Abstract
Epothilone A is a derivative of 16-membered polyketide natural product, which has comparable chemotherapeutic effect like taxol. Introduction of sialic acids to these chemotherapeutic agents could generate interesting therapeutic glycoconjugates with significant effects in clinical studies. Since, most of the organisms biosynthesize sialic acids in their cell surface, they are key mediators in cellular events (cell-cell recognition, cell-matrix interactions). Interaction between such therapeutic sugar parts and cellular polysaccharides could generate interesting result in drugs like epothilone A. Based on this hypothesis, epothilone A glucoside (epothilone A 6-O-β-D-glucoside) was further decorated by conjugating enzymatically galactose followed by sialic acids to generate epothilone A 7-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl, 4′-O-α-D-galactoside i.e., lactosyl epothilone A (lac epoA) and two sialosides of epothilone A namely epothilone A 7-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl, 4′-O-α-D-galactopyranosyl 3″-O-α-N-acetyl neuraminic acid and epothilone A 7-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl, 4′-O-α-D-galactopyranosyl 6″-O-α-N-acetylneuraminic acid i.e., 3′sialyllactosyl epothilone A: 3′SL-epoA, and 6′sialyllactosyl epothilone A: 6′SL-epoA, respectively. These synthesized analogs were spectroscopically analyzed and elucidated, and biologically validated using HUVEC and HCT116 cancer cell lines.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbari, V., Moghim, S., Reza, M.M.: Comparision of epothilone and taxol binding in yeast tubulin using molecular modeling. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 3, 167–175 (2001)
Jordan, M.A., Wilson, L.: Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nat. Rev. Cancer 4, 253–265 (2004)
He, L., Orr, G.A., Horitz, S.B.: Novel molecules that interact with microtubules and have functional activity similar to Taxol. Drug Discov. Today 6, 1153–1164 (2001)
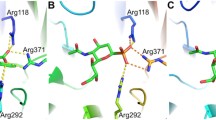
Shi, G., Wang, Y., Jin, Y., Chi, S., Shi, Q., Ge, M., Wang, S., Zhang, X., Xu, S.: Structural insight into the mechanism of epothilone A bound to beta-tubulin and its mutants at Arg282Gln and Thr274lle. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 30, 559–573 (2002)
Rogalska, A., Marczak, A., Gajek, A., Swed, M., Sliwinska, A., Drzewoski, J., Jozwiak, Z.: Induction of apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells by new anticancer compounds, epothilone A and B. Toxicol. In Vitro 27, 239–249 (2013)
Altmann, K.H., Pfeiffer, B., Arseniyadis, S., Pratt, B.A., Nicolaou, K.C.: The chemistry and biology of epothilones- the wheel keeps turning. ChemMedChem 2, 396–423 (2007)
Bollag, D.M., McQueney, P.A., Zhu, J., Hensens, O., Koupal, L., Liesch, J., Goetz, M., Lazarides, E., Woods, C.M.: Epothilones, a new class of microtubule-stabilizing agents with a taxol-like mechanism of action. Cancer Res. 55, 2325–2333 (1995)
Brabec, V., Kasparkova, J.: Modifications of DNA by platinum complexes. Relation to resistance of tumors to platinum antitumor drugs. Drug Resist. Updat. 8, 131–146 (2005)
Xie, X.K., Yang, D.S., Ye, Z.M., Tao, H.M.: Enhancement effect of adenovirus-mediated antisense c-myc and caffeine on the cytotoxicity of cisplatin in osteosarcoma cell lines. Chemotherapy 55, 433–440 (2008)
Tanaka, M., Kataoka, H., Mabuchi, M., Sakuma, S., Takahishi, S., Tujii, R., Akashi, H., Ohi, H., Yano, S., Morita, A., Joh, T.: Anticancer effects of novel photodynamic therapy with glycoconjugated chlorin for gastric and colon cancer. Anticancer Res. 31, 763–769 (2011)
Tanaka, M., Kataoka, H., Yano, S., Ohi, H., Kawamoto, K., Shibahara, T., Mizoshita, T., Mori, Y., Tanida, S., Kamiya, T., Joh, T.: Anti-cancer effects of newly developed chemotherapeutic agent, glycoconjugated palladium (II) complex, against cisplatin-resistant gastric cancer cells. BMC Cancer 13, 237 (2013)
Tiwari, V.K., Mishra, R.C., Sharma, A., Tripathi, R.P.: Carbohydrate based potential chemotherapeutic agents: recent developments and their scope in future drug discovery. Mini. Rev. Med. Chem. 12, 1497–519 (2012)
Traving, C., Schauer, R.: Structure, function and metabolism of sialic acids. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 54, 1330–1349 (1998)
Yu, H., Chokhwala, H.A., Huang, S., Chen, X.: One-pot three-enzyme chemoenzymatic approach to the synthesis of sialosides containing natural and non-natural functionalities. Nat. Protoc. 1, 2485–2492 (2006)
Varki, A., Schauer, R., Sialic acids. In: Verki, A., Cummings, R. D., Esko, J. D.; et al.: editors. Essentials of glycobiology. 2nd edition. Cold Spring Harbor (NY): Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2009. Chapter 14. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1920/
Parajuli, P., Pandey, R.P., Koirala, N., Yoon, Y.J., Kim, B.G., Sohng, J.K.: Enzymatic synthesis of epothilone A glycosides. AMB Express 4, 31 (2014)
