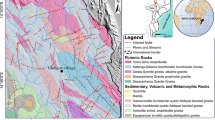
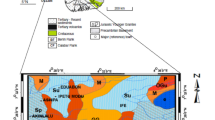
Abstract
An integrated [very low frequency (VLF) electromagnetic, magnetic, remote sensing, field, and geographic information system (GIS)] study was conducted over the basement complex in southern Sinai (Feiran watershed) for a better understanding of the structural controls on the groundwater flow. The increase in satellite-based radar backscattering values following a large precipitation event (34 mm on 17–18 January 2010) was used to identify water-bearing features, here interpreted as preferred pathways for surface water infiltration. Findings include: (1) spatial analysis in a GIS environment revealed that the distribution of the water-bearing features (conductive features) corresponds to that of fractures, faults, shear zones, dike swarms, and wadi networks; (2) using VLF (43 profiles), magnetic (7 profiles) techniques, and field observations, the majority (85 %) of the investigated conductive features were determined to be preferred pathways for groundwater flow; (3) northwest–southeast- to north–south-trending conductive features that intersect the groundwater flow (southeast to northwest) at low angles capture groundwater flow, whereas northeast–southwest to east–west features that intersect the flow at high angles impound groundwater upstream and could provide potential productive well locations; and (4) similar findings are observed in central Sinai: east–west-trending dextral shear zones (Themed and Sinai Hinge Belt) impede south to north groundwater flow as evidenced by the significant drop in hydraulic head (from 467 to 248 m above mean sea level) across shear zones and by reorientation of regional flow (south–north to southwest–northeast). The adopted integrated methodologies could be readily applied to similar highly fractured basement arid terrains elsewhere.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abouelmagd A, Sultan M, Sturchio N, Soliman F, Rashed M, Ahmed M, Kehew A, Milewski A, Chouinard K (2014) Paleoclimate record in the Nubian Sandstone Aquifer, Sinai Peninsula, Egypt. Quatern Res 81(1):158–167. doi:10.1016/j.yqres.2013.10.017
Agar RA (1987) The Najd fault system revisited; a two-way strike-slip orogen in the Saudi Arabian Shield. J Struct Geol 9(1):41–48. doi:10.1016/0191-8141(87)90042-3
Aggour TA (2007) Water resources of Wadi Feiran with emphasis on geomorphology and geology. Ann Geol Surv Egypt 29:357–387
Ahmed M, Sauck W, Sultan M, Yan E, Soliman F, Rashed M (2013) Geophysical constraints on the hydrogeologic and structural settings of the Gulf of Suez rift-related basins: case study from the El Qaa Plain, Sinai, Egypt. Surv Geophys 35:415–430. doi:10.1007/s10712-013-9259-6
Amer R, Sultan M, Ripperdan R, Ghulam A, Kusky T (2013) An integrated approach for groundwater potential zoning in shallow fracture zone aquifers. Int J Remote Sens 34(19):6539–6561. doi:10.1080/01431161.2013.804221
Babikera M, Gudmundsson A (2004) The effects of dykes and faults on groundwater flow in an arid land: the Red Sea Hills, Sudan. J Hydrol 297:256–273. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.04.018
Bartov Y, Steinitz G, Eyal M, Eyal Y (1979) The development of the Arava Rift Valley and the Red Sea. New evidence for Cenozoic strike-slip faults in Eastern Sinai. Abstracts, annual meeting of Sede Boqer, Israel Geological Society, p 8
Blenkinsop TG, Kadzviti S (2006) Fluid flow in shear zones: insights from the geometry and evolution of ore bodies at Renco Gold Mine, Zimbabwe. Geofluids 6:334–345. doi:10.1111/j.1468-8123.2006.00154.x
Bosworth W, McClay K (2001) Structural and stratigraphic evolution of the Gulf of Suez rift, Egypt: a synthesis. Mém Mus Nat D’hist Nat 186:567–606
Brown GF, Coleman RG (1972) The tectonic framework of the Arabian Peninsula, 24th Int. Geol Congr Montr 3:300–305
Central Agency for Public Mobilization and Statistics (CAPMAS) of the Arab Republic of Egypt (2014). http://www.capmas.gov.eg/?lang=2. Accessed 04 Dec 2014
