Abstract
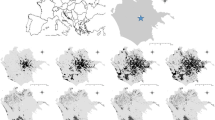
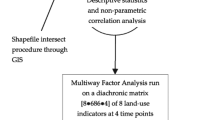
Identifying the intimate mechanisms underlying urban growth and the resulting impact on local-scale landscape structures is an intriguing issue worldwide. Metropolitan expansion in the last decades resulted in (more or less) scattered settlements consuming (or degrading) semi-natural areas devoted to agriculture and forestry. This process has progressively led to multi-faceted landscape configurations influenced by different socioeconomic, demographic, cultural and political factors. At the same time, lack of comparable information among metropolitan areas prevents a comprehensive investigation of patterns and processes of urban expansion. Based on these premises, our study investigates the micro-scale structure of urban landscapes using a spatially-explicit analysis based on Geographic Information Systems tools. This approach was applied to a comparative, fine-grained analysis of landscape structures in three Southern European metropolitan areas characterized by different socioeconomic contexts (Barcelona, Rome and Athens). Results of this paper shed light on the intrinsic linkage between landscape structure and social functions, providing an informed knowledge of land-use transformations in contemporary cities. Rethinking complex interactions between contemporary landscapes and the (evolving) socioeconomic background is particularly urgent in urban contexts characterized by weak planning systems and limited participation to land-use decisions.


