Abstract
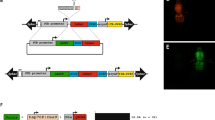
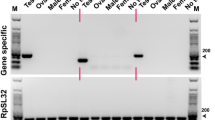
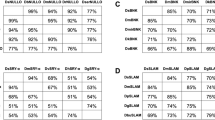
The sterile insect technique (SIT) is a highly effective biologically-based method for the population suppression of highly invasive insect pests of medical and agricultural importance. The efficacy of SIT could be significantly enhanced, however, by improved methods of male sterilization that avoid the fitness costs of irradiation. An alternative sterilization method is possible by gene-editing that targets genes essential for sperm maturation and motility, rendering them nonfunctional, similar to the CRISPR-Cas9 targeting of β2-tubulin in the genetic model system, Drosophila melanogaster. However, since genetic strategies for sterility are susceptible to breakdown or resistance in mass-reared populations, alternative targets for sterility are important for redundancy or strain replacement. Here we have identified and characterized the sequence and transcriptional expression of two genes in a Florida strain of Drosophila suzukii, that are cognates of the D. melanogaster spermatocyte-specific genes wampa and Prosalpha6T. Wampa encodes a coiled-coil dynein subunit required for axonemal assembly, and the proteasome subunit gene, Prosalpha6T, is required for spermatid individualization and nuclear maturation. The reading frames of these genes differed from their NCBI database entries derived from a D. suzukii California strain by 44 and 8 nucleotide substitutions/polymorphisms, respectively, though all substitutions were synonymous resulting in identical peptide sequences. Expression of both genes is predominant in the male testis, and they share similar transcriptional profiles in adult males with β2-tubulin. Their amino acid sequences are highly conserved in dipteran species, including pest species subject to SIT control, supporting their potential use in targeted male sterilization strategies.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated by the current study are available from NCBI GenBank as noted in the text and the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahmed HMM, Hildebrand L, Wimmer EA (2019) Improvement and use of CRISPR/Cas9 to engineer a sperm-marking strain for the invasive fruit pest Drosophila suzukii. BMC Biotechnol 19:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-019-0588-5
Alphey L, Nimmo D, O’Connell S, Alphey N (2008) Insect population suppression using engineered insects. Adv Exp Med Biol 627:93–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-78225-6_8
Bakri A, Mehta K, Lance DR (2021) Sterilizing insects with ionizing radiation. Sterile insect technique. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 233–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-4051-2_9
Bauerly E, Yi K, Gibson MC (2020) Wampa is a dynein subunit required for axonemal assembly and male fertility in Drosophila. Dev Biol 463:158–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2020.04.006
Bello B, Resendez-Perez D, Gehring WJ (1998) Spatial and temporal targeting of gene expression in Drosophila by means of a tetracycline-dependent transactivator system. Development 125:2193–2202. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.125.12.2193
Belote JM, Zhong L (2005) Proteasome gene duplications in mammals, flies and plants. Recent Res Dev Genes Genomes 1:107–129
Burt A, Crisanti A (2018) Gene drive: evolved and synthetic. ACS Chem Biol 13:343–346. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.7b01031
Catteruccia F, Benton JP, Crisanti A (2005) An Anopheles transgenic sexing strain for vector control. Nat Biotechnol 23:1414–1417. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1152
Chen Y, Lu Q, Goodenough DA, Jeansonne B (2002) Nonreceptor tyrosine kinase c-Yes interacts with occludin during tight junction formation in canine kidney epithelial cells. Mol Biol Cell 13:1227–1237. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.01
Chiu JC, Jiang X, Zhao L, Hamm CA, Cridland JM, Saelao P, Hamby KA, Lee EK, Kwok RS, Zhang G, Zalom FG, Walton VM, Begun DJ (2013) Genome of Drosophila suzukii, the spotted wing drosophila G3: Genes Genomes Genet 3:2257–2271. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.113.008185
Cini A, Ioriatti C, Anfora G (2012) A review of the invasion of Drosophila suzukii in Europe and a draft research agenda for integrated pest management. Bull Insectol 65:149–160
Gong P, Epton MJ, Fu G, Scaife S, Hiscox A, Condon KC, Condon GC, Morrison NI, Kelly DW, Dafa’Alla T, Coleman PG, Alphey L (2005) A dominant lethal genetic system for autocidal control of the Mediterranean fruitfly. Nat Biotechnol 23:453–456. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1071
Gossen M, Bujard H (1992) Tight control of gene expression in mammalian cells by tetracycline-responsive promoters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 89:5547–5551. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.89.12.5547
Grether ME, Abrams JM, Agapite J, White K, Steller H (1995) The head involution defective gene of Drosophila melanogaster functions in programmed cell death. Genes Dev 9:1694–1708. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.9.14.1694
Handler AM (2002) Prospects for using genetic transformation for improved SIT and new biocontrol methods. Genetica 116:137–149. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020924028450
Handler AM (2016) Enhancing the stability and ecological safety of mass-reared transgenic strains for field release by redundant conditional lethality systems. Insect Sci 23:225–234. https://doi.org/10.1111/1744-7917.12245
Heinrich JC, Scott MJ (2000) A repressible female-specific lethal genetic system for making transgenic insect strains suitable for a sterile-release program. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 97:8229–8232. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.140142697
Horn C, Wimmer EA (2003) A transgene-based, embryo-specific lethality system for insect pest management. Nat Biotechnol 21:64–70. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt769
Kandul NP, Liu J, Sanchez C, Wu HM, Marshall SL, Akbari JM, O.S (2019) Transforming insect population control with precision guided sterile males with demonstration in flies. Nat Commun 10:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07964-7
Kearse M, Moir R, Wilson A, Stones-Havas S, Cheung M, Sturrock S, Buxton S, Cooper A, Markowitz S, Duran C, Thierer T, Ashton B, Meintjes P, Drummond A (2012) Geneious Basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 28:1647–1649. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts199