Cigna F, Bateson L, Jordan C, Dashwood D (2014) Simulating SAR geometric distortions and predicting Persistent Scatterer densities for ERS-1/2 and ENVISAT C-band SAR and InSAR applications: nationwide feasibility assessment to monitor the landmass of Great Britain with SAR imagery. Remote Sens Environ 152:441–466. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2014.06.025
El-Sayed MM (2003) Neoproterozoic magmatism in NW Sinai, Egypt: magma source and evolution of collision related intracrustal anatectic leucogranite. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 92:145–164. doi:10.1007/s00531-003-0313-3
Eyal M (1975) Stages in the magmatic history of the Precambrian in Sinai and Southern Negev (in Hebrew). PhD Thesis, Hebrew University, Jerusalem
Eyal Y, Eyal M (1987) Mafic dyke swarms in the Arabian–Nubian Shield. Isr J Earth Sci 36:195–211
Fraser DC (1969) Contouring of VLF-EM data. Geophysics 34:958–967. doi:10.1190/1.1440065
Friz-Topfer A (1991) Geochemical characterization of Pan-African dyke swarms in southern Sinai: from continental margin to intraplate magmatism. Precambr Res 49:281–300. doi:10.1016/0301-9268(91)90038-C
Gaber A, Ghoneim E, Khalaf F, El-Baz F (2009) Delineation of paleolakes in the Sinai Peninsula, Egypt, using remote sensing and GIS. J Arid Environ 73(1):127–134. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2008.08.007
Garfunkel Z (1999) History and paleogeography during the Pan-African orogen to stable platform transition: reappraisal of the evidence from Elat area and northern Arabian–Nubian Shield. Israel J Earth Sci 48:135–157
Goddard JV, Evans JP (1995) Chemical-change and fluid-rock interaction in faults of crystalline thrust sheets, Northwestern Wyoming, USA. J Struct Geol 17:533–547. doi:10.1016/0191-8141(94)00068-B
Greiling RO, Abdeen MM, Dardir AA, El Akhal H, El Ramly MF, Kamal GED, Osman AF, Rashwan AA, Sadek MF (1994) A structural synthesis of the Proterozoic Arabian–Nubian Shield in Egypt. Geol Rundsch 83(3):484–501
Gudmundsson A (2000) Active fault zones and groundwater flow. Geophys Res Lett 27(18):2993–2996. doi:10.1029/1999GL011266
Huffman GJ, Adler RF, Bolvin DT, Gu G, Nelkin EJ, Bowman KP, Hong Y, Stocker EF, Wolff DB (2007) The TRMM multi-satellite precipitation analysis: quasi-global, multi-year, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scale. J Hydrometeorol 8:38–55
Iacumin M, Marzoli A, El Metwally AA, Piccirililo EM (1998) Neoproterozoic dyke swarms from southern Sinai (Egypt): geochemistry and petrogenetic aspects. J Afr Earth Sc 26(1):49–64
Issar A, Gilad D (1982) Groundwater flow systems in the arid crystalline province of southern Sinai. J Hydrol Sci 27(3):309–325
Jensen SK, Domingue JO (1988) Extracting topographic structure from digital elevation data for geographic information system analysis. Photogramm Eng Remote Sensing 54(11):1593–1600
Johnson PR, Woldehaimanot B (2003) Development of the Arabian–Nubian Shield: perspectives on accretion and deformation in the northern East African Orogen and the assembly of Gondwana: Geological Society. Lond Spec Publ 206:289–325. doi:10.1144/GSL.SP.2003.206.01.15
Klein J, Lajoie J (1980) Electromagnetic prospecting for minerals. Practical geophysics for the exploration geologists. Northwest Mining Association, Spokane, pp 239–290
Klitzsch E, List FK, Pohlmann G (1987) Geological map of Egypt. Conoco Coral and Egyptian General Petroleum Company, Cairo
Kummerow C, Barnes W, Kozu T, Shiue J, Simpson J (1998) The tropical rainfall measuring mission (TRMM) sensor package. J Atmos Ocean Technol 15:809–816
Kusky TM, El-Baz F, Morency JR, El-Shafei M (1998) Structural and tectonic features of the Sinai Peninsula, using Landsat data: implications for groundwater exploration. Egypt J Remote Sens Space Sci 1:69–100
Lu Z, Meyer DJ (2002) Study of high SAR backscattering caused by an increase of soil moisture over a sparsely vegetated area: implications for characteristics of backscattering. Int J Remote Sens 23(6):1063–1074
Martz W, Garbrecht J (2002) Channel network delineation and watershed segmentation in the TOPAZ digital landscape analysis system. In: Lyon GJ (ed) GIS for water resources and watershed management. Taylor & Francis Inc, London, pp 7–16. doi:10.1201/9780203217917.ch1
