Abstract
Land Use/Land Cover (LULC) changes represent anthropogenic transformation of natural landscape. These changes are an important tool in developing strategies for the management of natural resources as well as monitoring environmental changes. LULC mapping and monitoring is required to understand the causes and consequences of over exploitation of natural resources such as land, soil, forest and water. By assessing the uses and misuses of resources and identifying the reasons for misuses, the measures for sustainable development of resources in the fragile Himalayan watersheds can be identified and implemented. The main objective of the present study is to assess the land use/land cover changes in the Sarbari Khad watershed of Kullu Valley. The Sarbari Khad watershed is part of Beas River basin. The changes in LULC have been detected by using remote sensing and GIS (Geographical Information System) techniques for a period of twenty-one years (2000–2021). The satellite images of the National European Space Agency Sentinal-2 of November, 2021 and LandSat-7 image of November 2000 were processed with the help of ERDAS Imagine (2015) and Arc View (3.2a) software. This study reveals that substantial amount of deforestation and snow cover retreat has occurred during this period of two decades due to anthropogenic activities such as expansion of agriculture, especially horticulture, tourism and infrastructure development.

Source

Source

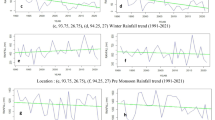
Source: Analyzed by researcher

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chakraborty, K., Joshi, P. K., & Sarma, K. K. (2009). Land use/land cover dynamics in umngot watershed of meghalaya using geospatial tools. Journal of Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 37(1), 99–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-009-0015-9
Chandel, V. B. S., & Brar, K. K. (2010a). Climate extremes and changing climate in western himalayas: A study of cloudburst incidences in Himachal Pradesh. Punjab Geographer, 6(1), 29–40.
Chandel, V. B. S., & Brar, K. K. (2010b). Seismicity and vulnerability in Himalayas: The case of Himachal Pradesh. India. Geomatics Natural Hazards and Risk, 1(1), 69–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475701003643441
Chandel, V. B. S., & Brar, K. K. (2011a). RS & GIS based landslide hazard zonation of mountainous terrains: A study from middle himalayan Kullu District, Himachal Pradesh, India. International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences, 2(1), 121–132.
Chandel, V. B. S., & Brar, K. K. (2011b). Multi-disaster risk and vulnerability in western Himalayan state of Himachal Pradesh. Punjab Geographer, 7(1), 9–19.
District Census Handbook (DCHB). (2011). Census of India: Himachal Pradesh. kullu village and town directory series-03 part xii-a directorate of census operations.
Gardner, J. S. (2002). Natural hazards risk in the Kullu District, Himachal Pradesh. India. Geographical Review, 92(2), 282–306.
Gardner, J. S., Sinclair, J., Berkes, F., & Singh, R. B. (2015). Accelerated tourism development and its impacts in Kullu-Manali, HP, India. Tourism Recreation Research, 27(3), 9–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508281.2002.11081370
Government of India (GOI). (2010) National mission for sustaining the Himalayan eco-system. National action plan on climate change. department of science & technology, ministry of science & technology, New Delhi.
ICIMOD. (2010). Climate change impact and vulnerability in the eastern himalayas—synthesis report. international centre for integrated mountain development. kathmandu, Nepal.
Jensen, J. R. (2005). Introductory digital Image processing: a remote sensing perspective (3rd ed.). Prentice Hall.
Jodha, N. S. (2000). Globalization and fragile mountain environments: policy challenges and choices. Mountain Research and Development., 20(4), 296–299.
Kaushik, S., Jaydeo, K., Dharpure, P. K., Joshi, A. L., & Ramanathan Singh, T. (2018). Climate change drives glacier retreat in Bhaga Basin located in Himachal Pradesh. Geocarto International. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2018.1557260