Kemphues KJ, Kaufman TC, Raff RA, Raff EC (1982) The testis-specific β-tubulin subunit in drosophila melanogaster has multiple functions in spermatogenesis. Cell 31:655–670. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(82)90321-X
Kemphues KJ, Raff EC, Kaufman TC (1983) Genetic analysis of β2t, the structural gene for a testis-specific β-tubulin subunit in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 105:345–356. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/105.2.345
Knipling E (1959) Sterile-male method of population control. Science 130:80. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.130.3380.9
Krafsur ES (1998) Sterile insect technique for suppressing and eradicating insect population: 55 years and counting. J Agric Urban Entomol 15:303–317
Li J, Handler AM (2017) Temperature-dependent sex-reversal by a transformer-2 gene-edited mutation in the spotted wing drosophila, Drosophila suzukii. Sci Rep 7:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12405-4
Li F, Scott MJ (2016) CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutagenesis of the white and sex lethal loci in the invasive pest, Drosophila suzukii. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 469:911–916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.12.081
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆CT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Marshall RS, Vierstra RD (2019) Dynamic regulation of the 26S proteasome: from synthesis to degradation. Front Mol Biosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2019.00040
Mitra S, Ray SK, Banerjee R (2016) Synonymous codons influencing gene expression in organisms. Res Rep Biochem Volume 6:57–65. https://doi.org/10.2147/rrbc.s83483
Nielsen MG, Gadagkar SR, Gutzwiller L (2010) <Tubuling evolution.pdf="”>
Raff EC (1984) Genetics of microtubule systems. J Cell Biol 99:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.99.1.1
Robinson A, Franz G (2000) The application of transgenic insect technology in the sterile insect technique. Insect transgenesis: methods and application. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 307–319
Robinson A, Franz G, Fisher K (1999) Genetic sexing strains in the medfly, Ceratitis capitata : development, mass rearing and field application. Trends Entomol 2:81–104
Schetelig MF, Handler AM (2012) Strategy for enhanced transgenic strain development for embryonic conditional lethality in Anastrepha suspensa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:9348–9353. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1203352109
Schetelig MF, Handler AM (2013) Germline transformation of the spotted wing drosophilid, Drosophila suzukii, with a piggyBac transposon vector. Genetica 141:189–193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-013-9717-6
Schetelig MF, Caceres C, Zacharopoulou A, Franz G, Wimmer EA (2009) Conditional embryonic lethality to improve the sterile insect technique in Ceratitis capitata (Diptera: Tephritidae). BMC Biol 7:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7007-7-4
Scolari F, Schetelig MF, Bertin S, Malacrida AR, Gasperi G, Wimmer EA (2008) Fluorescent sperm marking to improve the fight against the pest insect Ceratitis capitata (Wiedemann; Diptera: Tephritidae). N Biotechnol 25:76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2008.02.001
Singh GB (2015) Multiple sequence alignment, modeling and optimization in Science and Technologies. Brief Bioinform. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11403-3_7
Vreysen MJB, Robinson AS, Hendrichs J (2007) Area-wide control of insect pests: from research to field implementation. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-6059-5
Walsh DB, Bolda MP, Goodhue RE, Dreves AJ, Lee J, Bruck DJ, Walton VM, O’Neal SD, Zalom FG (2011) Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae): invasive pest of ripening soft fruit expanding its geographic range and damage potential. J Integr Pest Manag 2:3–9. https://doi.org/10.1603/IPM10010
Yan Y, Schwirz J, Schetelig MF (2021) Characterization of the Drosophila suzukii β2-tubulin gene and the utilization of its promoter to monitor sex separation and insemination. Gene. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.145366
Zhao Y, Schetelig MF, Handler AM (2020) Genetic breakdown of a Tet-off conditional lethality system for insect population control. Nat Commun 11:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16807-3
Zhong L, Belote JM (2007) The testis-specific proteasome subunit Prosα6T of D. melanogaster is required for individualization and nuclear maturation during spermatogenesis. Development 134:3517–3525. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.004770
Zimowska GJ, Nirmala X, Handler AM (2009) The β2-tubulin gene from three tephritid fruit fly species and use of its promoter for sperm marking. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 39:508–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2009.05.004
Acknowledgements
Grateful appreciation is extended to Richard Furlong and Shelley Olson for technical assistance with insect rearing and experimental procedures.
Funding
This project was supported by the Biotechnology Risk Assessment Research Grants Program Grant No. 2020-33522-3227 from the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture to A.M.H., and USDA-ARS Agreement 59-6036-1-002 and USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture Hatch project FLA-ENY-005943 to D.A.H.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QX, KT and AMH conceptualized the experimental approach and methodology; QX and KT performed experiments; QX, KT, DAH and AMH validated data and results; and AMH and DAH acquired funding and supervised research. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This is a biological, genetic and bioinformatic study of insect gene sequences and their expression using biochemical and in silico tools and resources on insect specimens that does not require ethical approval.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, Q., Tariq, K., Hahn, D.A. et al. Sequence and expression analysis of the spermatogenesis-specific gene cognates, wampa and Prosα6T, in Drosophila suzukii. Genetica 151, 215–223 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-023-00189-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-023-00189-7