Choi, Y.H., Kim, J.H., Park, J.H., Lee, N., Kim, D.H., Jang, K.S., Park, I.H., Kim, B.G.: Protein engineering of α2,3/2,6-sialyltransferase to improve the yield and productivity of in vitro sialyllactose synthesis. Glycobiology 24, 159–169 (2014)
Oh, T.J., Kim, D.H., Kang, S.Y., Yamaguchi, T., Sohng, J.K.: Enzymatic synthesis of vancomycin derivatives using galactosyltransferase and sialyltransferase. J. Antibiot (Tokyo) 64, 103–109 (2011)
Parajuli, P., Pandey, R.P., Pokhrel, A.R., Ghimire, G.P., Sohng, J.K.: Enzymatic glycosylation of the topical antibiotics mupirocin. Glycoconj. J. 31, 563–572 (2014)
Pandey, R.P., Gurung, R.B., Parajuli, P., Koirala, N., le Tuoi, T., Sohng, J.K.: Assessing acceptor substrate promiscuity of YjiC-mediated glycosylation towards flavonoids. Carbohydr. Res. 393, 26–31 (2014)
Pandey, R.P., Parajuli, P., Koirala, N., Park, J.W., Sohng, J.K.: Probing 3-hydroxyflavone for in vitro glycorandomization of flavonols by YjiC. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 79, 6833–6838 (2013)
Antoine, T., Priem, B., Heyraud, A., Greffe, L., Gilbert, M., Wakarchuk, W.W., Lam, J.S., Samain, E.: Large-scale in vivo synthesis of the carbohydrate moieties of gangliosides GM1 and GM2 by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Chembiochem 4, 406–412 (2003)
Wang, J., Zhang, H., Ying, L., Wang, C., Jiang, N., Zhou, Y., Wang, H., Bai, H.: Five new epothilone metabolites from Sorangium cellulosum strain So0157-2. J. Antibiot (Tokyo) 62, 483–487 (2009)
Park, H.J., Zhang, Y., Georgescu, S.P., Johnson, K.L., Kong, D., Galper, J.B.: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells and human dermal microvascular endothelial cells offer new insight into the relationship between lipid metabolism and angiogenesis. Stem Cell Rev. 2, 93–102 (2006)
Raiput, A., Dominquez San Martin, I., Rose, R., Beko, A., Levea, C., Sharratt, E., Mazurchuk, R., Hoffman, R.M., Brottain, M.G., Wang, J.J.: Characterization of HCT116 human colon cancer cells in an orthotopic model. Surg. Res. 147, 276–281 (2008)
Cazet, A., Julien, S., Bobowski, M., Krzewinski-Recchi, M.A., Harduin-Lepers, A., Groux-Degroote, S., Delannoy, P.: Consequences of the expression of sialylated antigens in breast cancer. Carbohydr. Res. 345, 1377–1388 (2010)
Audry, M., Jeanneau, C., Imberty, A., Harduin-Lepers, A., Delannoy, P., Breton, C.: Current trends in the structure-activity relationships of sialyltransferases. Glycobiology 21, 716–726 (2010)
Cheng, H., Cao, X., Xian, M., Cai, T.B., Ji, J.J., Tunac, J.B., Sun, D., Wang, P.G.: Synthesis and enzyme-specific activation of carbohydrate-geldanamycin conjugates with potent anticancer activity. J. Med. Chem. 48, 645–652 (2005)
Schulte, T.W., Akinaga, S., Soga, S., Sullivan, W., Stensgard, B., Toft, D., Neckers, L.M.: Antibiotic radicicol binds to the N-terminal domain of HSP90 and shares important biologic activities with geldanamycin. Cell Stress Chaperones 3, 100–108 (1998)
Vahdat, L. T.: Slinical studies with epothlones for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Semin. Oncol. 35, S22-30
Heuser, E., Lipp, K., Wiegandt, H.: Detection of sialic acid containing compounds and the behavior of gangliosides in polyacrylamide disc electrophoresis. Anal. Biochem. 60, 382–388 (1974)
Bisel, B., Pavone, F.S., Calamai, M.: GM1 and GM2 gangliosides: recent developments. Biomol. Concepts. 5, 87–93 (2014)
Bagriacik, E.U., Miller, K.S.: Cell surface sialic acid and the regulation of immunie cell interactions: the neuraminidase effect reconsidered. Glycobiology 3, 267–275 (1999)
Varki, A., Gagneux, P.: Multifarious roles of sialic acids in immnity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1253, 16–36 (2012)
Wang, B., Brand-Miller, J.: The role and potential of sialic acid in human nutrition. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 57, 1351–1369 (2003)
Hata, K., Koseki, K., Yamaguchi, K., Moriya, S., Suzuki, Y., Yingsakmongkon, S., Hirai, G., Sodeoka, M., von Itzstein, M., Miyagi, T.: Limited inhibitory effects of oseltamivir and zanamivir on human sialidases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52, 3484–3481 (2008)
Cowan, C. B., Patel, D.A., Good, T. A.: Exploring the mechanism of beta-amyloid toxicity attenuation by multivalent sialic acid polymers through the use of mathematical models. J. Theor. Biol. 258, 189–197
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (NRF-2014R1A2A2A01002875).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 20066 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parajuli, P., Pandey, R.P., Gurung, R.B. et al. Enzymatic synthesis of lactosylated and sialylated derivatives of epothilone A. Glycoconj J 33, 137–146 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-015-9646-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-015-9646-y