Source: own elaboration

Source: own elaboration

Source: own elaboration

Source: own elaboration

Source: own elaboration

Source: own elaboration

Source: own elaboration

Source: own elaboration

Source: own elaboration

Source: own elaboration

Source: own elaboration
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alphan, H. (2003). Land-use change and urbanisation of Adana, Turkey. Land Degradation and Development,14(6), 575–586.
Arapoglou, V. P., & Sayas, J. (2009). New facets of urban segregation in southern Europe. European Urban and Regional Studies,16(4), 345–362.
Bajocco, S., De Angelis, A., & Salvati, L. (2012). A satellite-based green index as a proxy for vegetation cover quality in a Mediterranean region. Ecological Indicators,23, 578–587.
Biasi, R., Brunori, E., Ferrara, C., & Salvati, L. (2017). Towards sustainable rural landscapes? A multivariate analysis of the structure of traditional tree cropping systems along a human pressure gradient in a mediterranean region. Agroforestry Systems,91(6), 1199–1217.
Biasi, R., Colantoni, A., Ferrara, C., Ranalli, F., & Salvati, L. (2015). In-between sprawl and fires: Long-term forest expansion and settlement dynamics at the wildland-urban interface in Rome, Italy. International Journal of Sustainable Development and World Ecology,22(6), 467–475.
Brunori, E., Salvati, L., Mancinelli, R., Smiraglia, D., & Biasi, R. (2017). Multi-temporal land-use and cover changing analysis: The environmental impact in Mediterranean area. International Journal of Sustainable Development and World Ecology,24(3–4), 276–288.
Buttoud, G. (2015). Research and innovation in sustainable forestry: Lessons learnt to inform the policy making community. Annals of Silvicultural Research,38(2), 74–77.
Cakir, G., Un, C., Baskent, E. Z., Kose, S., Sivrikaya, F., & Keles, S. (2008). Evaluating urbanization, fragmentation and land use/cover change pattern in Istambul city, Turkey from 1971 to 2002. Land Degradation and Development,19(6), 663–675.
Carlucci, M., Grigoriadis, E., Rontos, K., & Salvati, L. (2017). Revisiting a hegemonic concept: Long-term ‘Mediterranean urbanization’in between city re-polarization and metropolitan decline. Applied Spatial Analysis and Policy,10(3), 347–362.
Catalán, B., Saurí, D., & Serra, P. (2008). Urban sprawl in the Mediterranean? Patterns of growth and change in the Barcelona Metropolitan Region 1993–2000. Landscape and Urban Planning,85(3–4), 174–184.
Cecchini, M., Zambon, I., Pontrandolfi, A., Turco, R., Colantoni, A., Mavrakis, A., et al. (2018). Urban sprawl and the ‘olive’ landscape: Sustainable land management for ‘crisis’ cities. GeoJournal,84(1), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-018-9848-5.
Chorianopoulos, I., Pagonis, T., Koukoulas, S., & Drymoniti, S. (2010). Planning, competitiveness and sprawl in the Mediterranean city: The case of Athens. Cities,27(4), 249–259.
Colantoni, A., Grigoriadis, E., Sateriano, A., Venanzoni, G., & Salvati, L. (2016). Cities as selective land predators? A lesson on urban growth, deregulated planning and sprawl containment. Science of the Total Environment,545–546, 329–339.
Colantoni, A., Mavrakis, A., Sorgi, T., & Salvati, L. (2015). Towards a ‘polycentric’ landscape? Reconnecting fragments into an integrated network of coastal forests in Rome. Rendiconti Lincei,26(3), 615–624.
Corona, P. (2015). Forestry research to support the transition towards a bio-based economy. Annals of Silvicultural Research,38(2), 37–38.
Costa, F., Noble, A. G., & Pendleton, G. (1991). Evolving planning systems in Madrid, Rome, and Athens. GeoJournal,24(3), 293–303.
Cuadrado-Ciuraneta, S., Durà-Guimerà, A., & Salvati, L. (2017). Not only tourism: Unravelling suburbanization, second-home expansion and “rural” sprawl in Catalonia, Spain. Urban Geography,38(1), 66–89.
Delfanti, L., Colantoni, A., Recanatesi, F., Bencardino, M., Sateriano, A., Zambon, I., et al. (2016). Solar plants, environmental degradation and local socioeconomic contexts: A case study in a Mediterranean country. Environmental Impact Assessment Review,61, 88–93.
Delladetsima, P. M. (2006). The emerging property development pattern in Greece and its impact on spatial development. European Urban and Regional Studies,13(3), 245–278.
Di Feliciantonio, C., & Salvati, L. (2015). ‘Southern’ Alternatives of urban diffusion: Investigating settlement characteristics and socio-economic patterns in three Mediterranean regions. Tijdschrift voor Economische en Sociale Geografie,106(4), 453–470.