Kumar, S., Singh, V., & Saroha, J. (2022). Geospatial technology for sustainable development: A strategic framework for Sarbari Khad watershed of Himachal Pradesh. International Journal of Health Sciences. https://doi.org/10.53730/ijhs.v6nS2.8258
Manonmani, R., Suganya, M. D., & G. (2010). Remote sensing and GIS application in change detection study in urban zone using multi temporal satellite. International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences, 1(1), 60–65.
Negi, V., & Irfan, M. (2022). Land use/cover mapping and change detection using remote sensing techniques: a case of upper Kullu Valley, Himachal Pradesh. current world environment. 17(2).
Price, M. F. (1997). Chapter 13 in Action 1992–97: A task manager’s report. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), United Nations: mountain regions programmes, environmental change unit, university of Oxford, U.K.
Rai, S. C., Sharma, E., & Sundriyal, R. C. (1994). Conservation in the Sikkim Himalaya: Traditional knowledge and land-use of the Mamlay watershed. Environmental Conservation., 21(1), 30–34.
Sati, V. P. (2006). Natural hazards in an ecologically fragile mountain terrain: A case for the pindar Basin of Uttaranchal Himalaya. ENVIS Bulletin. Himalayan Ecology, 14(1), 22–30.
Shah, S., & Sharma, D. (2015). Land use change detection in Solan forest division, Himachal Pradesh India. Forest Ecosystems., 2, 26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40663-015-0050-7
Sharma, R. K., Sankhayan, P. L., Hofstad, O., & Singh, R. (2007). Land use changes in the western himalayan region: A study at watershed level in the state of Himachal Pradesh, India. International Journal of Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 33(2–3), 197–206.
Singh, V., & Dev, P. (2011). Ground water potential estimation of alluvial Terrain of Saharanpur City and adjoining region, Uttar Pradesh, India. Journal of Nepal Geological Society, 43(SI), 261–266. https://doi.org/10.3126/jngs.v43i0.25590
Singh, V., & Dev, P. (2012). Operation need of artificial recharge plan of ground water plan of ground water increase in Saharanpur area Uttar Pradesh. Bhu-Jal News Quaterly Journal, 27(1–4), 19–24.
Singh, V., & Panchal, V. K. (2015). Remote sensing data application in digital elevation model for feature extraction of Jaisalmer region, thar Desert, Rajasthan, India. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research & Development, 2(3), 244–248.
Thakur, N., Rishi, M., Keesari, T., Sharma, D. A., & Singh, R. (2018). Assessment of changes in land use and land cover patterns using RS and GIS: A case study of upper beas Basin of Kullu valley in Western Himalayas. India, Anusandhan (AUJAN), 7(14), 1–10.
Tucker, R. P. (1982). The forests of the western himalayas: The legacy of british colonial administration. Journal of Forest History, 26(3), 112–123.
Turner, B. L., & Meyer, W. B. (1994). Global land-use and land-cover change: An overview. In W. B. Meyer & B. L. Turner (Eds.), Changes in land use and land cover: A global perspective. Cambridge University Press.
Turner, B. L. (2001). Land-use and land-cover change: Advances in 15 decades of sustained international research. GAIA-Ecological Perspectives in Science, Humanities, and Economics, 10(4), 269–272.
Vaidya, P., Bhardwaj, S. K., & Sood, S. (2018). Land use land cover changes in Kullu Valley of Himachal Pradesh. Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 88(6), 902–906.
Vishwa, C. B., Kaur, B. K., & Simrit, K. (2013). Land use/cover change and its implications for Kullu district of Himachal Pradesh. India. International Journal of Geomatics Geosciences, 3(3), 538–551.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
This research did not contain any studies involving animal and human participants, nor did not take place on any private or protected area. No specific permissions were required for corresponding locations.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Singh, V. & Saroha, J. Interpretation of land use/land cover dynamics with the application of geospatial techniques in sarbari khad watershed of Himachal Pradesh, India. GeoJournal 88, 2623–2633 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-022-10769-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-022-10769-3