Meneisy M (1990) Vulcanicity. In: Said R (ed) The geology of Egypt. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 157–172
Moore JM (1979) Tectonics of the Najd transcurrent fault system, Saudi Arabia. J Geol Soc 136(4):441–452. doi:10.1144/gsjgs.136.4.0441
Moustafa AR (1997) Controls on the development and evolution of transfer zones: the influence of basement structure and sedimentary thickness in the Suez rift and Red Sea. J Struct Geol 19(6):755–768. doi:10.1016/S0191-8141(97)00007-2
Moustafa AR, Khalil MH (1994) Structural characteristics and tectonic evolution of north Sinai fold belts. In: Said R (ed) The geology of Egypt. A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 381–389
Moustafa AR, Salama ME, Khalil SM, Fouda HGA (2013) Sinai hinge belt: a major crustal boundary in NE Africa. J Geol Soc 171(2):239–254. doi:10.1144/jgs2013-021
Notti D, Garcia-Davallilo JC, Herrera G, Mora O (2010) Assessment of the performance of Xband satellite radar data for landslide mapping and monitoring: upper Tena valley case study. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 10:1865–1875. doi:10.5194/nhess-10-1865-2010
Notti D, Meisina C, Zucca F, Colombo A (2011) Models to predict Persistent Scatterers data distribution and their capacity to register movement along the slope. In Fringe workshop, 19–23 September 2011. ESA/ESRIN Frascati, Italy
Palacky GJ, Ritsema IL, Dejong SJ (1981) Electromagnetic prospecting for groundwater in Precambrian Terrains in the Republic of Upper Volta. Geophys Prospect 29:932–955. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2478.1981.tb01036.x
Paterson NR, Ronka V (1971) Five years of surveying with very low frequency—electromagnetic method. GeoExplorer 9:7–26. doi:10.1016/0016-7142(71)90085-8
Rosenthal E, Zilberbrand M, Livshitz Y (2007) The hydrochemical evolution of brackish groundwater in central and northern Sinai (Egypt) and in the western Negev (Israel). J Hydrol 337:294–314. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.01.042
Shalaby A (2010) The northern dome of Wadi Hafafit culmination, Eastern Desert, Egypt: structural setting in tectonic framework of a scissor-like wrench corridor. J Afr Earth Sc 57(3):227–241. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2009.08.003
Shendi E, Abouelmagd A (2004) New approach for ground geophysics in the development of groundwater in the basement terrains (A case study from South Sinai, Egypt). In: Proceedings of the 7th conference Geology of Sinai for Development, Ismailia, Egypt, pp 129–140
Shimron AE (1973) The Precambrian structural and metamorphic history of the Eilat Area with comparative notes of the Sinai Peninsula. PhD Thesis, Hebrew University, Jerusalem
Shoshany M, Svoray T, Curran P, Foody M, Perevolotsky A (2000) The relationship between ERS-2 SAR backscatter and soil moisture: generalization from a humid to semi-arid transect. Int J Remote Sens 21(11):2337–2343
Stern RJ, Gottfried D, Hedge CE (1984) Late Precambrian rifting and crustal evolution in the northeast Desert of Egypt. Geology 12:168–172. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1984)12<168:LPRACE>2.0.CO;2
Stern RJ, Sellers G, Gottfried D (1988) Bimodal dyke swarms in the North Eastern Desert of Egypt: significance for the origin of late Precambrian “A-type” granites in northern Afro-Arabia. In: El Gaby S, Greiling RO (eds) The Pan-African belt of Northeast Africa and adjacent areas. Vieweg, Weisbaden, pp 147–177
Sultan M, Arvidson RE, Sturchio NC, Guinness EA (1987) Lithologic mapping in arid regions with Landsat Thematic Mapper data. Meatiq Dome, Egypt. Geol Soc Am Bull 99:748–762. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1987)99<748:LMIARW>2.0.CO;2
Sultan M, Arvidson RE, Duncan IJ, Stern RJ, El Kaliouby B (1988) Extension of the Najd shear system from Saudi Arabia to the central Eastern Desert of Egypt based on integrated field and Landsat observations. Tectonics 7(6):1291–1306. doi:10.1029/TC007i006p01291
