Abstract
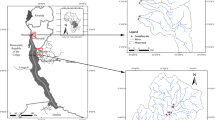
Along with the continuous urbanization process, massive riparian buffers are developed to satisfy the increasing demands for flood protection and economic growth. Such changes of land use types and landscape patterns pose a significant challenge to the protection of the eco-system of urban rivers. This research concentrates on revealing the potential relation between the water quality of the urban river and land characteristics including land use types and landscape patterns of the riparian area and discusses if the relationship varies with spatial scales. The study area of this research are the 800 m riparian buffer of the six river water quality monitoring sections along Huangpu River. Based on the long-term monthly collection data of six monitoring points in Huangpu River, Shanghai, China, and the land use data of 100 m downstream of 1 km upstream of the monitoring point. Using landscape indicators, GIS spatial analysis, and statistical methods, the responses of land use and landscape patterns to water quality in different scales are obtained. Results show that: (1) Urban Land (UL) and Agricultural Land (AL) have an enormous negative contribution to each buffer, which is the primary non-point source pollution and influencing factor. (2) The active contribution of Wetland (WL) and Forestry Land (FL) is the most significant in the small range buffer of 0–200 m. (3) The negative effect of Industrial Land (IL) on water quality is only significant in the small buffer. (4) The effect of landscape pattern on water quality is more significant on the large spatial scale than the small scale. At the same time, this paper extends the conclusion to discuss the land use of the 800 m buffer zone of Huang River by using point to the area, proving that the research result is helpful for the political decision of urban management and provides suggestions for the land optimization of riparian buffers.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahearn, D. S., Sheibley, R. W., Dahlgren, R. A., Anderson, M., Johnson, J., & Tate, K. W. (2005). Land use and land cover influence on water quality in the last free-flowing river draining the western Sierra Nevada, California. Journal of Hydrology, 313(3–4), 234–247.
Allan, J. D. (2004). Landscapes and riverscapest: The Influence of land use on stream ecosystems. Annual Review of Ecology Evolution and Systematics, 35, 257–284.
Amir, M., Leu, S., & Budovsky, A. (2015). New methodology for quantifying the effects of perennials on their patch productivity in semi-arid environments. Environmental Management, 55(5), 1139–1146.
Bahar, M. M., Ohmori, H., & Yamamuro, M. (2008). Relationship between river water quality and land use in a small river basin running through the urbanizing area of Central Japan. Limnology, 9(1), 19–26.
Braak, C. J., & Smilauer, P. (2002). CANOCO reference manual 590 and CanoDraw for Windows user’s guide: Software for 591 canonical community ordination (version 4.5). http://www.canoco.com, 2002.
Bu, H., Meng, W., Zhang, Y., & Wan, J. (2014). Relationships between land use patterns and water quality in the Taizi River basin, China. Ecological Indicators, 41, 187–197.
Cai, Y., Yang, X., Wan, L. H., et al. (2019). Influence of land use structure in riparian buffers on river water quality during the freezing and thawing period in Northern Cold Region. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 39(3), 679–687.
Da Silva, D. S., Lucotte, M., Paquet, S., et al. (2009). Influence of ecological factors and of land use on mercury levels in fish in the Tapajos River basin, Amazon. Environment Research, 165, 317–324.
Fedorko, E. J., Pontius, R. G., Aldrich, S. P., Claessens, L., Hopkinson, C., & Wollheim, W. M. (2004). Spatial distribution of land type in regression models of pollutant loading. Ecology and Population Biology, 207, 173.
Ferrier, R. C., Edwards, A. C., Hirst, D., Littlewood, I. G., Watts, C. D., & Morris, R. (2001). Water quality of Scottish rivers: Spatial and temporal trends. The Science of the Total Environment, 265(1–3), 327–342.
Gove, N. E., Edwards, R. T., & Conquest, L. L. (2001). Effects of scale on land use and water quality relationships: A longitudinal basin-wide perspective. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 37(6), 1721–1734.
Gregory, S. V., Swanson, F. J., McKee, W. A., & Cummins, K. W. (1991). An ecosystem perspective of riparian zones. BioScience, 41(8), 540–551.
Guo, Q. H., Ma, K. M., Yang, L., et al. (2010). Testing a dynamic complex hypothesis in the analysis of land use impact on lake water quality. Water Resource Management, 24(7), 1313–1332.
Haidary, A., Amiri, B. J., Adanowski, J., Fohrer, N., & Nakane, K. (2013). Assessing the impacts of four land use types on the water quality of wetlands in Japan. Water Resources Management, 27(7), 2217–2229.