Díaz-Palacios-Sisternes, S., Ayuga, F., & García, A. I. (2014). A method for detecting and describing land use transformations: An examination of Madrid’s southern urban-rural gradient between 1990 and 2006. Cities,40, 99–110.
Domene, E. (2017). Changing patterns of water consumption in the suburban Barcelona: Lifestiles and welfare as explanatory factors. Investigaciones Geográficas,61, 39–53.
Downs, A. (1998). How America’s cities are growing: The big picture. Brookins Review,16(4), 8–12.
Dura-Guimera, A. (2003). Population deconcentration and social restructuring in Barcelona, a European Mediterranean city. Cities,20(6), 387–394.
Duvernoy, I., Zambon, I., Sateriano, A., & Salvati, L. (2018). Pictures from the other side of the fringe: Urban growth and peri-urban agriculture in a post-industrial city (Toulouse, France). Journal of Rural Studies,57, 25–35.
European Environment Agency. (2006). Urban sprawl in Europe. The ignored challenge. European Environment Agency. Copenhagen, DK: Office for Official Publications of the European Communities.
Ewing, R. (1997). Is Los Angeles-style sprawl desirable. Journal of the American Planning Association,63(1), 107–126.
Ewing, R., Pendall, R., & Chen, D. (2003). Measuring sprawl and its transportation impacts. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board. https://doi.org/10.3141/1831-20.
Fabbio, G. (2013). An eighty years long history. Annals of Silvicultural Research. http://dx.doi.org/10.12899/asr-831.
Fiorini, L., Zullo, F., & Romano, B. (2016). Urban development of the coastal system of the Italian largest island: Sicily and Sardinia. Ocean and Coastal Management,143, 184–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2016.12.008.
Fregolent, L. (2012). La città a bassa densità: Problemi e gestione. Tema. Journal of Land Use, Mobility and Environment,5(1), 7–20.
Fregolent, L., & Tonin, S. (2016). Local public spending and urban sprawl: Analysis of this relationship in the Veneto region of Italy. Journal of Urban Planning and Development,142(3), 05016001.
Garcia-López, M. A., & Muniz, I. (2010). Employment decentralisation: Poly centricity or scatteration? The case of Barcelona. Urban Studies,47(14), 3035–3056.
González, R. C. L., Mantiñán, M. J. P., & Miró, S. V. (2016). The urban bubble process in Spain: An interpretation from the theory of the circuits of capital. Journal of Urban and Regional Analysis,8(1), 5.
Hansen, M. C., Potapov, P. V., Moore, R., Hancher, M., Turubanova, S., Tyukavina, A., et al. (2013). High-resolution global maps of 21st-century forest cover change. Science,342(6160), 850–853.
Hasse, J. E., & Lathrop, R. G. (2003). Land resource impact indicators of urban. Applied Geography,23(2–3), 159–175.
Kairis, O., Karavitis, C., Kounalaki, A., Salvati, L., & Kosmas, C. (2013). The effect of land management practices on soil erosion and land desertification in an olive grove. Soil Use and Management,29(4), 597–606.
King, R., Proudfoot, L., & Smith, B. (1997). The mediterranean. Environment and society. London: Arnold.
Kourliouros, E. (1997). Planning industrial location in Greater Athens: The interaction between deindustrialization and anti-industrialism during the 1980s. European Planning Studies,5(4), 435–460.
Krumholz, N. (1992). Roman impressions: Contemporary city planning and housing in Rome. Landscape and Urban Planning,22(2–4), 107–114.
Leontidou, L. (1990). The Mediterranean city in transition: Social change and urban development. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Leontidou, L., Afouxenidis, A., Kourliouros, E., & Marmaras, E. (2007). Infrastructure-related urban sprawl: Mega-events and hybrid peri-urban landscapes in southern Europe. Urban sprawl in Europe: Landscapes, Land-use Change and Policy, 71–98.
Marchetti, M., Vizzarri, M., Lasserre, B., Sallustio, L., & Tavone, A. (2015). Natural capital and bioeconomy: Challenges and opportunities for forestry. Annals of Silvicultural Research,38(2), 62–73.
Martellozzo, F., Amato, F., Murgante, B., & Clarke, K. (2018). Modelling the impact of urban growth on agriculture and natural land in Italy to 2030. Applied Geography,91, 156–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2017.12.004.
Marull, J., Pino, J., Tello, E., & Cordobilla, M. J. (2009). Social metabolism, landscape change and land-use planning in the Barcelona metropolitan region. Land Use Policy,27, 497–510.
Morelli, V. G., Rontos, K., & Salvati, L. (2014). Between suburbanisation and re-urbanisation? Revisiting the urban life cycle in a Mediterranean compact city. Urban Research and Practice,7(1), 74–88.
