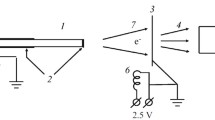
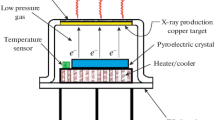
The results of experimental studies on the generation of x-rays when operating a piezoelectric kitchen lighter in a vacuum are presented. For the first time, a new method for increasing the intensity of x-ray radiation in the piezoelectric effect in a high vacuum through the use of an additional electron emitter is proposed and demonstrated. The maximum energy of x-ray bremsstrahlung reaches 14 keV. This means that electrons are accelerated in vacuum in the field of a piezoelectric ceramic to energy of at least 14 keV.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. D. Brownridge, “Pyroelectric x-ray generator,” Nature, 358, 287 – 288 (1992).
J. D. Brownridge and S. Raboy, “Investigations of pyroelectric generation of x-rays,” J. Appl. Phys., 86, 640 (1997).
J. Geuther and Y. Danon, “High-energy x-ray production with pyroelectric crystals,” J. Appl. Phys., 97, 104916 (2005).
K. A. Vokhmyanina, O. O. Ivashchuk, V. Yu. Ionidi, et al., “Possibility of using the piezoceramic PZT-19 in pyroelectric x-ray generators,” Steklo Keram., No. 11, 27 – 31 (2016); K. A. Vokhmyanina, O. O. Ivashchuk, V. Yu. Ionidi, et al., “Possibility of using the piezoceramic PZT-19 in pyroelectric x-ray generators,” Glass Ceram., 73(11 – 12), 415 – 419 (2016).
A. V. Shchagin, V. S. Miroshnik, V. I. Volkov, and A. N. Oleinik, “Ferroelectric ceramics in a pyroelectric accelerator,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 107, 233505 (2015).
J. R. Hird, C. G. Camara, and S. J. Putterman, “A triboelectric x-ray source,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 68, 133501 (2011).
C. G. Camara, J. V. Escobar, J. R. Hird, and S. J. Putterman, “Correlation between nanosecond x-ray flashes and stick-slip friction in peeling tape,” Nature, 455, 1089 – 1092 (2008).
M. Hockley and Z. Huang, “Strong electron and ion emissions induced by a pyroelectric crystal,” J. Appl. Phys., 113, 034902 (2013).
V. I. Nagaichenko, V. S. Miroshnik, A. M. Yegorov and A. V. Shchagin, “Research of the spectra of the charged particles beam in the pyroelectric accelerator,” Vopr. Atom. Nauki Tekh., Ser. Yaderno-Fiz. Issled., No. 2(53), 34 – 39 (2010); V. I. Nagaichenko, V. S. Miroshnik, A. M. Yegorov and A. V. Shchagin, “Research of the spectra of the charged particles beam in the pyroelectric accelerator,” Probl. Atomic Sci. Technol., Ser. Nucl. Phys. Invest., No. 2(53), 34 – 39 (2010).
B. Naranjo, J. K. Gimzewski, and S. Putterman, “Observation of nuclear fusion driven by a pyroelectric crystal,” Nature, 434, 1115 – 1117 (2005).
J. Geuther, Ya. Danon, and F. Saglime, “Nuclear reactions induced by a pyroelectric accelerator,” Phys. Rev. Lett., 96, 054803 (2006).
W. Tornow, S. M. Shafroth, and J. D. Brownridge, “Evidence for neutron production in deuterium gas with a pyroelectric crystal without tip,” J. Appl. Phys., 104, 034905 (2008).
D. Gillich, A. Kovanen, and B. Herman, “Pyroelectric crystal neutron production in a portable prototype vacuum system,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A, 602, 306 (2009).
J. Kawai, et al., “X-ray fluorescence analysis with a pyroelectric x-ray generator,” X-Ray Spectrom., 34, 521 (2005).
E. L. Neidholdt and J. L. Beauchamp, “Compact ambient pressure pyroelectric ion source for mass spectrometry,” Anal. Chem., 79, 3945 (2007).
S. Imashuku and K.Wagatsuma, “Portable pyroelectric electron probe microanalyzer with a spot size of 40 μm,” Rev. Sci. Instrum., 88, 023117 (2017).
S. Imashuku, N. Fuyuno, J. Kawai, and K. Hanasaki, “Portable rare-earth element analyzer using pyroelectric crystal,” Rev. Sci. Instrum., 84, 126105 (2013).
O. O. Ivashchuk, A. V. Shchagin, A. S. Kubankin, et al., “Pyroelectric accelerator and x-ray source in pulsed mode,” JINST, 15, Ñ02002 (2020).
L. Orlikov, K. M. Mambetowa, S. I. Arestov, and S. M. Shandarov, “Pulse source of electrons based on the pyroeffect,” in: 7th International Congress on Energy Fluxes and Radiation Effects (EFRE) [in Russian], Tomsk (2020), pp. 359 – 363.
B. Gall, S. D. Kovaleski, J. A. VanGordon, et al., “Investigation of the piezoelectric effect as a means to generate x-rays,” IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci., 41, 106 – 111 (2013).
O. O. Ivashchuk, A. V. Shchagin, V. S. Miroshnik, et al., “Ceramic piezoelectric transformer in vacuum for acceleration of electrons and production of x-rays,” Materials, 11, 1188 (2018).
A. V. Shchagin, V. S. Miroshnik, V. I. Volkov, et al., “Piezoelectric transformer aided x-ray generation in vacuum,” Steklo Keram., No. 11, 24 – 26 (2017); A. V. Shchagin, V. S. Miroshnik, V. I. Volkov, et al., “Piezoelectric transformer aided x-ray generation in vacuum,” Glass Ceram., 74(11 – 12), 404 – 405 (2017).
K. A. Vokhmyanina, V. S. Sotnikova, A. A. Kaplii, et al., “Possibility of using dielectric channels as deflecting systems for controlling accelerated electron beams,” Steklo Keram., No. 10, 15 – 18 (2017); K. A. Vokhmyanina, V. S. Sotnikova, A. A. Kaplii, et al., “Possibility of using dielectric channels as deflecting systems for controlling accelerated electron beams,” Glass Ceram., 74(9 – 10), 355 – 357 (2017).
O. O. Ivashchuk, A. V. Shchagin, A. S. Kubankin, et al., “Piezoelectric Accelerator,” Sci. Rep., 8, 816488 (2018).
O. O. Ivashchuk, A. V. Shchagin, A. S. Kubankin, et al., “Quartz accelerator of charged particles,” Probl. Atomic Sci. Technol., Ser. Nucl. Phys. Invest., 3(127), 59 (2020).
A. V. Kukuruza and G. A. Deryabin, Piezoelectric Lighter, Pat. BY 935 U [in Russian] (2003).
Pyroelectric X-Ray Source COOL-X, Amptek; URL: http://www.amptek.com/pdf/coolx.pdf.
This work was performed with financial support from the competitive part of the state task on the creation and development of laboratories, project No. FZWG-2020-0032 (2019-1569) and using equipment from the Center for Collective Use at the Federal Research Center for Crystallography and Photonics with the support of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation (project RFMEFI62119X0035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Steklo i Keramika, No. 12, pp. 34 – 38, December, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ivashchuk, O.O., Shchagin, A.V., Kubankin, A.S. et al. X-Ray Generation during Piezoelectric Lighter Operation in Vacuum. Glass Ceram 77, 469–472 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10717-021-00334-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10717-021-00334-8