Harding, J. S., Benfield, E. F., Bolstad, P. V., Helfman, P. V., & Jones, E. B. D. (1998). Stream biodiversity: The ghost of land use past. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 95(25), 14843–14847.
Hu, H. B., Liu, H. Y., Hao, J. F., & An, J. (2012). Influence of spatial difference on water quality in Jiuxiang river watershed, Nanjing. Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 33(3), 794–801.
Hunsaker, C. T., & Levine, D. A. (1995). Hierarchical approaches to the study of water quality in rivers. BioScience, 45(3), 193–202.
Jerry, A. G. (2002). Geographic techniques and recent applications of remote sensing to landscape-water quality studies. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 138(1–4), 181–197.
Johnson, L. B., Richars, C. E., Host, G., & Arthur, J. W. (1997). Landscape influences on water chemistry in Midwestern stream ecosystems. Freshwater Biology, 37(1), 193–208.
Jones, K. B., Neale, A. C., Nash, M. S., Van Remortel, R. D., Wickham, J. D., Riitters, K. H., et al. (2001). Predicting nutrient and sediment loadings to streams from landscape metrics: A multiple watershed study from the United States Mid-Atlantic Region. Landscape Ecology, 16(4), 301–312.
Kang, J., Lee, S. W., Cho, K. H., Ki, S. J., Cha, S. M., & Kim, J. H. (2010). Linking land-use type and stream water quality using spatial data of fecal indicator bacteria and heavy metals in the Yeongsan river basin. Water Research, 44(14), 4143–4157.
Lee, B. C., Matsui, S., Shimizu, Y., & Matsuda, T. (2005). Characterizations of the first flush in storm water runoff from an urban roadway. Environmental Technology, 26, 773–782.
Lee, S., Hwang, S., Lee, S., Hwang, H., & Sung, H. (2009). Landscape ecological approach to the relationships of land use patterns in watersheds to water quality characteristics. Landscape and Urban Planning, 92(2), 80–89.
Lepš, J., & Šmilauer, P. (2003). Multivariate analysis of ecological data using CANOCO. Cambridge: Cambridge Press.
Li, S., Gu, S., Tan, X., & Zhang, Q. (2009). Water quality in the upper Han River basin, China: The impacts of land use/land cover in riparian buffer zone. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 165(1–3), 317–324.
Liu, X. T. (2013). Bulletin of first water census and second water resource census of Shanghai. China Water & Power Press, 12.
Lopez, R. D., Nash, M. S., Heggem, D. T., & Ebert, D. W. (2008). Watershed vulnerability predictions for the Ozarks using landscape models. Journal of Environment Quality, 37(5), 1769.
Mehaffey, M. H., Nash, M. S., Wade, T. G., Ebert, D. W., Jones, K. B., & Rager, A. (2005). Linking land cover and water quality in New York city’s water supply watersheds. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 107(1–3), 29–44.
Mialet, B., Gouzou, J., Azémar, F., Maris, T., Sossou, C., Toumi, N., et al. (2011). Response of zooplankton to improving water quality in the Scheldt estuary (Belgium). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 93(1), 47–57.
Nash, M. S., Heggem, D. T., Ebert, D., Wade, T. G., & Hall, R. K. (2009). Multi-scale landscape factors influencing stream water quality in the state of Oregon. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 156(1–4), 343–360.
Rhodes, A. L., Newton, R. M., & Pufall, A. (2001). Influences of land use on water quality of a diverse New England watershed. Environmental Science and Technology, 35(18), 3640–3645.
Schoonover, J. E., & Lockaby, B. G. (2006). Land cover impacts on stream nutrients and fecal coliform in the lower Piedmont of West Georgia. Journal of Hydrology, 331(3–4), 371–382.
Shanghai Municipal Bureau of Ecology and Environment (2015). Shanghai Environmental Bulletin 2014. http://sthj.sh.gov.cn/fa/cms/upload/uploadFiles/2015-06-02/file2002.pdf.
Shen, Z., Hou, X., Li, W., et al. (2015). Impact of landscape pattern at multiple spatial scales on water quality: A case study in a typical urbanized watershed in China. Ecological Indicators, 48, 417–427.
Shen, Y., Lü, J., Chen, D., & Shi, Y. (2011). Response of stream pollution characteristics to catchment land cover in Cao-E river basin, china. Pedosphere, 21(1), 115–123.