Sultan M, Becker R, Arvidson RE, Shore P, Stern RJ, El Alfy Z, Guinness EA (1992) Nature of the Red Sea crust: a controversy revisited. Geology 20(7):593–596. doi:10.1130/00917613(1992)020<0593:NOTRSC>2.3.CO;2
Sultan M, Becker R, Arvidson RE, Shore P, Stern RJ, El Alfy Z, Attia RI (1993) New constraints on Red Sea rifting from correlations of Arabian and Nubian Neoproterozoic outcrops. Tectonics 12(6):1303–1319. doi:10.1029/93TC00819
Sultan M, Sturchio N, Hassan FA, Hamdan MAR, Mahmood AM, ElAlfy Z, Stein T (1997) Precipitation source inferred from stable isotopic composition of Pleistocene groundwater and carbonate deposits in the Western Desert of Egypt. Quatern Res 48:29–37. doi:10.1006/qres.1997.1907
Sultan M, Yan E, Sturchio N, Wagdy A, Abdel Gelil K, Manocha N, Becker R, Milewski A (2007) Natural discharge: a key to sustainable utilization of fossil groundwater. J Hydrol 335:25–36. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.10.034
Sultan M, Wagdy A, Manocha N, Sauck W, Abdel Gelil K, Youssef AF, Becker R, Milewski A, El Alfy Z, Jones C (2008) An integrated approach for identifying aquifers in transcurrent fault systems: the Najd shear system of the Arabian Nubian shield. J Hydrol 349:475–488. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.11.029
Sultan M, Yousef AF, Metwally S, Becker R, Milewski A, Sauck W, Sturchio N, Mohamed A, Wagdy A, El Alfy Z, Becker D, Sagintayev Z, El Sayed M, Welton B (2011) Red sea rifting controls on aquifer distribution: constraints from geochemical, geophysical, and remote sensing data. Geol Soc Am Bull 123:911–924. doi:10.1130/B30146.1
Sultan YM, Abu Alam T, Stuwe K (2012) Tectonic setting of south Sinai metamorphic belts. Geophysical research abstracts, EGU general assembly 14, EGU2012-8344, Vienna, Austria
Telford WM, Geldart LP, Sheriff RE (1990) Applied geophysics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 62–134
Thorweihe U (1982) Hydrogeologie des Dakhla-Beckens (Ägypten) [Hydrogeology of the Dakhla Basin (Egypt)]. Berl Geowiss Abh (A) 38:1–53
Toth J (2009) Gravitational systems of groundwater flow—theory, evaluation, utilization. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 297
Wagner W, Scipal K (2000) Large-scale soil moisture mapping in Western Africa using the ERS scatterometer. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 38:1777–1782
Wang C, Qi J, Moran S, Marsett R (2004) Soil moisture estimation in a semiarid rangeland using ERS-2 and TM imagery. Remote Sens Environ 90:178–189. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2003.12.001
Wang SG, Li X, Han J, Jin R (2011) Estimation of surface soil moisture and roughness from multi-angular ASAR imagery in the watershed allied telemetry experimental research (WATER). Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 15:1415–1426. doi:10.5194/hess-15-1415-2011
Wickel AJ, Jackson TJ, Wood EF (2001) Multitemporal monitoring of soil moisture with RADARSAT SAR during the 1997 Southern Great Plains hydrology experiment. Int J Remote Sens 22:1571–1583
Younes AI, McClay K (2002) Development of accommodation zones in the Gulf of Suez—Red Sea rift, Egypt. AAPG Bull 86(6):1003–1026. doi:10.1306/61EEDC10-173E-11D7-8645000102C1865D
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by the NATO Science for Peace grant (SFP 982614) awarded to Western Michigan University, and by the Earth Sciences Remote Sensing facility at Western Michigan University. We also acknowledge the support of ESA data grant 11920 for the provision of the ENVISAT radar scenes. We thank Dr. Khaled Mamoun from Suez Canal University and our field guides Mohamed El Shaeir and Mohamed Mansour for facilitating field work in Sinai, and our colleagues (Kyle Chouinard and Malgorzata Krawczyk) at the Earth Sciences Remote Sensing facility for their inputs and for their helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamed, L., Sultan, M., Ahmed, M. et al. Structural Controls on Groundwater Flow in Basement Terrains: Geophysical, Remote Sensing, and Field Investigations in Sinai. Surv Geophys 36, 717–742 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-015-9331-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-015-9331-5