.J., Jr.: Removal of clinically relevant SARS-CoV-2 variants by an affinity resin containing Galanthus nivalis agglutinin. PLoS ONE 17(7), e0272377 (2022)
Idrees, M., Khan, S., Memon, N.H., Zhang, Z.: Effect of the Phytochemical Agents against the SARS-CoV and Some of them Selected for Application to COVID-19: A Mini-Review. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 22(4), 444–450 (2021)
Wang, W., Sun, J., Liu, C., Xue, Z.: Application of immunostimulants in aquaculture: current knowledge and future perspectives. Aquac. Res. 48(1), 1–23 (2017)
Lavelle, E.C., Grant, G., Pusztai, A., Pfüller, U., Leavy, O., McNeela, E., Mills, K.H., O’Hagan, D.T.: Mistletoe lectins enhance immune responses to intranasally co-administered herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D2. Immunology 107(2), 268–274 (2002)
Nascimento da Silva, L.C., Mendonça, J.S., de Oliveira, W.F., Batista, K.L., Zagmignan, A., Viana, I.F., dos Santos, Correia. M.T.: Exploring lectin–glycan interactions to combat COVID-19: Lessons acquired from other enveloped viruses. Glycobiology. 31(4), 358–571(2021)
Kumar, A., Sharma, A., Tirpude, N.V., Padwad, Y., Hallan, V., Kumar, S.: Plant-derived immuno-adjuvants in vaccines formulation: a promising avenue for improving vaccines efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 virus. Pharmacol. Rep. 74(6), 1238–1254 (2022)
Katoch, R., Tripathi, A.: Research advances and prospects of legume lectins. J. Biosci. 46(4) (2021)
Sander, V.A., Corigliano, M.G., Clemente, M.: Promising plant-derived adjuvants in the development of coccidial vaccines. Front. Vet. Sci. 6, 20 (2019)
Tripathi, S., Maiti, T.K.: Efficiency of heat denatured lectins from Abrus precatorius as immunoadjuvants. Food Agric. Immunol. 15(3–4), 279–287 (2003)
Cardoso, M.R., Mota, C.M., Ribeiro, D.P., Noleto, P.G., Andrade, W.B., Souza, M.A., Silva, N.M., Mineo, T.W., Mineo, J.R., Silva, D.A.: Adjuvant and immunostimulatory effects of a D-galactose-binding lectin from Synadenium carinatum latex (ScLL) in the mouse model of vaccination against neosporosis. Vet. Res. 43, 1–3 (2012)
Kang, J., Zuo, Y., Guo, Q., Wang, H., Liu, Q., Liu, Q., Xia, G., Kang, Y.: Xylaria hypoxylon lectin as adjuvant elicited Tfh cell responses. Scand. J. Immunol. 82(5), 436–442 (2015)
Frantz, M., Jung, M.L., Ribereau-Gayon, G., Anton, R.: Modulation of mistletoe (Viscum album L.) lectins cytotoxicity by carbohydrates and serum glycoproteins. Arzneimittelforschung. 50(05), 471–478 (2000)
Moyle, P.M.: Biotechnology approaches to produce potent, self-adjuvanting antigen-adjuvant fusion protein subunit vaccines. Biotechnol. Adv. 35(3), 375–389 (2017)
Vetter, V., Denizer, G., Friedland, L.R., Krishnan, J., Shapiro, M.: Understanding modern-day vaccines: what you need to know. Ann. Med. 50(2), 110–120 (2018)
Shi, S., Zhu, H., Xia, X., Liang, Z., Ma, X., Sun, B.: Vaccine adjuvants: Understanding the structure and mechanism of adjuvanticity. Vaccine. 37(24), 3167–3178 (2019)
Azizi, A., Kumar, A., Diaz-Mitoma, F., Mestecky, J.: Enhancing oral vaccine potency by intestinal M cells. PLoS Pathog. 6(11), e1001147 (2010)
Unitt, J., Hornigold, D.: Plant lectins are novel Toll-like receptor agonists. Biochem. Pharmacol. 81(11), 1324–1328 (2011)
Montassier, H.J., Maria de Fatima, S.M., Piza, V.M., Okino, C.H., Brentano, L., Richtzenhain, L.J.: Development of a microplate lectin-capture RT-PCR (MLC-RT-PCR) for the detection of avian infectious bronchitis virus. (2013)
Wang, B., Anzai, J.I.: Recent progress in lectin-based biosensors. Materials. 8(12), 8590–8607 (2015)