Shivoga, W. A., Muchiri, M., Kibichi, S., Odanga, J., Miller, S. N., Baldyga, T. J., et al. (2007). Influences of land use/cover on water quality in the upper and middle reaches of River Njoro. Kenya, Lakes & Reservoirs: Research & Management, 12(2), 97–105.
Sirombra, M. G., & Mesa, L. M. (2012). A method for assessing the ecological quality of riparian forests in subtropical Andean streams: QBRy index. Ecological Indicators, 20, 324–331.
Sliva, L., & Williams, D. D. (2001). Buffer zone versus whole catchment approaches to studying land use impact on river water quality. Water Research, 35(14), 3462–3472.
Sonoda, K., Yeakley, J. A., & Walker, C. E. (2001). Near-stream landuse effects on streamwater nutrient distribution in an urbanizing watershed. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 37(6), 1517–1532.
Tong, S. T. Y., & Chen, W. L. (2002). Modeling the relationship between land use and surface water quality. Journal of Environmental Management, 66(4), 377–393.
Tu, J. (2009). Combined impact of climate and land use changes on streamflow and water quality in eastern Massachusetts, USA. Journal of Hydrology, 379(3–4), 268–283.
Tu, J. (2013). Spatial variations in the relationships between land use and water quality across an urbanization gradient in the watersheds of northern georgia, USA. Environmental Management, 51(1), 1–17.
Uthicke, S., & Nobes, K. (2008). Benthic Foraminifera as ecological indicators for water quality on the Great Barrier Reef. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 78(4), 763–773.
Uuemaa, E., Roosaare, J., & Mander, Ü. (2005). Scale dependence of landscape metrics and their indicatory value for nutrient and organic matter losses from catchments. Ecological Indicators, 5(4), 350–369.
Wan, R., Cai, S., Li, H., Yang, G., Li, Z., & Nie, X. (2014). Inferring land use and land cover impact on stream water quality using a Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach in the Xitiaoxi River Watershed, China. Journal of Environmental Management, 133, 1–11.
Wang, Y. K., Cheng, R. H., Zeng, P., et al. (2019). Spatial differentiation of water quality in river networks in Shanghai and its response to landuse in riparian zones. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 35(7), 925–932.
Worrall, F., & Burt, T. P. (1999). The impact of land-use change on water quality at the catchment scale: The use of export coefficient and structural models. Journal of Hydrology, 221(1), 75–90.
Wu, J. G., Jelinski, D. E., Luck, M., & Tueller, P. T. (2000). Multiscale analysis of landscape heterogeneity: Scale variance and pattern metrics. Geographic Information Sciences, 6(1), 6–19.
Xia, L. L., Liu, R. Z., & Zao, Y. W. (2012). Correlation analysis of landscape pattern and water quality in Baiyangdian watershed. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 13, 2188–2196.
Xu, H. S., Du, H. Y., & Cai, C. L. (2019). Spatial characteristics of landscape pattern based on ecological restoration in the riparian zone of Huangpu River. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 43(4), 125–131.
Ye, L., Cai, Q., Liu, R., & Cao, M. (2009). The influence of topography and land use on water quality of Xiangxi River in Three Gorges Reservoir region. Environmental Geology, 58(5), 937–942.
Yu, D.-y., Shi, P.-j., Liu, Y.-p., et al. (2009). Detecting land use-water quality relationships from the viewpoint of ecological restoration in an urban area. Ecological Engineering, 109, 432–446.
Yue, J., & Wang, Y. L. (2005). Progresses and perspectives in the study of riparian zone. Progress in Geography, 24(5), 33–40.
Zhang, J. C., & Peng, B. Z. (2003). Study on riparian zone and the restoration and rebuilding of its degraded ecosystem. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 23(1), 56–63.
Zhao, J., Lin, L., Yang, K., et al. (2015). Influence of land use on water quality in a reticular river network area: A case study in Shanghai, China. Landscape and Urban Planning, 137, 20–29.
Zhou, T., Wu, J., & Peng, S. (2012). Assessing the effects of landscape pattern on river water quality at multiple scales: A case study of the Dongjiang River watershed, China. Ecological Indicators, 23, 166–175.
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2016M590459), China Scholarship Fund (No. 201808320046), the Top-notch Academic Programs Project of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (No. PPZY2015A063), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD) and the Youth Science and Technology Innovation Fund of Nanjing Forestry University (No. CX2016003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., Cai, C., Du, H. et al. Responses of water quality to land use in riparian buffers: a case study of Huangpu River, China. GeoJournal 86, 1657–1669 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-020-10150-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-020-10150-2