Morote, Á. F., Saurí, D., & Hernández, M. (2017). Residential tourism, swimming pools, and water demand in the Western Mediterranean. The Professional Geographer,69(1), 1–11.
Munafò, M., Salvati, L., & Zitti, M. (2013). Estimating soil sealing rate at national level—Italy as a case study. Ecological Indicators,26, 137–140.
Muñoz, F. (2003). Lock living: Urban sprawl in Mediterranean cities. Cities,20(6), 381–385.
Pileri, P., & Maggi, M. (2010). Sustainable planning? First results in land uptakes in rural, natural and protected areas: The Lombardia case study (Italy). Journal of Land Use Science,5(2), 105–122.
Pili, S., Grigoriadis, E., Carlucci, M., Clemente, M., & Salvati, L. (2017). Towards sustainable growth? A multi-criteria assessment of (changing) urban forms. Ecological Indicators,76, 71–80.
Portnov, B. A., & Safriel, U. N. (2004). Combating desertification in the Negev: Dryland agriculture vs. dryland urbanization. Journal of Arid Environments,56(4), 659–680.
Romano, B., Fiorini, L., Marucci, A., & Zullo, F. (2017a). Urban growth control DSS techniques for de-sprinkling process in Italy. Sustainability,9(10), 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9101852.
Romano, B., Zullo, F., Fiorini, L., Ciabò, S., & Marucci, A. (2017b). Sprinkling: An approach to describe urbanization dynamics in Italy. Sustainability,9(1), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9010097.
Romano, B., Zullo, F., Fiorini, L., Marucci, A., & Ciabo, S. (2017c). Land transformation of Italy due to half a century of urbanisation. Land Use Policy,67, 387–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.06.006.
Salvati, L. (2014). Agro-forest landscape and the ‘fringe’ city: A multivariate assessment of land-use changes in a sprawling region and implications for planning. Science of the Total Environment,490, 715–723.
Salvati, L., & Sabbi, A. (2011). Exploring long-term land cover changes in an urban region of southern Europe. International Journal of Sustainable Development & World Ecology, 18(4), 273–282.
Salvati, L., Gargiulo Morelli, V., Rontos, K., & Sabbi, A. (2013). Latent exurban development: City expansion along the rural-to-urban gradient in growing and declining regions of southern Europe. Urban Geography,34(3), 376–394.
Salvati, L., Gemmiti, R., & Perini, L. (2012). Land degradation in Mediterranean urban areas: An unexplored link with planning? Area,44(3), 317–325.
Salvati, L., Mavrakis, A., Serra, P., & Carlucci, M. (2015). Lost in translation, found in entropy: An exploratory data analysis of latent growth factors in a Mediterranean city (1960–2010). Applied Geography, 60, 107–119.
Schneider, A., & Woodcock, C. E. (2008). Compact, dispersed, fragmented, extensive? A comparison of urban growth in twenty-five global cities using remotely sensed data, pattern metrics and census information. Urban Studies,45(3), 659–692.
Serra, P., Vera, A., Tulla, A. F., & Salvati, L. (2014). Beyond urban-rural dichotomy: Exploring socioeconomic and land-use processes of change in Spain (1991–2011). Applied Geography,55, 71–81.
Terzi, F., & Bolen, F. (2009). Urban sprawl measurement of Istanbul. European Planning Studies,17(10), 1559–1570.
Tombolini, I., Zambon, I., Ippolito, A., Grigoriadis, S., Serra, P., & Salvati, L. (2015). Revisiting “Southern” sprawl: Urban growth, socio-spatial structure and the influence of local economic contexts. Economies, 3(4), 237–259.
Torrens, P. M. (2008). A toolkit for measuring sprawl. Applied Spatial Analysis and Policy,1(1), 5–36.
Tsai, Y. H. (2005). Quantifying urban form: Compactness versus ‘sprawl’. Urban Studies,42(1), 141–161.
Zambon, I., Benedetti, A., Ferrara, C., & Salvati, L. (2018). Soil matters? A multivariate analysis of socioeconomic constraints to urban expansion in Mediterranean Europe. Ecological Economics,146, 173–183.
Zambon, I., Serra, P., Sauri, D., Carlucci, M., & Salvati, L. (2017). Beyond the ‘Mediterranean city’: Socioeconomic disparities and urban sprawl in three Southern European cities. Geografiska Annaler: Series B, Human Geography,99(3), 319–337.
Zitti, M., Ferrara, C., Perini, L., Carlucci, M., & Salvati, L. (2015). Long-term urban growth and land use efficiency in Southern Europe: Implications for sustainable land management. Sustainability (Switzerland),7(3), 3359–3385.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zambon, I., Salvati, L. Unraveling latent transformations in metropolitan structures: a local-scale analysis of urban landscapes and social functions. GeoJournal 85, 863–881 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-019-09996-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-019-09996-y