Simão, E.P., Silva, D.B., Cordeiro, M.T., Gil, L.H., Andrade, C.A., Oliveira, M.D.: Nanostructured impedimetric lectin-based biosensor for arboviruses detection. Talanta 208, 120338 (2020)
Oliveira, M.D., Nogueira, M.L., Correia, M.T., Coelho, L.C., Andrade, C.A.: Detection of dengue virus serotypes on the surface of gold electrode based on Cratylia mollis lectin affinity. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 155(2), 789–795 (2011)
Andrade, C.A., Oliveira, M.D., De Melo, C.P., Coelho, L.C., Correia, M.T., Nogueira, M.L., Singh, P.R., Zeng, X.: Diagnosis of dengue infection using a modified gold electrode with hybrid organic–inorganic nanocomposite and Bauhinia monandra lectin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 362(2), 517–523 (2011)
Silva, M.L.: Lectin-based biosensors as analytical tools for clinical oncology. Cancer Lett. 436, 63–74 (2018)
de Oliveira, W.F., dos Santos Silva, P.M., Coelho, L.C., dos Santos Correia, M.T.: Biomarkers, biosensors and biomedicine. Curr. Med. Chem. 27(21), 3519–3533 (2020)
Mislovičová, D., Gemeiner, P., Kozarova, A., Kožár, T., Lectinomics I.: Relevance of exogenous plant lectins in biomedical diagnostics. Biologia. 64(1), 1–9 (2009)
Beyer, V.P., Monaco, A., Napier, R., Yilmaz, G., Becer, C.R.: Bottlebrush glycopolymers from 2-oxazolines and acrylamides for targeting dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule-3-grabbing nonintegrin and mannose-binding lectin. Biomacromol 21(6), 2298–2308 (2020)
Gupta, A., Gupta, G.S.: Applications of mannose-binding lectins and mannan glycoconjugates in nanomedicine. J. Nanopart. Res. 24(11), 228 (2022)
Azimzadeh, M., Nasirizadeh, N., Rahaie, M., Naderi-Manesh, H.: Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease using a biosensor based on electrochemically-reduced graphene oxide and gold nanowires for the quantification of serum microRNA-137. RSC Adv. 7(88), 55709–55719 (2017)
Velusamy, V., Arshak, K., Korostynska, O., Oliwa, K., Adley, C.: An overview of foodborne pathogen detection: In the perspective of biosensors. Biotechnol. Adv. 28(2), 232–254 (2010)
Abbas, H.S., Kotakonda, M.: Lectins Are the Sparkle of Hope for Combating Coronaviruses and the Global COVID-19. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 12(2), 319–328 (2021)
Mu, J., Hirayama, M., Sato, Y., Morimoto, K., Hori, K.: A novel high-mannose specific lectin from the green alga Halimeda renschii exhibits a potent anti-influenza virus activity through high-affinity binding to the viral hemagglutinin. Mar. Drugs 15(8), 255 (2017)
Wallis, R., Dodd, R.B.: Interaction of mannose-binding protein with associated serine proteases: effects of naturally occurring mutations. J. Biol. Chem. 275(40), 30962–30969 (2000)
Funding
RA and KY are grateful to Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), New Delhi, India, for providing financial assistance in the form of approved ICMR Adhoc Project No. 2021-9508 (RFC No. ITR/Adhoc/2/2023-24 dated 05/09/2023; File No. 17X (3)/Adhoc/34/2022-ITR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors confirm contribution to the paper as follows: KY, RA, AY and UND conceived the original idea and designed the contents of the manuscript; AG, KY, AY and DK drafted the manuscript. AG, AS and MAK prepared diagrams. RA, KY, AY, and UND critically edited and revised the final version of the manuscript. All authors provided critical feedback and helped shape the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, A., Yadav, K., Yadav, A. et al. Mannose-specific plant and microbial lectins as antiviral agents: A review. Glycoconj J 41, 1–33 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-023-10142-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-023-10142-7